* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
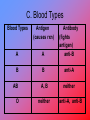
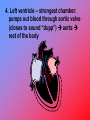
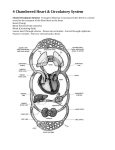
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM -Blood, heart, blood vessels Introduction to the Circulatory System – 0:58 I. BLOOD A. Functions 1. carries food, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones & enzyme 2. transports wastes 3. clots blood 4. helps fight infection 5. distributes heat Blood – 4:11 B. Composition 1. plasma – liquid part of blood Solid Parts 2. R.B.C. – carries oxygen & carbon dioxide Anemia – caused by lack of r.b.c. or iron 3. w.b.c. – helps fight infection 4. platelets – clot blood C. Blood Types Blood Types Antigen (causes rxn) A A Antibody (fights antigen) anti-B B B anti-A AB O A, B neither neither anti-A, anti-B - Universal DONOR – type O (can donate to anyone) – no antigens - Universal recipient – type AB (can receive from anyone) – no antibodies Rh factor: + or Rh + : has + antigen Rh - : has + antibody Blood – 4:11 II. Heart A. Chambers/valves 1. right atrium (receives blood from body) Right AV (or tricuspid) valve closes to sound “lub” 2. right ventricle – pumps blood through to pulmonary (semilunar) valve closes to sound “dupp” to lungs (give off carbon dioxide & takes in oxygen 3. Left Atrium – receives oxygenated blood from lungs left AV (or bicuspid) valve closes to sound “lub” (at same as right AV valve) 4. Left ventricle – strongest chamber: pumps out blood through aortic valve (closes to sound “dupp”) aorta rest of the body Heart – 4:33 B. Terms 1. Heart attack – clot in heart (usually in coronary arteries 2. blood pressure – pressure in artery walls; ex. 120/80 – pressure when contraction/ relaxation of ventricles 3. heart murmur – faulty valve (often) 4. CPR – cardio (heart); pulmonary (lung) recessitation III. BLOOD VESSELS A. Arteries – carry blood AWAY from the heart; most carry oxygen & are bright red; thicker & stronger B. Arterioles – small arteries C. Capillaries – connect arterioles to venules; microscopic; exchange of gases & nutrient takes place here between blood & cells D. Venules – small veins E. Veins – carry blood to heart; most carry carbon dioxide & are deep purple; less elastic; some have valves; - varicose veins/hemorrhoids – flabby veins F. Other Terms 1. stroke – blood clot in vessel in brain 2. high blood pressure – pressure too high in arteries which can lead to heart attack, stroke, kidney damage, blindness Blood Vessels – 4:17 CIRCULATION Right Atrium right ventricle lungs left Atrium left ventricle aorta/arteries arterioles capillaries venules veins back to heart (right atrium) Healthy Circulatory System – 0:37 Summary – 0:58 THE END!!!