HTN_chol - S. Blake Wachter, MD, PhD Advanced Heart Failure
... (LDL-C) and/or non–high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non–HDL-C) targets. New, pooled risk assessment. Use of biomarkers and noninvasive tests. ...
... (LDL-C) and/or non–high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non–HDL-C) targets. New, pooled risk assessment. Use of biomarkers and noninvasive tests. ...
12-2
... the ventricular muscle An increase in heart size would increase the size of the complex T wave- indicates the ventricular repolarization ...
... the ventricular muscle An increase in heart size would increase the size of the complex T wave- indicates the ventricular repolarization ...
Heart Transplantation
... Donors are people with “brain death” or irreversible brain injury who still has other healthy organs. A team of physicians, nurses, and technicians goes to the hospital of the donor to remove donated organs once brain death of the donor has been ...
... Donors are people with “brain death” or irreversible brain injury who still has other healthy organs. A team of physicians, nurses, and technicians goes to the hospital of the donor to remove donated organs once brain death of the donor has been ...
AnatIICaseStudy1
... Tachycardia: the tachycardia would most likely be caused by the atrial fibrillation. The intrinsic conduction system is being thrown off, meaning the pacemaker (SA node) is not able to regulate the pace at which the heart is beating. Light headedness: Would likely be caused by insufficient blood cir ...
... Tachycardia: the tachycardia would most likely be caused by the atrial fibrillation. The intrinsic conduction system is being thrown off, meaning the pacemaker (SA node) is not able to regulate the pace at which the heart is beating. Light headedness: Would likely be caused by insufficient blood cir ...
Looking at a heart
... SAFETY: Wear eye protection whenever there is a risk to the eyes, for example, when changing scalpel blades, cutting cartilage or if the heart you are working with has been preserved. Clean the work area carefully after the investigation. Investigation 1 – Looking at the outside of a heart a Note th ...
... SAFETY: Wear eye protection whenever there is a risk to the eyes, for example, when changing scalpel blades, cutting cartilage or if the heart you are working with has been preserved. Clean the work area carefully after the investigation. Investigation 1 – Looking at the outside of a heart a Note th ...
four valves
... ventricles occur causes vibrations of ventricular walls" and this known as sound "3" ". Sound "3" best heard at the apex with bell of stethoscope. Its indicate Pathological alterations in ventricular filling in early diastole. it represents a normal finding in children Sound "4": occur after Sound ...
... ventricles occur causes vibrations of ventricular walls" and this known as sound "3" ". Sound "3" best heard at the apex with bell of stethoscope. Its indicate Pathological alterations in ventricular filling in early diastole. it represents a normal finding in children Sound "4": occur after Sound ...
circulatory system - Franklin Middle School
... • The human heart is a muscular pump composed of cardiac muscle that allows for continued rhythmic contraction. • It is located in the middle of your chest right behind the sternum and just to the left. • It is the size of your fist. ...
... • The human heart is a muscular pump composed of cardiac muscle that allows for continued rhythmic contraction. • It is located in the middle of your chest right behind the sternum and just to the left. • It is the size of your fist. ...
Heart
... the wrist (about 1 inch from the top of wrist, on the thumb side). Locate the artery by feeling for a pulse with the index and middle fingers; apply light pressure to feel the pulse. When measuring the pulse during rest, count the number of beats in 60 seconds; when measuring the pulse during ex ...
... the wrist (about 1 inch from the top of wrist, on the thumb side). Locate the artery by feeling for a pulse with the index and middle fingers; apply light pressure to feel the pulse. When measuring the pulse during rest, count the number of beats in 60 seconds; when measuring the pulse during ex ...
Diagnostic procedures in cardiology
... Dyspnea. Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea: Relieved by sitting up standing. It is more specific cardiac disease Chest pain. Characteristics of myocardial ischemia: dull, aching, sensation of pressure or tightness, commonly accompanied by anxiety or uneasiness. Protracted episodes suggest myocardial infa ...
... Dyspnea. Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea: Relieved by sitting up standing. It is more specific cardiac disease Chest pain. Characteristics of myocardial ischemia: dull, aching, sensation of pressure or tightness, commonly accompanied by anxiety or uneasiness. Protracted episodes suggest myocardial infa ...
More about Hypertension Hypertension may also be caused by a
... treatment is of the underlying condition. Hypertension of an unknown cause, called essential hypertension, may be familial. It is said to affect women more often than men. The systolic pressure continues to increase as the affected person grows older. The diastolic pressure rises until middle age. E ...
... treatment is of the underlying condition. Hypertension of an unknown cause, called essential hypertension, may be familial. It is said to affect women more often than men. The systolic pressure continues to increase as the affected person grows older. The diastolic pressure rises until middle age. E ...
Slide ()
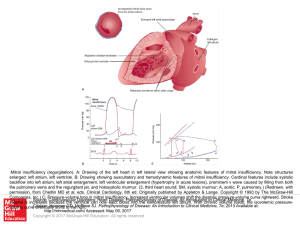
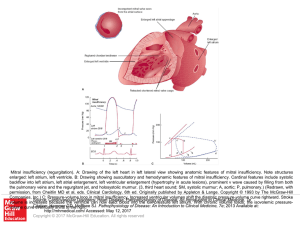
... backflow into left atrium, left atrial enlargement, left ventricular enlargement (hypertrophy in acute lesions), prominent v wave caused by filling from both the pulmonary veins and the regurgitant jet, and holosystolic murmur. (3, third heart sound; SM, systolic murmur; A, aortic; P, pulmonary.) (R ...
... backflow into left atrium, left atrial enlargement, left ventricular enlargement (hypertrophy in acute lesions), prominent v wave caused by filling from both the pulmonary veins and the regurgitant jet, and holosystolic murmur. (3, third heart sound; SM, systolic murmur; A, aortic; P, pulmonary.) (R ...
Slide ()
... backflow into left atrium, left atrial enlargement, left ventricular enlargement (hypertrophy in acute lesions), prominent v wave caused by filling from both the pulmonary veins and the regurgitant jet, and holosystolic murmur. (3, third heart sound; SM, systolic murmur; A, aortic; P, pulmonary.) (R ...
... backflow into left atrium, left atrial enlargement, left ventricular enlargement (hypertrophy in acute lesions), prominent v wave caused by filling from both the pulmonary veins and the regurgitant jet, and holosystolic murmur. (3, third heart sound; SM, systolic murmur; A, aortic; P, pulmonary.) (R ...
Cardiovascular System Notes
... close all the way; this creates a clicking sound at the end of a contraction. 2. Heart Murmurs – valves do not close completely, causing an (often) harmless murmur sound. Sometimes holes can occur in the septum f the heart which can also cause a murmur 3. Myocardial Infarction (MI) - a blood clot ob ...
... close all the way; this creates a clicking sound at the end of a contraction. 2. Heart Murmurs – valves do not close completely, causing an (often) harmless murmur sound. Sometimes holes can occur in the septum f the heart which can also cause a murmur 3. Myocardial Infarction (MI) - a blood clot ob ...
HERE
... • smaller than RBCs • "little bags of chemicals" that function in clotting and plugging up breaks in vessels Blood Clotting- a complex series of chemical reactions, involving platelets and plasma "clotting factors". Often referred to as the "clotting cascade". ...
... • smaller than RBCs • "little bags of chemicals" that function in clotting and plugging up breaks in vessels Blood Clotting- a complex series of chemical reactions, involving platelets and plasma "clotting factors". Often referred to as the "clotting cascade". ...
Chapter 47 - Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
... • smaller than RBCs • "little bags of chemicals" that function in clotting and plugging up breaks in vessels Blood Clotting- a complex series of chemical reactions, involving platelets and plasma "clotting factors". Often referred to as the "clotting cascade". ...
... • smaller than RBCs • "little bags of chemicals" that function in clotting and plugging up breaks in vessels Blood Clotting- a complex series of chemical reactions, involving platelets and plasma "clotting factors". Often referred to as the "clotting cascade". ...
Pediatrics Congenital Heart Disease
... Signs Demonstrates cardinal signs Clubbing of fingers and Cardiac catheterization may toes in older children be required to show Loud harsh ejection systolic detailed anatomy of murmur coronary artery ...
... Signs Demonstrates cardinal signs Clubbing of fingers and Cardiac catheterization may toes in older children be required to show Loud harsh ejection systolic detailed anatomy of murmur coronary artery ...
SNC2D1 Date: Name: MAIN FUNCTION OF THE CIRCULATORY
... - Carries blood ___________ the heart - _______ pressure, _______ walls - Has ___________ to make sure that blood moves in the right direction - Tiny blood vessels with _______________ walls to allow ___________________ to occur Ex. ________________ must diffuse from the blood cells to the _________ ...
... - Carries blood ___________ the heart - _______ pressure, _______ walls - Has ___________ to make sure that blood moves in the right direction - Tiny blood vessels with _______________ walls to allow ___________________ to occur Ex. ________________ must diffuse from the blood cells to the _________ ...
Chapter 8 Physics of the Cardiovascular System
... ù Often little or no collateral circulation ù Coronary arteries are first to suffer complete blockage (SaO2 ~ 0% in venous return from heart) Ÿ Partial blockage ù Angina pectoris: pain during exertion ù Develop collateral circulation in a few days Ÿ Sudden (acute) blockage ù Blood clot forms rapidly ...
... ù Often little or no collateral circulation ù Coronary arteries are first to suffer complete blockage (SaO2 ~ 0% in venous return from heart) Ÿ Partial blockage ù Angina pectoris: pain during exertion ù Develop collateral circulation in a few days Ÿ Sudden (acute) blockage ù Blood clot forms rapidly ...
Mediastinum is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. It
... • Narrowing or blockage of O2 rich blood flow in coronary arteries = coronary occlusion = problems with sufficient oxidative phosphylation to allow myocardial contraction • Venous Drainage – Parallel vessels – Rarely a problem – Drain directly to right atrium • Little Hb‐O2 left ...
... • Narrowing or blockage of O2 rich blood flow in coronary arteries = coronary occlusion = problems with sufficient oxidative phosphylation to allow myocardial contraction • Venous Drainage – Parallel vessels – Rarely a problem – Drain directly to right atrium • Little Hb‐O2 left ...
C11.2 Notes - Destiny High School
... 1. Describe the mechanisms that regulate the heart. 2. Describe different types of arrhythmia, or abnormal contractility conditions that can be detected via electrocardiogram. 3. Identify the components of the conduction system of the heart. Regulation of the Heart ...
... 1. Describe the mechanisms that regulate the heart. 2. Describe different types of arrhythmia, or abnormal contractility conditions that can be detected via electrocardiogram. 3. Identify the components of the conduction system of the heart. Regulation of the Heart ...
close
... • All cells of the conducting fibers are autorhythmic • The cells of the SA node set the heart rate because their rhythm is fastest. • They set the pace. • If the SA node is damaged, the other pacemakers still function, the pace lowers. ...
... • All cells of the conducting fibers are autorhythmic • The cells of the SA node set the heart rate because their rhythm is fastest. • They set the pace. • If the SA node is damaged, the other pacemakers still function, the pace lowers. ...
Myocardial infarction

Myocardial infarction (MI) or acute myocardial infarction (AMI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow stops to a part of the heart causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Often it is in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat, or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms, with women more likely than men to present atypically. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, or cardiac arrest.Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, and excessive alcohol intake, among others. The mechanism of an MI often involves the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque, leading to complete blockage of a coronary artery. MIs are less commonly caused by coronary artery spasms, which may be due to cocaine, significant emotional stress, and extreme cold, among others. A number of tests are useful to help with diagnosis, including electrocardiograms (ECGs), blood tests, and coronary angiography. An ECG may confirm an ST elevation MI if ST elevation is present. Commonly used blood tests include troponin and less often creatine kinase MB.Aspirin is an appropriate immediate treatment for a suspected MI. Nitroglycerin or opioids may be used to help with chest pain; however, they do not improve overall outcomes. Supplemental oxygen should be used in those with low oxygen levels or shortness of breath. In ST elevation MIs treatments which attempt to restore blood flow to the heart are typically recommended and include angioplasty, where the arteries are pushed open, or thrombolysis, where the blockage is removed using medications. People who have a non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) are often managed with the blood thinner heparin, with the additional use angioplasty in those at high risk. In people with blockages of multiple coronary arteries and diabetes, bypass surgery (CABG) may be recommended rather than angioplasty. After an MI, lifestyle modifications, along with long term treatment with aspirin, beta blockers, and statins, are typically recommended.Worldwide, more than 3 million people have ST elevation MIs and 4 million have NSTEMIs each year. STEMIs occur about twice as often in men as women. About one million people have an MI each year in the United States. In the developed world the risk of death in those who have had an STEMI is about 10%. Rates of MI for a given age have decreased globally between 1990 and 2010.