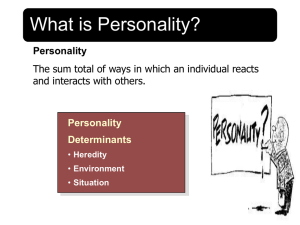
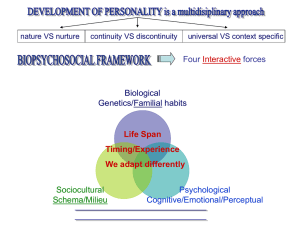
SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY
... Self-disclosure occurs more when two people like one another. Self-disclosure follows a reciprocity norm: Low levels of self-disclosure are met with low levels in return, whereas moderate self-disclosure elicits more personal replies. However, overdisclosure tends to inhibit self-disclosure by other ...
... Self-disclosure occurs more when two people like one another. Self-disclosure follows a reciprocity norm: Low levels of self-disclosure are met with low levels in return, whereas moderate self-disclosure elicits more personal replies. However, overdisclosure tends to inhibit self-disclosure by other ...
SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY
... Self-disclosure occurs more when two people like one another. Self-disclosure follows a reciprocity norm: Low levels of self-disclosure are met with low levels in return, whereas moderate self-disclosure elicits more personal replies. However, overdisclosure tends to inhibit self-disclosure by other ...
... Self-disclosure occurs more when two people like one another. Self-disclosure follows a reciprocity norm: Low levels of self-disclosure are met with low levels in return, whereas moderate self-disclosure elicits more personal replies. However, overdisclosure tends to inhibit self-disclosure by other ...
Fall 2015 Chapter 13 Pt 1
... And importance is manipulated by telling participants that they will receive $20 if they are the most accurate participant in the experiment (or not telling them this). ...
... And importance is manipulated by telling participants that they will receive $20 if they are the most accurate participant in the experiment (or not telling them this). ...
The Cognitive Approach
... He proposed that we experience negative emotion to the extent that our actual self falls short of our ideal self or our ought self. However, the first kind of discrepancy should result in feelings of disappointment or depression, whereas the second kind of discrepancy should result in feelings o ...
... He proposed that we experience negative emotion to the extent that our actual self falls short of our ideal self or our ought self. However, the first kind of discrepancy should result in feelings of disappointment or depression, whereas the second kind of discrepancy should result in feelings o ...
History of Psychologists
... he taught his patients to relax deeply and he then created situations that would cause anxiety by working with minor ones and then with more top level anxiety producing situations. ...
... he taught his patients to relax deeply and he then created situations that would cause anxiety by working with minor ones and then with more top level anxiety producing situations. ...
Attitude - Living Word
... • Conscientiousness concerns the way in which we control, regulate, and direct our impulses. • Impulses are not inherently bad; occasionally time constraints require a snap decision, and acting on our first impulse can be an effective response. • Also, in times of play rather than work, acting spont ...
... • Conscientiousness concerns the way in which we control, regulate, and direct our impulses. • Impulses are not inherently bad; occasionally time constraints require a snap decision, and acting on our first impulse can be an effective response. • Also, in times of play rather than work, acting spont ...
Social Psychology - CCRI Faculty Web
... Personality Psychologists could study the traits that might make one person more likely than another to speak, and Social Psychologists might examine aspects of the classroom situation that would influence any student’s decision about speaking. ...
... Personality Psychologists could study the traits that might make one person more likely than another to speak, and Social Psychologists might examine aspects of the classroom situation that would influence any student’s decision about speaking. ...
d. the fundamental attribution error.
... 8. Which of the following factors does NOT promote conformity? a. doubting your abilities or knowledge b. having already expressed your commitment to an opinion or idea c. having to go against four or five people who all agree on an opinion or idea d. having to give your response in front of a grou ...
... 8. Which of the following factors does NOT promote conformity? a. doubting your abilities or knowledge b. having already expressed your commitment to an opinion or idea c. having to go against four or five people who all agree on an opinion or idea d. having to give your response in front of a grou ...
Chapter 14, Modules 32
... 6. Describe the impact of cognitive dissonance on attitudes and behavior. 7. Define conformity and explain the results of Asch’s study. 8. Outline the conditions under which conformity is likely to occur. 9. Define obedience and describe Milgram’s classic study on obedience (include results). 10. Wh ...
... 6. Describe the impact of cognitive dissonance on attitudes and behavior. 7. Define conformity and explain the results of Asch’s study. 8. Outline the conditions under which conformity is likely to occur. 9. Define obedience and describe Milgram’s classic study on obedience (include results). 10. Wh ...
Chapter 12: Social Psychology
... Define and provide examples of the attributional biases, including the actor-observer discrepancy, the self-serving bias, and the self-effacing bias. ...
... Define and provide examples of the attributional biases, including the actor-observer discrepancy, the self-serving bias, and the self-effacing bias. ...
Social Judgment Theory Paper
... commuting so this news is of huge importance to them. This forces their ego to represent a strong, concrete position on the matter. This person will believe that no matter what the circumstance is, gas prices should not be raised. They have this strong opinion because the importance of gas prices a ...
... commuting so this news is of huge importance to them. This forces their ego to represent a strong, concrete position on the matter. This person will believe that no matter what the circumstance is, gas prices should not be raised. They have this strong opinion because the importance of gas prices a ...
Social Psychology – Modules 53-55
... Hormones and other substances in the blood influence the neural systems that activate and inhibit aggression A raging bull will become gentle when testosterone levels are reduced – vice ...
... Hormones and other substances in the blood influence the neural systems that activate and inhibit aggression A raging bull will become gentle when testosterone levels are reduced – vice ...
Accent notes and task
... Linguists and sociologists have long been interested in the way people are able to make judgements about people simply from their accent. A number of studies have tested this by playing a sample group recordings of several different speakers reading the same passage and asking group members to rate ...
... Linguists and sociologists have long been interested in the way people are able to make judgements about people simply from their accent. A number of studies have tested this by playing a sample group recordings of several different speakers reading the same passage and asking group members to rate ...
File - BBA Group A 2010
... 1. never suffer from a sense of time urgency with its accompanying impatience; 2. feel no need to display or discuss either their achievements or accomplishments; 3. play for fun and relaxation, rather than to exhibit their superiority at any cost; 4. can relax without guilt. ...
... 1. never suffer from a sense of time urgency with its accompanying impatience; 2. feel no need to display or discuss either their achievements or accomplishments; 3. play for fun and relaxation, rather than to exhibit their superiority at any cost; 4. can relax without guilt. ...
Workplace Emotions, Attitudes, and Stress
... How emotions influence attitudes: 1. Feelings and beliefs are influenced by cumulative ...
... How emotions influence attitudes: 1. Feelings and beliefs are influenced by cumulative ...
pleasure principle”.
... conditioning) and reciprocal determinism Bandura , Social Cognitive Theory Cognitive – people try and understand Social – other people are an important source of information Self-efficacy – the result of experience which results in a person’s belief about their own abilities/talents. This sense ...
... conditioning) and reciprocal determinism Bandura , Social Cognitive Theory Cognitive – people try and understand Social – other people are an important source of information Self-efficacy – the result of experience which results in a person’s belief about their own abilities/talents. This sense ...
CBT for M Studen..
... Principle No. 4. Cognitive therapy is goal oriented and problem focused. Principle No. 5. Cognitive therapy initially emphasizes the present. Principle No. 6. Cognitive therapy is educative, aims to teach the patient to be her own therapist, and ...
... Principle No. 4. Cognitive therapy is goal oriented and problem focused. Principle No. 5. Cognitive therapy initially emphasizes the present. Principle No. 6. Cognitive therapy is educative, aims to teach the patient to be her own therapist, and ...
social & group influences (cont.)
... interpreting and categorizing objects and events and deciding whether to approach or avoid them ...
... interpreting and categorizing objects and events and deciding whether to approach or avoid them ...
Social Learning Theory
... between two points of view (that of the actor and the observer). 3. Self-Serving Bias – The tendency we have to attribute positive outcomes to our own dispositions and negative outcomes to ...
... between two points of view (that of the actor and the observer). 3. Self-Serving Bias – The tendency we have to attribute positive outcomes to our own dispositions and negative outcomes to ...
Sociology - chsdistefano
... cultural change rarely occurs without opposition. * Social change usually occurs as a result of a compromise between opposing forces. * Some people will never accept change, but, in time, will adapt to it. * Reasons why people resist social change: 1. ethnocentrism – tendency to view one’s own cultu ...
... cultural change rarely occurs without opposition. * Social change usually occurs as a result of a compromise between opposing forces. * Some people will never accept change, but, in time, will adapt to it. * Reasons why people resist social change: 1. ethnocentrism – tendency to view one’s own cultu ...
Attitudes, Values & Job Satisfaction
... An attitude is defined as a learned predisposition to respond in a consistently favourable or unfavourable manner with respect to a given object. While Values represent global beliefs that influence behaviour, across all situations, attitudes relate only to behaviour directed towards specific obj ...
... An attitude is defined as a learned predisposition to respond in a consistently favourable or unfavourable manner with respect to a given object. While Values represent global beliefs that influence behaviour, across all situations, attitudes relate only to behaviour directed towards specific obj ...
Brief Intervention
... Why Brief Intervention? Need for prevention services specifically targeting youth with problems associated with their drug use (“indicated” population in the IOM prevention model). The gap between treatment need and treatment availability is significantly increasing for adolescents. Tightening of t ...
... Why Brief Intervention? Need for prevention services specifically targeting youth with problems associated with their drug use (“indicated” population in the IOM prevention model). The gap between treatment need and treatment availability is significantly increasing for adolescents. Tightening of t ...
Chicken/Egg/Chegg! - 1Source Safety and Health, Inc.
... what to do and what not to do. From our research into the causes of the injuries occurring there, we concluded the most effective way to bring about lasting behavioral change is to start by raising people's awareness. The next step is to have them examine the core beliefs and attitudes that shape th ...
... what to do and what not to do. From our research into the causes of the injuries occurring there, we concluded the most effective way to bring about lasting behavioral change is to start by raising people's awareness. The next step is to have them examine the core beliefs and attitudes that shape th ...
Attitude change

Attitudes are associated beliefs and behaviors towards some object. They are not stable, and because of the communication and behavior of other people, are subject to change by social influences, as well as by the individual's motivation to maintain cognitive consistency when cognitive dissonance occurs--when two attitudes or attitude and behavior conflict. Attitudes and attitude objects are functions of affective and cognitive components. It has been suggested that the inter-structural composition of an associative network can be altered by the activation of a single node. Thus, by activating an affective or emotional node, attitude change may be possible, though affective and cognitive components tend to be intertwined.