![ChemChapter_4[1]Light](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001894151_1-323884b777914f52c04d2bb917d4088a-300x300.png)
ChemChapter_4[1]Light
... orientation of the orbital around the nucleus. • Spin Quantum Number – (s) – indicates the direction of the spin of the electron on its own ...
... orientation of the orbital around the nucleus. • Spin Quantum Number – (s) – indicates the direction of the spin of the electron on its own ...
Notes
... could move only in certain allowed circular orbits without radiating energy (classically, an accelerating charge (such as the electron moving in a circle) would continuously radiate energy and spiral into the nucleus in a very short time). Bohr called these allowed orbits stationary states. A photon ...
... could move only in certain allowed circular orbits without radiating energy (classically, an accelerating charge (such as the electron moving in a circle) would continuously radiate energy and spiral into the nucleus in a very short time). Bohr called these allowed orbits stationary states. A photon ...
Chapter 29: Light Waves Interference Constructive Interference
... • Quantum = discrete, individual, point-like object • Different from waves, as we typically think of them • 1 quantum = 1 “piece”, or 1 step (think of increasing energy in small chunks, rather than continuously) ...
... • Quantum = discrete, individual, point-like object • Different from waves, as we typically think of them • 1 quantum = 1 “piece”, or 1 step (think of increasing energy in small chunks, rather than continuously) ...
Chapter 7 Student Learning Map
... duality explanation used to explain light and electrons? What is the relationship between the speed, frequency, and wavelength of electromagnetic radiation? What is the significance of the photoelectric effect in describing the behavior of the electron and light? ...
... duality explanation used to explain light and electrons? What is the relationship between the speed, frequency, and wavelength of electromagnetic radiation? What is the significance of the photoelectric effect in describing the behavior of the electron and light? ...
Materiality: Is It Real?
... Mass is what comprises matter. It is the flip side of the energy manifestation of field. Its popularity as the basis of our material reality is the result of man’s practical nature. Physics is concerned with physical phenomena for which it is necessary to have practical explanations. Every physical ...
... Mass is what comprises matter. It is the flip side of the energy manifestation of field. Its popularity as the basis of our material reality is the result of man’s practical nature. Physics is concerned with physical phenomena for which it is necessary to have practical explanations. Every physical ...
Atomic and Molecular Physics for Physicists Ben-Gurion University of the Negev
... This leads to the cat paradox, as in reality we have never seen a macroscopic superposition. What is the justification for the superposition state: It is the only way we know to explain some experimental observations! ...
... This leads to the cat paradox, as in reality we have never seen a macroscopic superposition. What is the justification for the superposition state: It is the only way we know to explain some experimental observations! ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Duality of Matter
... Actually, we need not speak of particles at all. For many experiments it is more convenient to speak of matter waves . . . The two pictures are of course mutually exclusive, because a certain thing cannot at the same time be a particle . . . and a wave . . . but the two complement each other. By pla ...
... Actually, we need not speak of particles at all. For many experiments it is more convenient to speak of matter waves . . . The two pictures are of course mutually exclusive, because a certain thing cannot at the same time be a particle . . . and a wave . . . but the two complement each other. By pla ...
Electron Configuration - Warren County Public Schools
... radiation, is the frequency, h is a constant, known as Planck’s constant: 6.626 x 10-34 J•s. ...
... radiation, is the frequency, h is a constant, known as Planck’s constant: 6.626 x 10-34 J•s. ...
Chapter 4 - Rothschild Science
... Includes radio waves, radar, microwaves, visible light, infrared light, ultraviolet light, X-rays, and gamma rays ...
... Includes radio waves, radar, microwaves, visible light, infrared light, ultraviolet light, X-rays, and gamma rays ...
Key Concepts for Exam #2
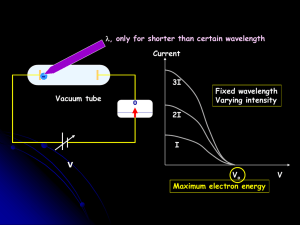
... light increases, the kinetic energy of ejected electrons remains constant and the number of electrons increases. In addition, as the frequency of light increases, the kinetic energy of ejected electrons increases and the number of electrons remains constant. If the frequency of the light is below th ...
... light increases, the kinetic energy of ejected electrons remains constant and the number of electrons increases. In addition, as the frequency of light increases, the kinetic energy of ejected electrons increases and the number of electrons remains constant. If the frequency of the light is below th ...
The Wave
... In metals, the outermost electrons are not tightly bound If given energy electrons can be freed Classically, we increase the energy of an EM wave by increasing the intensity (e.g. brightness) Energy a A2 But this doesn’t work ?? ...
... In metals, the outermost electrons are not tightly bound If given energy electrons can be freed Classically, we increase the energy of an EM wave by increasing the intensity (e.g. brightness) Energy a A2 But this doesn’t work ?? ...
Exam sample
... 7. “No two electrons in the same atom may have the same values for all four quantum numbers” is a statement of: a. Hund’s Rule. b. deBroglie’s Hypothesis. c. the Pauli Exclusion Principle. d. the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle. 8. All s orbitals are: a. shaped like four-leaf clovers. b. dumbbell- ...
... 7. “No two electrons in the same atom may have the same values for all four quantum numbers” is a statement of: a. Hund’s Rule. b. deBroglie’s Hypothesis. c. the Pauli Exclusion Principle. d. the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle. 8. All s orbitals are: a. shaped like four-leaf clovers. b. dumbbell- ...
Chapter 8 - Fayetteville State University
... A. electrons in orbit around nuclei lose energy so slowly that the universe should exist for at least another five billion years. B. quantum theory is not applicable to the ultra-structure of an atom. C. electrons around a nucleus can have only certain particular energies and can only occupy certain ...
... A. electrons in orbit around nuclei lose energy so slowly that the universe should exist for at least another five billion years. B. quantum theory is not applicable to the ultra-structure of an atom. C. electrons around a nucleus can have only certain particular energies and can only occupy certain ...
A system consist of two particles,each of which has two possible
... 1. A system consist of two particles,each of which has two possible quantum stats with energies Eo and 2Eo .Write the complete expression for the partition function if: (a) The particle are distinguishable. (b) The particle obey Maxwell-Boltzmann statistics. (c) The particle obey Fermi-Dirac statist ...
... 1. A system consist of two particles,each of which has two possible quantum stats with energies Eo and 2Eo .Write the complete expression for the partition function if: (a) The particle are distinguishable. (b) The particle obey Maxwell-Boltzmann statistics. (c) The particle obey Fermi-Dirac statist ...
BWilliamsLtalk - FSU High Energy Physics
... with this device. In a Geiger counter there is a tiny bit of radioactive substance, so small that perhaps in the course of one hour one of the atoms decays, but also, with equal probability, perhaps none; if it happens, the counter tube discharges and through a relay releases a hammer which shatters ...
... with this device. In a Geiger counter there is a tiny bit of radioactive substance, so small that perhaps in the course of one hour one of the atoms decays, but also, with equal probability, perhaps none; if it happens, the counter tube discharges and through a relay releases a hammer which shatters ...
Lecture 1 - UW Canvas
... It exchanges energy suddenly at a point in space. It obeys the laws of conservation of energy and momentum in collisions. It does not exhibit interference or diffraction. ...
... It exchanges energy suddenly at a point in space. It obeys the laws of conservation of energy and momentum in collisions. It does not exhibit interference or diffraction. ...