transposition of the great arteries (tga)
... The baby’s body is not being supplied with enough oxygenated blood. If this situation continues, the baby will become very unwell from lack of oxygen supply to the body and could die. A VSD will allow some mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated which may provide the baby’s body with slightly more oxy ...
... The baby’s body is not being supplied with enough oxygenated blood. If this situation continues, the baby will become very unwell from lack of oxygen supply to the body and could die. A VSD will allow some mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated which may provide the baby’s body with slightly more oxy ...
Heartnotes2017 - Lindbergh School District
... fibrillation, the atria quiver instead of beating effectively. Blood isn't pumped completely out, so it may pool and clot. If a blood clot leaves the atria and lodges in an artery in the brain (thrombosis), a stroke results. ~15 percent of strokes occur in people with atrial fibrillation ...
... fibrillation, the atria quiver instead of beating effectively. Blood isn't pumped completely out, so it may pool and clot. If a blood clot leaves the atria and lodges in an artery in the brain (thrombosis), a stroke results. ~15 percent of strokes occur in people with atrial fibrillation ...
Cardiovascular physiology.
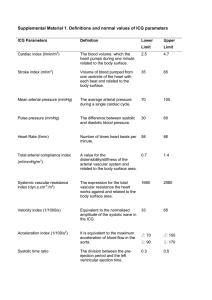
... • Mean arterial pressure = (S + 2D)/3 or • D + 1/3 PP • Pulse pressure=S – D (120-80=40 mmHg) ...
... • Mean arterial pressure = (S + 2D)/3 or • D + 1/3 PP • Pulse pressure=S – D (120-80=40 mmHg) ...
Personal Fitness Worksheet #1 - U
... A risk factor is a major factor in your life that would increase your risk for a premature death. List the primary risk factors and put a star before each risk factor that you can control. *1. Inactivity – only 40% of U.S. adults get the recommended amount of physical activity 2. __________________ ...
... A risk factor is a major factor in your life that would increase your risk for a premature death. List the primary risk factors and put a star before each risk factor that you can control. *1. Inactivity – only 40% of U.S. adults get the recommended amount of physical activity 2. __________________ ...
Ch 37 Test Review- 3 points Bonus
... Give a description of each of the following disorders of the circulatory system. Atherosclerosis Heart attack Anemia Hypertension Stroke Trace a red blood cell from the right ventricle through the path of circulation in the body if it was traveling to the brain and back to the right ventricle. Trac ...
... Give a description of each of the following disorders of the circulatory system. Atherosclerosis Heart attack Anemia Hypertension Stroke Trace a red blood cell from the right ventricle through the path of circulation in the body if it was traveling to the brain and back to the right ventricle. Trac ...
AED Study Notes
... From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD. ...
... From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD. ...
The Heart
... beats per minute. • That’s about 100,000 beats per day and 35 million beats in a year. ...
... beats per minute. • That’s about 100,000 beats per day and 35 million beats in a year. ...
Diagnosing Heart Failure (HF)
... symptoms of HF (SOB at rest or on exercise, fatigue, tiredness, SOA) and signs of HF (tachycardia, tachypnoea, pulmonary rales, pleural effusion, raised JVP, peripheral oedema, hepatomegaly) and objective evidence of a structural or functional abnormality of the heart at rest (eg abnormality o ...
... symptoms of HF (SOB at rest or on exercise, fatigue, tiredness, SOA) and signs of HF (tachycardia, tachypnoea, pulmonary rales, pleural effusion, raised JVP, peripheral oedema, hepatomegaly) and objective evidence of a structural or functional abnormality of the heart at rest (eg abnormality o ...
- St. William the Abbot School
... Notes Chapter 16 – The Circulatory System The cardiovascular system carries needed substances to cells and carries waste products away from cells. Blood also contains cells that fight disease. The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood through blood vessels of the cardiovascular system. The hear ...
... Notes Chapter 16 – The Circulatory System The cardiovascular system carries needed substances to cells and carries waste products away from cells. Blood also contains cells that fight disease. The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood through blood vessels of the cardiovascular system. The hear ...
Time: Monday May 2nd, 2011 5:00pm Location: Buchanan A202
... can be fatal if left untreated. In two dimensions, these reentrant arrhythmias can be modeled as one or more spiral waves in a system of excitable media. The appearance of spiral waves due to structural inhomogeneities – such as damaged tissue or scar tissue is well-studied and well-explained. Howev ...
... can be fatal if left untreated. In two dimensions, these reentrant arrhythmias can be modeled as one or more spiral waves in a system of excitable media. The appearance of spiral waves due to structural inhomogeneities – such as damaged tissue or scar tissue is well-studied and well-explained. Howev ...
Beat Still My Heart
... Nervous system responses cause either increased outflow of blood from arteries (sympathetic NS) or decrease heart rate and stroke volume (parasympathetic NS) ...
... Nervous system responses cause either increased outflow of blood from arteries (sympathetic NS) or decrease heart rate and stroke volume (parasympathetic NS) ...
HPD 130 Outline - Clackamas Community College
... Develops skills at the provider level in accordance with American Heart Association Advanced Cardiac Life Support guidelines. Successful completion of the course and all required AHA tests lead to certification as an AHA ACLS Provider. Course Objectives: ACE is designed to provide the knowledge and ...
... Develops skills at the provider level in accordance with American Heart Association Advanced Cardiac Life Support guidelines. Successful completion of the course and all required AHA tests lead to certification as an AHA ACLS Provider. Course Objectives: ACE is designed to provide the knowledge and ...
Figure 19.4E Gross anatomy of the heart
... The Closed Circulatory System •Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and is distinct from the interstitial fluid. –The heart pumps blood into large vessels that branch into smaller ones leading into the organs. ...
... The Closed Circulatory System •Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and is distinct from the interstitial fluid. –The heart pumps blood into large vessels that branch into smaller ones leading into the organs. ...
Word
... defibrillators (ICDs) that can treat life-threatening arrhythmias in the lower chambers of the heart, while also detecting previously undiagnosed and/or asymptomatic atrial fibrillation (AF), a condition that involves an irregular quivering or rapid heart rhythm in the upper chambers (atria) of the ...
... defibrillators (ICDs) that can treat life-threatening arrhythmias in the lower chambers of the heart, while also detecting previously undiagnosed and/or asymptomatic atrial fibrillation (AF), a condition that involves an irregular quivering or rapid heart rhythm in the upper chambers (atria) of the ...
Biology 118
... 26. At rest or during exercise, ______ remains relatively constant. a. systemic artery PO2 * b. blood flow c. systolic BP d. HR 27. If baroreceptor firing increases, the ____ increases its signaling to the heart, to ____, as part of a normal negative feedback response. a. parasympathetic system – d ...
... 26. At rest or during exercise, ______ remains relatively constant. a. systemic artery PO2 * b. blood flow c. systolic BP d. HR 27. If baroreceptor firing increases, the ____ increases its signaling to the heart, to ____, as part of a normal negative feedback response. a. parasympathetic system – d ...
Introduction to the circulatory system
... pulmonary artery). Deoxygenated blood has less oxygen and is found in the veins (except in the pulmonary vein.) ...
... pulmonary artery). Deoxygenated blood has less oxygen and is found in the veins (except in the pulmonary vein.) ...
Congestive Heart Failure
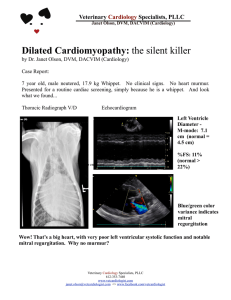
... ii. Ventricular dilation and myocardial hypertrophy: with hemodynamic overload, the increased blood volume and pressure causes increased wall tension. To compensate for this increased wall tension, myocyte enlarge in an attempt to relieve tension on any one myocyte. Hypertrophy is damaging on severa ...
... ii. Ventricular dilation and myocardial hypertrophy: with hemodynamic overload, the increased blood volume and pressure causes increased wall tension. To compensate for this increased wall tension, myocyte enlarge in an attempt to relieve tension on any one myocyte. Hypertrophy is damaging on severa ...
HeartStructure
... •The aorta, the largest artery in your body, is almost the diameter of a garden hose •The heart pumps about 1 million barrels of blood during an average lifetime ...
... •The aorta, the largest artery in your body, is almost the diameter of a garden hose •The heart pumps about 1 million barrels of blood during an average lifetime ...
Anatomy of the Cardiovascular system Notes
... – Veins - carry blood toward the heart. – Capillaries - attach arteries and veins. ...
... – Veins - carry blood toward the heart. – Capillaries - attach arteries and veins. ...
Myocardial infarction

Myocardial infarction (MI) or acute myocardial infarction (AMI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow stops to a part of the heart causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Often it is in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat, or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms, with women more likely than men to present atypically. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, or cardiac arrest.Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, and excessive alcohol intake, among others. The mechanism of an MI often involves the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque, leading to complete blockage of a coronary artery. MIs are less commonly caused by coronary artery spasms, which may be due to cocaine, significant emotional stress, and extreme cold, among others. A number of tests are useful to help with diagnosis, including electrocardiograms (ECGs), blood tests, and coronary angiography. An ECG may confirm an ST elevation MI if ST elevation is present. Commonly used blood tests include troponin and less often creatine kinase MB.Aspirin is an appropriate immediate treatment for a suspected MI. Nitroglycerin or opioids may be used to help with chest pain; however, they do not improve overall outcomes. Supplemental oxygen should be used in those with low oxygen levels or shortness of breath. In ST elevation MIs treatments which attempt to restore blood flow to the heart are typically recommended and include angioplasty, where the arteries are pushed open, or thrombolysis, where the blockage is removed using medications. People who have a non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) are often managed with the blood thinner heparin, with the additional use angioplasty in those at high risk. In people with blockages of multiple coronary arteries and diabetes, bypass surgery (CABG) may be recommended rather than angioplasty. After an MI, lifestyle modifications, along with long term treatment with aspirin, beta blockers, and statins, are typically recommended.Worldwide, more than 3 million people have ST elevation MIs and 4 million have NSTEMIs each year. STEMIs occur about twice as often in men as women. About one million people have an MI each year in the United States. In the developed world the risk of death in those who have had an STEMI is about 10%. Rates of MI for a given age have decreased globally between 1990 and 2010.