Personnel covered - Northern Illinois University
... Allergy to animals Allergy to animals is common and therefore one of the most important occupational problems occurring in workers exposed to animals. Allergies can be manifested in a number of ways, including allergic rhinitis (a condition characterized by runny nose and sneezing similar to hay fev ...
... Allergy to animals Allergy to animals is common and therefore one of the most important occupational problems occurring in workers exposed to animals. Allergies can be manifested in a number of ways, including allergic rhinitis (a condition characterized by runny nose and sneezing similar to hay fev ...
5 Protocols for Various Health Conditions
... 1. Any child with a rash that appears to be Tinea will be excluded from school until treatment has begun. The lesion must be covered until the nurse determines that the treatment is effective. 2. Any child with active Tinea lesions in the scalp will be excluded from school until treatment has begun ...
... 1. Any child with a rash that appears to be Tinea will be excluded from school until treatment has begun. The lesion must be covered until the nurse determines that the treatment is effective. 2. Any child with active Tinea lesions in the scalp will be excluded from school until treatment has begun ...
How vaccines work.
... 1) Live-attenuated vaccines: Active, but very weak • Vaccines made when the virus is weakened to such a level that they reproduce only about 20 times in the body. By comparison, natural viruses reproduce thousands of times. • "Live-attenuated vaccines can cause very mild illness in a small proportio ...
... 1) Live-attenuated vaccines: Active, but very weak • Vaccines made when the virus is weakened to such a level that they reproduce only about 20 times in the body. By comparison, natural viruses reproduce thousands of times. • "Live-attenuated vaccines can cause very mild illness in a small proportio ...
DOG Vaccinations
... vaccination program, many dogs will come down with a serious or even fatal disease. Nursing puppies receive antibodies from their mother’s milk (called maternal antibodies) that protect against disease during the first months of its life. If the pups mother had all her shots brought up to date just ...
... vaccination program, many dogs will come down with a serious or even fatal disease. Nursing puppies receive antibodies from their mother’s milk (called maternal antibodies) that protect against disease during the first months of its life. If the pups mother had all her shots brought up to date just ...
Dracunculiasis (Guinea Worm Disease): A Report
... No more than 1-2 mm wide (thin like spaghetti or angel hair pasta) ...
... No more than 1-2 mm wide (thin like spaghetti or angel hair pasta) ...
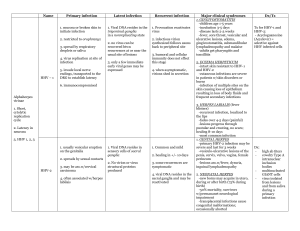
Communicable Disease Chart - Hamilton
... gastrointestinal symptoms Infections in children may without respiratory also be associated with some symptoms (cough & fever) gastrointestinal symptoms is unrelated and not caused such as nausea, vomiting and by the influenza virus. diarrhea. Symptoms typically last 5-7 days, cough may persist for ...
... gastrointestinal symptoms Infections in children may without respiratory also be associated with some symptoms (cough & fever) gastrointestinal symptoms is unrelated and not caused such as nausea, vomiting and by the influenza virus. diarrhea. Symptoms typically last 5-7 days, cough may persist for ...
1a-Infection-and
... • Use of lighter-than-normal pressure • Avoiding percussion or joint mobilizations • Assisting the client on or off the massage table (blood pressure medication, pregnancy, elderly, or frail) ...
... • Use of lighter-than-normal pressure • Avoiding percussion or joint mobilizations • Assisting the client on or off the massage table (blood pressure medication, pregnancy, elderly, or frail) ...
Meningitis and Encephalitis
... Chronic Meningitis i. Meningitis lasting loner that 4 weeks ii. Patient is usually not as toxic looking as a patient with acute meningitis iii. TB meningitis 1. Always suspected in a patient with aseptic/chronic meningitis 2. S/S- fever, malaise, and intermittent H/A 3. Treat with INH, PZA, Rifampin ...
... Chronic Meningitis i. Meningitis lasting loner that 4 weeks ii. Patient is usually not as toxic looking as a patient with acute meningitis iii. TB meningitis 1. Always suspected in a patient with aseptic/chronic meningitis 2. S/S- fever, malaise, and intermittent H/A 3. Treat with INH, PZA, Rifampin ...
presentation -STD`s - Association of School Nurses of
... • Untreated may resolve, remain unchanged, or increase • Cyrotherapy, patient applied creams, surgical removal ...
... • Untreated may resolve, remain unchanged, or increase • Cyrotherapy, patient applied creams, surgical removal ...
myoclonus - Pediatric Neurology Briefs
... positive throat culture and/or rapid antigen detection, and in 3 cases, very high antideoxyribonuclease antibody titers. All patients were treated with penicillin, amoxicillin or a cephalosporin for 10 days, and eradication of GABHS was followed by immediate resolution of the OCD symptoms. Recurrenc ...
... positive throat culture and/or rapid antigen detection, and in 3 cases, very high antideoxyribonuclease antibody titers. All patients were treated with penicillin, amoxicillin or a cephalosporin for 10 days, and eradication of GABHS was followed by immediate resolution of the OCD symptoms. Recurrenc ...
Common Childhood Diseases
... through saliva. Young children may be infected by saliva on the hands of care givers. Spread between children can also occur by sharing mouthed objects or toys that have infected saliva on them. Kissing can increase spread among young adults. Infectious mononucleosis is common in group settings of a ...
... through saliva. Young children may be infected by saliva on the hands of care givers. Spread between children can also occur by sharing mouthed objects or toys that have infected saliva on them. Kissing can increase spread among young adults. Infectious mononucleosis is common in group settings of a ...
International Symposium on Infectious Diseases of Livestock
... carrier animals are believed to be most informative for the countries where similar problems are very common. Alum precipitated vaccine and Oil adjuvant vaccine have been used in most of the countries in the tropical region. Cooperative research and field trials of those vaccines have been requested ...
... carrier animals are believed to be most informative for the countries where similar problems are very common. Alum precipitated vaccine and Oil adjuvant vaccine have been used in most of the countries in the tropical region. Cooperative research and field trials of those vaccines have been requested ...
Common Childhood Diseases (Word)
... through saliva. Young children may be infected by saliva on the hands of care givers. Spread between children can also occur by sharing mouthed objects or toys that have infected saliva on them. Kissing can increase spread among young adults. Infectious mononucleosis is common in group settings of a ...
... through saliva. Young children may be infected by saliva on the hands of care givers. Spread between children can also occur by sharing mouthed objects or toys that have infected saliva on them. Kissing can increase spread among young adults. Infectious mononucleosis is common in group settings of a ...
COMMUNICABLE DISEASES AND INFECTIOUS DISEASE CONTROL
... person. Any theoretical transmission would most likely involve exposure of open skin lesions or mucous membranes to blood or other body fluids of an infected person. It is possible for individuals who have no symptoms of disease to have infectious organisms present in their body fluids. These indivi ...
... person. Any theoretical transmission would most likely involve exposure of open skin lesions or mucous membranes to blood or other body fluids of an infected person. It is possible for individuals who have no symptoms of disease to have infectious organisms present in their body fluids. These indivi ...
Herpes Viruses - Website of Neelay Gandhi
... 4. mitogenic stimulation causes lytic infection 5. clinical significance unclear 1. typically occurs in early infancy w/high fever and rash ...
... 4. mitogenic stimulation causes lytic infection 5. clinical significance unclear 1. typically occurs in early infancy w/high fever and rash ...
Non-Communicable Diseases
... 12. Explain how to do a self-exam for either breast cancer or testicular cancer. 13. Breast Cancer, Alzheimer’s, and Prostate Cancer are all examples of non-communicable diseases. List three more examples of non-communicable diseases. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 14. What does the ...
... 12. Explain how to do a self-exam for either breast cancer or testicular cancer. 13. Breast Cancer, Alzheimer’s, and Prostate Cancer are all examples of non-communicable diseases. List three more examples of non-communicable diseases. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 14. What does the ...
Infection Control - Nicole
... Protect the hands of the wearer from contamination with organic matter and microorganisms Protect the hands of the wearer from exposure to chemicals that may damage your skin Reduce cross infection by preventing the transfer of organisms from person to person ...
... Protect the hands of the wearer from contamination with organic matter and microorganisms Protect the hands of the wearer from exposure to chemicals that may damage your skin Reduce cross infection by preventing the transfer of organisms from person to person ...
FP7 Project - ICONZ – Africa
... the intention of keeping it as simple and flexible as possible. The size and complexity of the database has posed some problems to the developers and designers of the website but it is now operational. Detailed information for each disease and the scoring results from the prioritisation and gap anal ...
... the intention of keeping it as simple and flexible as possible. The size and complexity of the database has posed some problems to the developers and designers of the website but it is now operational. Detailed information for each disease and the scoring results from the prioritisation and gap anal ...
Communicable Diseases Information
... A vaccine against chickenpox was first licensed in March 1995. It has been recommended for persons over 12 months of age. Older children and adults who have previously had chickenpox do not need to be vaccinated. Contact your doctor or local health department for further information about the chicke ...
... A vaccine against chickenpox was first licensed in March 1995. It has been recommended for persons over 12 months of age. Older children and adults who have previously had chickenpox do not need to be vaccinated. Contact your doctor or local health department for further information about the chicke ...
Foodborne Viruses in the European Union
... • Associated with poor hygiene and sanitation - primarily transmitted from person-to-person via the faecal-oral route • Incubation period commonly 28-30 days (range 15-50) ...
... • Associated with poor hygiene and sanitation - primarily transmitted from person-to-person via the faecal-oral route • Incubation period commonly 28-30 days (range 15-50) ...
Leptospirosis

Leptospirosis (also known as field fever, rat catcher's yellows, and pretibial fever among others names) is an infection caused by corkscrew-shaped bacteria called Leptospira. Symptoms can range from none to mild such as headaches, muscle pains, and fevers; to severe with bleeding from the lungs or meningitis. If the infection causes the person to turn yellow, have kidney failure and bleeding, it is then known as Weil's disease. If it causes lots of bleeding from the lungs it is known as severe pulmonary haemorrhage syndrome.Up to 13 different genetic types of Leptospira may cause disease in humans. It is transmitted by both wild and domestic animals. The most common animals that spread the disease are rodents. It is often transmitted by animal urine or by water or soil containing animal urine coming into contact with breaks in the skin, eyes, mouth, or nose. In the developing world the disease most commonly occurs in farmers and poor people who live in cities. In the developed world it most commonly occurs in those involved in outdoor activities in warm and wet areas of the world. Diagnosis is typically by looking for antibodies against the bacteria or finding its DNA in the blood.Efforts to prevent the disease include protective equipment to prevent contact when working with potentially infected animals, washing after this contact, and reducing rodents in areas people live and work. The antibiotic doxycycline, when used in an effort to prevent infection among travellers, is of unclear benefit. Vaccines for animals exist for certain type of Leptospira which may decrease the risk of spread to humans. Treatment if infected is with antibiotics such as: doxycycline, penicillin, or ceftriaxone. Weil's disease and severe pulmonary haemorrhage syndrome result in death rates greater than 10% and 50%, respectively, even with treatment.It is estimated that seven to ten million people are infected by leptospirosis a year. The number of deaths this causes is not clear. The disease is most common in tropical areas of the world but may occur anywhere. Outbreaks may occur in slums of the developing world. The disease was first described by Weil in 1886 in Germany. Animals who are infected may have no symptoms, mild symptoms, or severe symptoms. Symptoms may vary by the type of animal. In some animals Leptospira live in the reproductive tract, leading to transmission during mating.