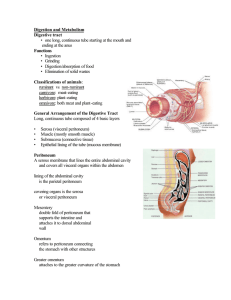
CHAPTER 8 – DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES On completion of
... photographs, biopsy, or brushing may be done. Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase (GGT) – test performed on blood serum to determine the level of GGT. Increased values may indicate cirrhosis, liver necrosis, hepatitis, alcoholism, neoplasms, acute pancreatitis, acute myocardial infarction, nephrosis, and acu ...
... photographs, biopsy, or brushing may be done. Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase (GGT) – test performed on blood serum to determine the level of GGT. Increased values may indicate cirrhosis, liver necrosis, hepatitis, alcoholism, neoplasms, acute pancreatitis, acute myocardial infarction, nephrosis, and acu ...
NOTES: Introduction to Histology (Ch 5)
... -separated from the small intestine by a powerful circular muscle: ...
... -separated from the small intestine by a powerful circular muscle: ...
Biol 155 Human Physiology - University of British Columbia
... Bile is stored and concentrated Stimulated by cholecystokinin and vegal stimulation Dumps into small intestine Production of gallstones possible ...
... Bile is stored and concentrated Stimulated by cholecystokinin and vegal stimulation Dumps into small intestine Production of gallstones possible ...
Layers of the digestive tube - Chicagoland Jewish High School
... Muscularis Externa, Serosa Muscularis Externa: 2 layers of smooth muscle Inner circular fibers Outer longitudinal fibers Neural network in between Enteric nervous system ...
... Muscularis Externa, Serosa Muscularis Externa: 2 layers of smooth muscle Inner circular fibers Outer longitudinal fibers Neural network in between Enteric nervous system ...
GIT_323
... Secretion of bile is one of the important function of liver. Bile is a yellow-to-green watery solution containing bile salt, bile pigment (chiefly bilirubin) cholesterol phospholipids & electrolytes. Its function is to emulsify large fat globules into smaller ones. It is stored in gall bladder and t ...
... Secretion of bile is one of the important function of liver. Bile is a yellow-to-green watery solution containing bile salt, bile pigment (chiefly bilirubin) cholesterol phospholipids & electrolytes. Its function is to emulsify large fat globules into smaller ones. It is stored in gall bladder and t ...
Review
... What is the function of the stomach? What causes a peptic ulcer in most cases? What does gastric juice consist of? What are the functions of HCl? How does the stomach tolerate such acidity? What is the only indispensible function of the stomach? What does the intrinsic factor do? In what digestive o ...
... What is the function of the stomach? What causes a peptic ulcer in most cases? What does gastric juice consist of? What are the functions of HCl? How does the stomach tolerate such acidity? What is the only indispensible function of the stomach? What does the intrinsic factor do? In what digestive o ...
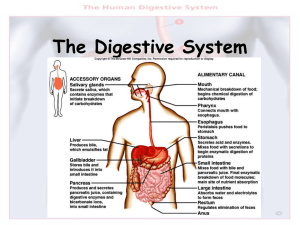
Digestive System
... • normally not more than 1 pair of canine teeth occur in each jaw at a given time • may be completely absent in the mare, gelding and ruminant ...
... • normally not more than 1 pair of canine teeth occur in each jaw at a given time • may be completely absent in the mare, gelding and ruminant ...
Practice Exam 1 - Iowa State University
... 17. The propulsive function that occurs in the esophagus is called: a. Segmentation b. Peristalsis c. Ingestion d. Swallowing 18. Which of the two following molecules form carbonic acid? a. H2O, Clb. Cl-, H+ c. HCO3 , CO2 d. CO2 , H2O 19. Which regulatory chemical stimulates gastric gland activity ...
... 17. The propulsive function that occurs in the esophagus is called: a. Segmentation b. Peristalsis c. Ingestion d. Swallowing 18. Which of the two following molecules form carbonic acid? a. H2O, Clb. Cl-, H+ c. HCO3 , CO2 d. CO2 , H2O 19. Which regulatory chemical stimulates gastric gland activity ...
Gastric secretions
... In response to fat and protein Increases total amount of enzymes secreted Increases smooth muscle activity of gall bladder ...
... In response to fat and protein Increases total amount of enzymes secreted Increases smooth muscle activity of gall bladder ...
why sunrider foods - Diana`s Healthy Lifestyles
... digestion by discouraging us from eating salt, sugar, and junk food. These 3 food products alone can greatly enhance our health because food choices will begin to change naturally and regeneration can begin. QUINARY - The Quinary nourishes and supports the five main systems of your body, (Digestive, ...
... digestion by discouraging us from eating salt, sugar, and junk food. These 3 food products alone can greatly enhance our health because food choices will begin to change naturally and regeneration can begin. QUINARY - The Quinary nourishes and supports the five main systems of your body, (Digestive, ...
The Digestive System - Effingham County Schools
... into chyme - liquid food. • Absorption = water, alcohol, and drugs • Glands of stomach ...
... into chyme - liquid food. • Absorption = water, alcohol, and drugs • Glands of stomach ...
Digestion I Pretest 1. The stomach is directly connected to the above
... to ____________________. Thus the small nutrient molecules that are absorbed by the villi are _______________, ______________________, __________________, ________________________, and __________________________. Fat products enter the _____________________, and the other molecules enter the _______ ...
... to ____________________. Thus the small nutrient molecules that are absorbed by the villi are _______________, ______________________, __________________, ________________________, and __________________________. Fat products enter the _____________________, and the other molecules enter the _______ ...
Figure 14.4a
... • Mucous lining is thick and made up of several types of cells • 1) Mucous Cells – produce a sticky alkaline mucous • 2) Parietal Cells – Produce hydrochloric acid • 3) Chief Cells – Produce protein digesting enzymes. (pepsinogens) Released in an inactive form, they become active (Pepsin) when mixed ...
... • Mucous lining is thick and made up of several types of cells • 1) Mucous Cells – produce a sticky alkaline mucous • 2) Parietal Cells – Produce hydrochloric acid • 3) Chief Cells – Produce protein digesting enzymes. (pepsinogens) Released in an inactive form, they become active (Pepsin) when mixed ...
Anatomy_and_Physiology_files/Digestive notes
... Hyoid and larynx raise causing the epiglottis to close off larynx Tongue compresses against the soft palate, sealing the oral cavity from the pharynx Longitudinal muscles pull the pharynx up toward the food Muscles of the lower pharynx relax to open the esophagus Peristaltic wave forces food into th ...
... Hyoid and larynx raise causing the epiglottis to close off larynx Tongue compresses against the soft palate, sealing the oral cavity from the pharynx Longitudinal muscles pull the pharynx up toward the food Muscles of the lower pharynx relax to open the esophagus Peristaltic wave forces food into th ...
File
... The liver manufactures the following important substances: Bile Fibrinogen and prothrombin Heparin Blood proteins ...
... The liver manufactures the following important substances: Bile Fibrinogen and prothrombin Heparin Blood proteins ...
Digestion - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... Gall bladder • Pouch structure located near the liver which concentrates and stores bile • Bile duct – a long tube that carries BILE. The top half of the common bile duct is associated with the liver, while the bottom half of the common bile duct is associated with the pancreas, through which it pa ...
... Gall bladder • Pouch structure located near the liver which concentrates and stores bile • Bile duct – a long tube that carries BILE. The top half of the common bile duct is associated with the liver, while the bottom half of the common bile duct is associated with the pancreas, through which it pa ...
Mechanical digestion
... of complex, non-absorbable food molecules into small, absorbable nutrient molecules by hydrolysis Enzymes speed up the reaction and enables digestion to occur ...
... of complex, non-absorbable food molecules into small, absorbable nutrient molecules by hydrolysis Enzymes speed up the reaction and enables digestion to occur ...
The Digestive and Excretory Systems
... Digestion = chemically - breaks it down into tiny pieces = mechanical – mixes food with digestive juices acid in the stomach kills bacteria Slowly releases food into intestine Cardiac sphincter Pyloric sphincter ...
... Digestion = chemically - breaks it down into tiny pieces = mechanical – mixes food with digestive juices acid in the stomach kills bacteria Slowly releases food into intestine Cardiac sphincter Pyloric sphincter ...
File
... o Tryptase- breaks down proteins o Nuclease- breaks down nucleic acids How is insulin related to the digestive system? o Insulin is released in amounts appropriate to the amount of glucose entering the body. What is the size of the liver and where is it located? o It is a large, approximately 3 poun ...
... o Tryptase- breaks down proteins o Nuclease- breaks down nucleic acids How is insulin related to the digestive system? o Insulin is released in amounts appropriate to the amount of glucose entering the body. What is the size of the liver and where is it located? o It is a large, approximately 3 poun ...
DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION
... The Duodenum is located at the junction of the stomach and the small intestine. The duodenum is the first part of the small intestine. It is C-shaped and about 25 cm long. This is the place where the ultimate destruction of food digestion reaches its completion and where the acidity of chyme is ...
... The Duodenum is located at the junction of the stomach and the small intestine. The duodenum is the first part of the small intestine. It is C-shaped and about 25 cm long. This is the place where the ultimate destruction of food digestion reaches its completion and where the acidity of chyme is ...
Human Digestion
... Gall bladder • Pouch structure located near the liver which concentrates and stores bile • Bile duct – a long tube that carries BILE. The top half of the common bile duct is associated with the liver, while the bottom half of the common bile duct is associated with the pancreas, through which it pa ...
... Gall bladder • Pouch structure located near the liver which concentrates and stores bile • Bile duct – a long tube that carries BILE. The top half of the common bile duct is associated with the liver, while the bottom half of the common bile duct is associated with the pancreas, through which it pa ...
L13_FatDigst
... • In both structures, polar heads are facing the aqueous environment while the hydrophobic tails are buried in the core • Micelles can also be formed using bile salts ...
... • In both structures, polar heads are facing the aqueous environment while the hydrophobic tails are buried in the core • Micelles can also be formed using bile salts ...
Nutrition - Athens Academy
... 61. Which of the following is the correct sequence? A. acetyl-CoA formation, glycolysis, electron-transport chain, citric acid cycle B. acetyl-CoA formation, citric acid cycle, electron transport chain, glycolysis C. citric acid cycle, glycolysis, acetyl-CoA formation, electron transport chain D. gl ...
... 61. Which of the following is the correct sequence? A. acetyl-CoA formation, glycolysis, electron-transport chain, citric acid cycle B. acetyl-CoA formation, citric acid cycle, electron transport chain, glycolysis C. citric acid cycle, glycolysis, acetyl-CoA formation, electron transport chain D. gl ...
Ascending cholangitis

Ascending cholangitis or acute cholangitis (or sometimes cholangitis without a modifier - from Greek chol-, bile + ang-, vessel + itis-, inflammation) is an infection of the bile duct (cholangitis), usually caused by bacteria ascending from its junction with the duodenum (first part of the small intestine). It tends to occur if the bile duct is already partially obstructed by gallstones.Cholangitis can be life-threatening, and is regarded as a medical emergency. Characteristic symptoms include yellow discoloration of the skin or whites of the eyes, fever, abdominal pain, and in severe cases, low blood pressure and confusion. Initial treatment is with intravenous fluids and antibiotics, but there is often an underlying problem (such as gallstones or narrowing in the bile duct) for which further tests and treatments may be necessary, usually in the form of endoscopy to relieve obstruction of the bile duct.