Nestling disease in Budgerigars and its connection with the problem of
... 1. Nestling disease in Budgerigars. a.) Pathogen: The causative virus is a small virus without an envelope that is very resistant and infectious for long periods of time not only in the environment, but also in the bird room or aviary as well as on cages and equipment. It survives temperatures of ...
... 1. Nestling disease in Budgerigars. a.) Pathogen: The causative virus is a small virus without an envelope that is very resistant and infectious for long periods of time not only in the environment, but also in the bird room or aviary as well as on cages and equipment. It survives temperatures of ...
February - Children`s Hospital of Philadelphia
... The decision not to vaccinate, or even to delay vaccination, does not occur in a vacuum, nor is it inconsequential. Last year, California parents claimed a record number of personal belief exemptions to mandatory school vaccinations. That was the same year that state health officials reported the mo ...
... The decision not to vaccinate, or even to delay vaccination, does not occur in a vacuum, nor is it inconsequential. Last year, California parents claimed a record number of personal belief exemptions to mandatory school vaccinations. That was the same year that state health officials reported the mo ...
Immunisationsienabeth
... has shown that vaccines keep people’s health protected from lethal diseases Some example like the Chicken Pox, Measles, Hepatitis B, Whooping cough ...
... has shown that vaccines keep people’s health protected from lethal diseases Some example like the Chicken Pox, Measles, Hepatitis B, Whooping cough ...
Climate Change and Infectious Disease in Humans
... of diseases transmitted by blood-sucking vectors, such as mosquitoes and ticks, but might also include other species. However this is complex, with considerable uncertainties about the potential public health effects. There are theoretical models to predict the influence of increased average tempera ...
... of diseases transmitted by blood-sucking vectors, such as mosquitoes and ticks, but might also include other species. However this is complex, with considerable uncertainties about the potential public health effects. There are theoretical models to predict the influence of increased average tempera ...
The (gamma) Proteobacteria
... Unique life cycle with two cellular forms Elementary body is infectious stage (extracellular) Reticulate body is reproductive stage (intracellular) ...
... Unique life cycle with two cellular forms Elementary body is infectious stage (extracellular) Reticulate body is reproductive stage (intracellular) ...
5.1.1: Contagious
... tissues. Entrance to the host typically occurs through openings to the body such as the mouth, eyes, nose, genital openings, or through breaks in the skin. Infectious agents that are easily transmitted are considered highly contagious. Those agents that that are very likely to cause disease once tra ...
... tissues. Entrance to the host typically occurs through openings to the body such as the mouth, eyes, nose, genital openings, or through breaks in the skin. Infectious agents that are easily transmitted are considered highly contagious. Those agents that that are very likely to cause disease once tra ...
SPLENOMEGALY
... insensitive for detecting splenomegaly (between 27 and 58 percent, depending on the examiner’s index of suspicion), the absence of splenomegaly should not be used as evidence against the diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis. ...
... insensitive for detecting splenomegaly (between 27 and 58 percent, depending on the examiner’s index of suspicion), the absence of splenomegaly should not be used as evidence against the diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis. ...
Chapter 4: BASIC FACTS ABOUT TUBERCULOSIS (TB)
... The likelihood of and timing for developing active TB disease after becoming infected with TB bacteria is highly variable. Some people, particularly young children and those with advanced immune suppression (e.g., HIV/AIDS) are highly susceptible to developing TB disease soon afterward (primary TB d ...
... The likelihood of and timing for developing active TB disease after becoming infected with TB bacteria is highly variable. Some people, particularly young children and those with advanced immune suppression (e.g., HIV/AIDS) are highly susceptible to developing TB disease soon afterward (primary TB d ...
Protecting Yourself From Exposure To
... Hepatitis B and C infects the liver. Hepatitis B and C can survive for at least one week in dried blood on environmental surfaces such as a worktable, knife, tools, broken glass, sharp metal, etc. For this reason, this virus is the primary concern in the work setting. Symptoms are very like a mild “ ...
... Hepatitis B and C infects the liver. Hepatitis B and C can survive for at least one week in dried blood on environmental surfaces such as a worktable, knife, tools, broken glass, sharp metal, etc. For this reason, this virus is the primary concern in the work setting. Symptoms are very like a mild “ ...
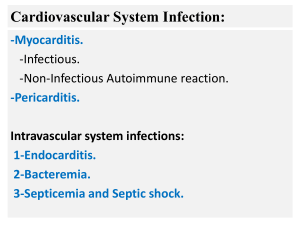
Cardiovascular System Infection
... Example: Aspergillosis Aspergillosis develops mainly in individuals who ...
... Example: Aspergillosis Aspergillosis develops mainly in individuals who ...
Milwaukee Journal Sentinel Safety Training Presentations
... • Vaccination available since 1982 • HBV can survive for at least one week in dried blood ...
... • Vaccination available since 1982 • HBV can survive for at least one week in dried blood ...
The sore throat
... tonsils. There is normally not an exudate present, as would be seen with certain bacterial pharyngitis. Coxsackie virus causes small vesicles to form with erythematous bases that can ulcerate and spread over the anterior tonsillar pillars, palate and pharyngeal wall. Herpes simplex virus is normally ...
... tonsils. There is normally not an exudate present, as would be seen with certain bacterial pharyngitis. Coxsackie virus causes small vesicles to form with erythematous bases that can ulcerate and spread over the anterior tonsillar pillars, palate and pharyngeal wall. Herpes simplex virus is normally ...
Communicable Disease 1995 - 2004
... Many insect-borne diseases are major health problems for developing countries. Malaria is estimated to infect over 300 million people, killing one million per year.44,45 Fortunately, many insect-borne diseases are so rare in Ontario that they are not required to be reported. The reportable insect-bo ...
... Many insect-borne diseases are major health problems for developing countries. Malaria is estimated to infect over 300 million people, killing one million per year.44,45 Fortunately, many insect-borne diseases are so rare in Ontario that they are not required to be reported. The reportable insect-bo ...
A new generation of airborne surface disinfection
... Source: Communicable Diseases Surveillance in Singapore ...
... Source: Communicable Diseases Surveillance in Singapore ...
infection control and tb
... stay home from work or school. Notify supervisor for medical help, report infection exposure. • When you are well stay a safe distance (2-3 feet) from those who are sick. • If you are given medication to treat an infection, be sure to finish your prescription. Stopping too soon may lead to resistanc ...
... stay home from work or school. Notify supervisor for medical help, report infection exposure. • When you are well stay a safe distance (2-3 feet) from those who are sick. • If you are given medication to treat an infection, be sure to finish your prescription. Stopping too soon may lead to resistanc ...
Bloodborne Pathogen - Nucarecarolina.com
... clothing or equipment worn by a member for protection against a hazard. General work clothes (uniforms, jumpsuits, etc.) not intended to function as protection against a hazard are not PPE. • Universal Precautions- an approach to infection control where all human blood and certain human body fluids ...
... clothing or equipment worn by a member for protection against a hazard. General work clothes (uniforms, jumpsuits, etc.) not intended to function as protection against a hazard are not PPE. • Universal Precautions- an approach to infection control where all human blood and certain human body fluids ...
Consent for the Publication of Infectious Disease Society of America
... case. I confirm that the submitted case information and images have not been published previously or submitted for publication elsewhere, and that all contributing authors have agreed to its submission and publication. I confirm that, if this case is accepted, I transfer copyright of this material t ...
... case. I confirm that the submitted case information and images have not been published previously or submitted for publication elsewhere, and that all contributing authors have agreed to its submission and publication. I confirm that, if this case is accepted, I transfer copyright of this material t ...
Biological Terrain - Prevention and Healing
... Pasteur’s germ theory provides a theory of infections which became the foundation of modern medicine. It states that germs are airborne and specific germs cause specific disease. This theory then led to a treatment plan. As an example, Streptococcus bacillus is the cause of infectious strep throat i ...
... Pasteur’s germ theory provides a theory of infections which became the foundation of modern medicine. It states that germs are airborne and specific germs cause specific disease. This theory then led to a treatment plan. As an example, Streptococcus bacillus is the cause of infectious strep throat i ...
bloodborne pathogens - Diocese of St. Petersburg
... (inflammation) of the liver and presents with symptoms similar to Hepatitis B. • Frequently people infected with Hepatitis C may not know or do not have any symptoms. If the is present for years, the liver becomes permanently scarred. (cirrhosis) Hepatitis C can lead to death. • About 1 in 10 people ...
... (inflammation) of the liver and presents with symptoms similar to Hepatitis B. • Frequently people infected with Hepatitis C may not know or do not have any symptoms. If the is present for years, the liver becomes permanently scarred. (cirrhosis) Hepatitis C can lead to death. • About 1 in 10 people ...
Substance misuse and TB
... treatment is carefully monitored by a healthcare team. Substitute drugs, such as methadone, and TB medication affect each other. When a member of your family starts treatment for TB they may require an increased substitute drug dose. The dose will then need to be reduced at the end of TB treatment o ...
... treatment is carefully monitored by a healthcare team. Substitute drugs, such as methadone, and TB medication affect each other. When a member of your family starts treatment for TB they may require an increased substitute drug dose. The dose will then need to be reduced at the end of TB treatment o ...
infectious and non-infectious diseases
... Some diseases do not fit well into any of the 3 categories listed – write another type if it is more appropriate Cause - If your disease fits easily into one of the types of disease the cause should be obvious. If not there may be many suspected causes or the cause/s may not be known well at all ...
... Some diseases do not fit well into any of the 3 categories listed – write another type if it is more appropriate Cause - If your disease fits easily into one of the types of disease the cause should be obvious. If not there may be many suspected causes or the cause/s may not be known well at all ...
Bloodborne Pathogen in the Workplace
... virus-bearing serum, most often during blood transfusions and by contaminated needles and syringes. • Hepatitis B is transmitted primarily through "blood to blood" contact. • Hepatitis B virus is very durable, and it can survive in dried blood for up to seven days. This virus is the primary concern ...
... virus-bearing serum, most often during blood transfusions and by contaminated needles and syringes. • Hepatitis B is transmitted primarily through "blood to blood" contact. • Hepatitis B virus is very durable, and it can survive in dried blood for up to seven days. This virus is the primary concern ...
Detection of tularaemia infection in NSW wildlife: Information for
... This is the first diagnosis of tularaemia in an Australian animal and has now been confirmed by PCR testing and culture at the Australian Animal Health Laboratory in Geelong. This finding is not unexpected given that there have been reported human cases of Tularaemia in Australia, including one case ...
... This is the first diagnosis of tularaemia in an Australian animal and has now been confirmed by PCR testing and culture at the Australian Animal Health Laboratory in Geelong. This finding is not unexpected given that there have been reported human cases of Tularaemia in Australia, including one case ...
Leptospirosis

Leptospirosis (also known as field fever, rat catcher's yellows, and pretibial fever among others names) is an infection caused by corkscrew-shaped bacteria called Leptospira. Symptoms can range from none to mild such as headaches, muscle pains, and fevers; to severe with bleeding from the lungs or meningitis. If the infection causes the person to turn yellow, have kidney failure and bleeding, it is then known as Weil's disease. If it causes lots of bleeding from the lungs it is known as severe pulmonary haemorrhage syndrome.Up to 13 different genetic types of Leptospira may cause disease in humans. It is transmitted by both wild and domestic animals. The most common animals that spread the disease are rodents. It is often transmitted by animal urine or by water or soil containing animal urine coming into contact with breaks in the skin, eyes, mouth, or nose. In the developing world the disease most commonly occurs in farmers and poor people who live in cities. In the developed world it most commonly occurs in those involved in outdoor activities in warm and wet areas of the world. Diagnosis is typically by looking for antibodies against the bacteria or finding its DNA in the blood.Efforts to prevent the disease include protective equipment to prevent contact when working with potentially infected animals, washing after this contact, and reducing rodents in areas people live and work. The antibiotic doxycycline, when used in an effort to prevent infection among travellers, is of unclear benefit. Vaccines for animals exist for certain type of Leptospira which may decrease the risk of spread to humans. Treatment if infected is with antibiotics such as: doxycycline, penicillin, or ceftriaxone. Weil's disease and severe pulmonary haemorrhage syndrome result in death rates greater than 10% and 50%, respectively, even with treatment.It is estimated that seven to ten million people are infected by leptospirosis a year. The number of deaths this causes is not clear. The disease is most common in tropical areas of the world but may occur anywhere. Outbreaks may occur in slums of the developing world. The disease was first described by Weil in 1886 in Germany. Animals who are infected may have no symptoms, mild symptoms, or severe symptoms. Symptoms may vary by the type of animal. In some animals Leptospira live in the reproductive tract, leading to transmission during mating.