In Pursuit of a Contextual Diagnostic Approach to Behavior Change
... Message Appeals: “[T]he manner in which a frequency of competing messages is low. communication is stated plays an important role in Filters: The human mind cannot process all determining its effectiveness.” (Aronson, 2008.) incoming information, and thus filters out much of Some communications are ...
... Message Appeals: “[T]he manner in which a frequency of competing messages is low. communication is stated plays an important role in Filters: The human mind cannot process all determining its effectiveness.” (Aronson, 2008.) incoming information, and thus filters out much of Some communications are ...
Handouts Ch 5
... cognitionA general cognitive ability of an individual to rely primarily on bodily cues within themselves and to be less oriented toward social engagement with others. ...
... cognitionA general cognitive ability of an individual to rely primarily on bodily cues within themselves and to be less oriented toward social engagement with others. ...
GENERAL PSYCHOLOGY 1st year Physiotheraphy, 1st year
... 33. What was the content of unconscious in Freud’s theory of personality? 34. Explain one of the ego’s defense mechanisms. 35. What are the main criticisms of the psychoanalytic theories? 36. What are the assumptions of the trait theory? 37. What are the main criticisms of the trait theory? 38. What ...
... 33. What was the content of unconscious in Freud’s theory of personality? 34. Explain one of the ego’s defense mechanisms. 35. What are the main criticisms of the psychoanalytic theories? 36. What are the assumptions of the trait theory? 37. What are the main criticisms of the trait theory? 38. What ...
Social Psychology Notes Social Psychology Is concerned with the
... 7 confederates-Confederates of the experiment gave the same wrong answers ...
... 7 confederates-Confederates of the experiment gave the same wrong answers ...
Social Influence - Trinity College, Dublin
... Social validation Use beliefs, attitudes, actions of similar others as standard of comparison for selfevaluation Rule: more willing to comply with request for behaviour if consistent with what similar others are doing . ...
... Social validation Use beliefs, attitudes, actions of similar others as standard of comparison for selfevaluation Rule: more willing to comply with request for behaviour if consistent with what similar others are doing . ...
View/Open
... with requesting (knowledge of task environment) Do you know how to do it/able to use tools? ...
... with requesting (knowledge of task environment) Do you know how to do it/able to use tools? ...
Intro to Social Psychology
... someone is made to play a role which is contradictory to their own personal attitude, they will attempt to either stop playing the contradictory role or replace their previous attitude with an attitude that will allow them to keep playing that role. Thus, the way a person acts can change their attit ...
... someone is made to play a role which is contradictory to their own personal attitude, they will attempt to either stop playing the contradictory role or replace their previous attitude with an attitude that will allow them to keep playing that role. Thus, the way a person acts can change their attit ...
Cognitive component - UPM EduTrain Interactive Learning
... experiences often occur when we do what others want us to do. – Seeking approval and avoiding disapproval are assumed to be central motivators for people. – Learned component of motivation has its roots in this theory. – Children learn a great deal through imitation and observation. – We are intrins ...
... experiences often occur when we do what others want us to do. – Seeking approval and avoiding disapproval are assumed to be central motivators for people. – Learned component of motivation has its roots in this theory. – Children learn a great deal through imitation and observation. – We are intrins ...
History and Approaches History Hippocrates
... Bruce Biddle • known for role theory • people are aware of their social roles and their observable behavior can be attributed to adopting those roles ...
... Bruce Biddle • known for role theory • people are aware of their social roles and their observable behavior can be attributed to adopting those roles ...
Slide 1
... • effects of social variables & cognitions – individual behavior & social interactions • social cognition• social influence- ...
... • effects of social variables & cognitions – individual behavior & social interactions • social cognition• social influence- ...
Chapter Fifteen - University of Mississippi
... Feelings and emotions toward a situation (i.e., how we feel). Cognitive component Perceived knowledge (i.e., why we feel the way we feel). Intentional component Expected behavior in a given situation (i.e., what we intend do about the situation). ...
... Feelings and emotions toward a situation (i.e., how we feel). Cognitive component Perceived knowledge (i.e., why we feel the way we feel). Intentional component Expected behavior in a given situation (i.e., what we intend do about the situation). ...
Final Exam Review 1
... d. Places too great an emphasis on positive traits 29. In studying personality, a social-cognitive theorist would MOST LIKELY make use of a. Personality inventories b. Projective tests c. Observing behavior in different situations d. Factor analysis 30. Which of the following is true? a. Attitudes a ...
... d. Places too great an emphasis on positive traits 29. In studying personality, a social-cognitive theorist would MOST LIKELY make use of a. Personality inventories b. Projective tests c. Observing behavior in different situations d. Factor analysis 30. Which of the following is true? a. Attitudes a ...
Jeopardy - Litteacher.com
... show less evidence of egocentrism than others. So, his stages, while applicable in a broad sense, do not exactly reflect reality as it is. ...
... show less evidence of egocentrism than others. So, his stages, while applicable in a broad sense, do not exactly reflect reality as it is. ...
Mark 432 – Lesson 2
... 5. Hierarchy of Effects Model (Objective 6): The type of learning model we use can influence whether we will be successful at moving the consumer through the Hierarchy of Effects model. Awareness → Beliefs → Attitudes → Behavior Beliefs – The knowledge and feelings a person has accumulated about an ...
... 5. Hierarchy of Effects Model (Objective 6): The type of learning model we use can influence whether we will be successful at moving the consumer through the Hierarchy of Effects model. Awareness → Beliefs → Attitudes → Behavior Beliefs – The knowledge and feelings a person has accumulated about an ...
Goals of Psych - Deerfield High School
... behavior. If people cannot justify their behavior, they’re likely to change their beliefs about it in order to decrease discomfort ...
... behavior. If people cannot justify their behavior, they’re likely to change their beliefs about it in order to decrease discomfort ...
B. Organismic Model
... B. Learning Theory 2: Social Learning 1) Social Learning: we learn about many behaviors before we attempt them for the first time by observing the behaviors of others and from imagining the consequences of our own. ...
... B. Learning Theory 2: Social Learning 1) Social Learning: we learn about many behaviors before we attempt them for the first time by observing the behaviors of others and from imagining the consequences of our own. ...
Module 1: Discovering Psychology
... however, in 1991 there were more male full-time psychologists than women ...
... however, in 1991 there were more male full-time psychologists than women ...
Theory of reasoned action (TRA) Theory of
... suggested the theory could not explain in sufficient detail the actins of people who have little or no control over their behaviour ...
... suggested the theory could not explain in sufficient detail the actins of people who have little or no control over their behaviour ...
Thinking Cognition mental activities associated with thinking
... Peak-end rule; judge past experiences on how they were at peak (pleasant or unpleasant) and how they ended. All other information discarded, including pleasantness or unpleasantness, and how long experience lasted. This heuristic was first suggested by Daniel Kahneman ...
... Peak-end rule; judge past experiences on how they were at peak (pleasant or unpleasant) and how they ended. All other information discarded, including pleasantness or unpleasantness, and how long experience lasted. This heuristic was first suggested by Daniel Kahneman ...
Social Learning Theory
... between two points of view (that of the actor and the observer). 3. Self-Serving Bias – The tendency we have to attribute positive outcomes to our own dispositions and negative outcomes to ...
... between two points of view (that of the actor and the observer). 3. Self-Serving Bias – The tendency we have to attribute positive outcomes to our own dispositions and negative outcomes to ...
social comparison - Warren County Public Schools
... self-serving bias tendency to attribute success to internal or dispositional factors while blaming any failure on external or situational factors ...
... self-serving bias tendency to attribute success to internal or dispositional factors while blaming any failure on external or situational factors ...
Unit 13: Social Psychology
... so greatly values this feature, that he would pay more for a ticket on an airline with a better on time record. When Mr. B arrives on time, he is calm. When he even thinks that he might arrive late, he gets very ...
... so greatly values this feature, that he would pay more for a ticket on an airline with a better on time record. When Mr. B arrives on time, he is calm. When he even thinks that he might arrive late, he gets very ...
social influence
... About 100,000,000 women are missing in the world. There is a preference for male children in China and India, even with sex-selected abortion outlawed. In 2003, as in 1941, two-thirds of Americans surveyed expressed a gender ...
... About 100,000,000 women are missing in the world. There is a preference for male children in China and India, even with sex-selected abortion outlawed. In 2003, as in 1941, two-thirds of Americans surveyed expressed a gender ...
Robbins & Judge Organizational Behavior 13e
... – The closer the match between attitude and behavior, the stronger the relationship: • Specific attitudes predict specific behavior • General attitudes predict general behavior – The more frequently expressed an attitude, the better predictor it is. – High social pressures reduce the relationship an ...
... – The closer the match between attitude and behavior, the stronger the relationship: • Specific attitudes predict specific behavior • General attitudes predict general behavior – The more frequently expressed an attitude, the better predictor it is. – High social pressures reduce the relationship an ...
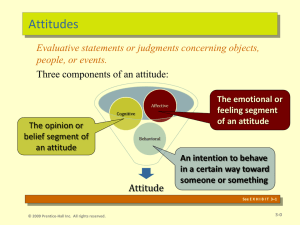
Attitude change

Attitudes are associated beliefs and behaviors towards some object. They are not stable, and because of the communication and behavior of other people, are subject to change by social influences, as well as by the individual's motivation to maintain cognitive consistency when cognitive dissonance occurs--when two attitudes or attitude and behavior conflict. Attitudes and attitude objects are functions of affective and cognitive components. It has been suggested that the inter-structural composition of an associative network can be altered by the activation of a single node. Thus, by activating an affective or emotional node, attitude change may be possible, though affective and cognitive components tend to be intertwined.