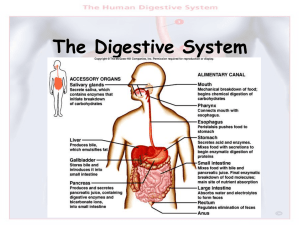
The Digestive System - Gastroenterological Society of Australia
... 6. Liver and Gall Bladder The liver produces bile, a fluid that helps to digest fats. Bile is first stored in the gall bladder until it is needed after meals. It is then released into a tube called the ‘bile duct’ and travels down into the duodenum. 7. The Small Intestine The small bowel is five me ...
... 6. Liver and Gall Bladder The liver produces bile, a fluid that helps to digest fats. Bile is first stored in the gall bladder until it is needed after meals. It is then released into a tube called the ‘bile duct’ and travels down into the duodenum. 7. The Small Intestine The small bowel is five me ...
The digestive system
... Located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestiv ...
... Located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestiv ...
Digestive System - Petal School District
... Hepatitis- inflammation of the liver A- infectious hepatitis- transmitted in food or water that has been contaminated by feces of an infected person. Most benign type. B- transmitted by all body fluids including breast milk, saliva, and urine. (vaccine) C- also transmitted through blood and body flu ...
... Hepatitis- inflammation of the liver A- infectious hepatitis- transmitted in food or water that has been contaminated by feces of an infected person. Most benign type. B- transmitted by all body fluids including breast milk, saliva, and urine. (vaccine) C- also transmitted through blood and body flu ...
عرض تقديمي من PowerPoint
... connects with small intestine via pyloric inhibits local reflexes, activates sympathetic fibers iii. Gallbladder ...
... connects with small intestine via pyloric inhibits local reflexes, activates sympathetic fibers iii. Gallbladder ...
Lab 11 Anatomy of the Digestive System, Digestive Histology
... two questions to make up a question with 1 point value ...
... two questions to make up a question with 1 point value ...
1Digestive System
... Duodenum is first 25cm of the small intestine. 7m in length, 2.5m in diameter. ...
... Duodenum is first 25cm of the small intestine. 7m in length, 2.5m in diameter. ...
digestive glands - Study Hall Educational Foundation
... • Bile takes part in the digestion of fats present in the ingested food. • Bile emulsifies fats which help in breaking them into small globules. In this way, fat globules are easily exposed to the action of fat-hydrolyzing, enzymes. • Although the bile juice received from the liver does not contain ...
... • Bile takes part in the digestion of fats present in the ingested food. • Bile emulsifies fats which help in breaking them into small globules. In this way, fat globules are easily exposed to the action of fat-hydrolyzing, enzymes. • Although the bile juice received from the liver does not contain ...
The Digestive system
... strong, muscular layer on its wall. It stores bile between meals, reabsorbs water to concentrate bile, and contracts to release bile into the small intestine. ...
... strong, muscular layer on its wall. It stores bile between meals, reabsorbs water to concentrate bile, and contracts to release bile into the small intestine. ...
Pancreatic Secretions
... is then opens becoming bilirubin. Bilirubin is bright yellow and with increase accumulation of this you will see yellow discoloration of the skin, eyes known as jaundice. ...
... is then opens becoming bilirubin. Bilirubin is bright yellow and with increase accumulation of this you will see yellow discoloration of the skin, eyes known as jaundice. ...
Digestive System Study Guide WORD BANK 1
... 1. ______________- slippery secretion that coats the inner walls of the digestive tract – helps with the movement of food – also protects the stomach and small intestine from gastric juices. 2.______________- wavelike motion that pushes food and helps to break it down. 3._______________- group of di ...
... 1. ______________- slippery secretion that coats the inner walls of the digestive tract – helps with the movement of food – also protects the stomach and small intestine from gastric juices. 2.______________- wavelike motion that pushes food and helps to break it down. 3._______________- group of di ...
The Digestive System The Digestive System: Function
... into chyme - liquid food. • Absorption = water, alcohol, and drugs • Glands of stomach ...
... into chyme - liquid food. • Absorption = water, alcohol, and drugs • Glands of stomach ...
Bio12 Digestion Powerpoint
... It is here that secretions sent from the liver and pancreas break down fat and peptides, and secretions of the duodenum itself also break down other nutrients. walls of the duodenum are lined with millions of interstitial glands that produce juices containing enzymes that finish the digestion of p ...
... It is here that secretions sent from the liver and pancreas break down fat and peptides, and secretions of the duodenum itself also break down other nutrients. walls of the duodenum are lined with millions of interstitial glands that produce juices containing enzymes that finish the digestion of p ...
Digestive System - Health and Science Pipeline Initiative
... • Each lobe has lobules – Contains hepatocytes – Surround sinusoids – Feed into central vein ...
... • Each lobe has lobules – Contains hepatocytes – Surround sinusoids – Feed into central vein ...
digestive system
... • Each lobe has lobules – Contains hepatocytes – Surround sinusoids – Feed into central vein ...
... • Each lobe has lobules – Contains hepatocytes – Surround sinusoids – Feed into central vein ...
Digestive System
... • Produces blood proteins such as fibrinogen and prothrombin, which aid in clotting of the blood • Produces cholesterol • Detoxifies substances such as alcohol and pesticides, destroys bacteria that have been taken into the blood from the intestine ...
... • Produces blood proteins such as fibrinogen and prothrombin, which aid in clotting of the blood • Produces cholesterol • Detoxifies substances such as alcohol and pesticides, destroys bacteria that have been taken into the blood from the intestine ...
Digestive System PPT
... • 5. Produces blood proteins such as fibrinogen and prothrombin, which aid in the clotting of blood • 6. Produces cholesterol • 7. Detoxifies (renders less harmful) substances such as alcohol and pesticides, and destroys bacteria that have been taken into the blood from the intestine ...
... • 5. Produces blood proteins such as fibrinogen and prothrombin, which aid in the clotting of blood • 6. Produces cholesterol • 7. Detoxifies (renders less harmful) substances such as alcohol and pesticides, and destroys bacteria that have been taken into the blood from the intestine ...
Chapter 17
... • slower and less frequent than those of small intestine • mixing movements • peristalsis • mass movements usually follow meals ...
... • slower and less frequent than those of small intestine • mixing movements • peristalsis • mass movements usually follow meals ...
Digestive System: True-False Review
... Peristalsis occurs in the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Different orientations of muscles in the stomach maximize churning ability. Gastric pits are tiny depressions in the serosa. Villi are not found in the stomach. Rugae are folds in the mucosa of the intestine. Pancreatic juice (with pancre ...
... Peristalsis occurs in the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Different orientations of muscles in the stomach maximize churning ability. Gastric pits are tiny depressions in the serosa. Villi are not found in the stomach. Rugae are folds in the mucosa of the intestine. Pancreatic juice (with pancre ...
Digestive System - Direktori File UPI
... • Each lobe has lobules – Contains hepatocytes – Surround sinusoids – Feed into central vein ...
... • Each lobe has lobules – Contains hepatocytes – Surround sinusoids – Feed into central vein ...
Digestive System 24
... The digestive system is responsible for many body processes. Its functions begin when food is taken into the mouth, or _1_. The process called _2_ occurs as food is broken down both chemically and mechanically. For the broken-down foods to be made available to the body cells, they must be absorbed t ...
... The digestive system is responsible for many body processes. Its functions begin when food is taken into the mouth, or _1_. The process called _2_ occurs as food is broken down both chemically and mechanically. For the broken-down foods to be made available to the body cells, they must be absorbed t ...
Extracellular fluids
... HCl – creates the acid environment (pH~1-2 in adults), denatures proteins (making them more susceptible to proteolysis), and kills bacteria Mucins – form mucus which protects the stomach from the gastric juice Peptides: gastrin – produced by G-cells of the stomach, stimulates secretion of HCl and pe ...
... HCl – creates the acid environment (pH~1-2 in adults), denatures proteins (making them more susceptible to proteolysis), and kills bacteria Mucins – form mucus which protects the stomach from the gastric juice Peptides: gastrin – produced by G-cells of the stomach, stimulates secretion of HCl and pe ...
Ascending cholangitis

Ascending cholangitis or acute cholangitis (or sometimes cholangitis without a modifier - from Greek chol-, bile + ang-, vessel + itis-, inflammation) is an infection of the bile duct (cholangitis), usually caused by bacteria ascending from its junction with the duodenum (first part of the small intestine). It tends to occur if the bile duct is already partially obstructed by gallstones.Cholangitis can be life-threatening, and is regarded as a medical emergency. Characteristic symptoms include yellow discoloration of the skin or whites of the eyes, fever, abdominal pain, and in severe cases, low blood pressure and confusion. Initial treatment is with intravenous fluids and antibiotics, but there is often an underlying problem (such as gallstones or narrowing in the bile duct) for which further tests and treatments may be necessary, usually in the form of endoscopy to relieve obstruction of the bile duct.