Multiple choice questions
... stabilize the DNA double helix stabilize protein structures form between two electronegative atoms form between adenin and guanine have a bond energy of 20-30 kcal mol-1 ...
... stabilize the DNA double helix stabilize protein structures form between two electronegative atoms form between adenin and guanine have a bond energy of 20-30 kcal mol-1 ...
What holds chromosomes together: Researchers
... Bacillus subtilis. The researchers showed that the To ensure that the genetic material is equally and bacterial SMC-kleisin complex has two arms made accurately distributed to the two daughter cells of identical SMC proteins that form a ring. The arms during cell division, the DNA fibers must have a ...
... Bacillus subtilis. The researchers showed that the To ensure that the genetic material is equally and bacterial SMC-kleisin complex has two arms made accurately distributed to the two daughter cells of identical SMC proteins that form a ring. The arms during cell division, the DNA fibers must have a ...
Chapter 11: Organization of DNA in Eukaryotes 11.2: mtDNA
... chloroplasts, allowing these (believed to be) prokaryotes to reside inside of the cytoplasm in a symbiotic relationship. After some time, these mitochondria and chloroplast could no longer live on their own outside of the eukaryote. How large is mtDNA in humans? About 16,000 base pairs, or 16 kiloba ...
... chloroplasts, allowing these (believed to be) prokaryotes to reside inside of the cytoplasm in a symbiotic relationship. After some time, these mitochondria and chloroplast could no longer live on their own outside of the eukaryote. How large is mtDNA in humans? About 16,000 base pairs, or 16 kiloba ...
What is a protein?
... Transcription. (The DNA code is transcribed or copied into RNA.) •In RNA, _______ and ________ are paired together and __________ and __________ are paired together. •Many copies of the ___________________ are made and leave the ______________________. •The ______________________ binds with a riboso ...
... Transcription. (The DNA code is transcribed or copied into RNA.) •In RNA, _______ and ________ are paired together and __________ and __________ are paired together. •Many copies of the ___________________ are made and leave the ______________________. •The ______________________ binds with a riboso ...
ANSWERS - midterm study guide
... 5. How many copes of each chromosome does a normal human have? ______________________________________ 6. Contrast dominant and recessive. ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Who is considered to be the founder of genetics? _________ ...
... 5. How many copes of each chromosome does a normal human have? ______________________________________ 6. Contrast dominant and recessive. ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Who is considered to be the founder of genetics? _________ ...
Study Guide for LS
... molecules. When DNA copies itself it splits down the middle where the two bases meet. The bases on each side of the molecule can be used as a pattern for a new complementary side. ...
... molecules. When DNA copies itself it splits down the middle where the two bases meet. The bases on each side of the molecule can be used as a pattern for a new complementary side. ...
DNA to Proteins….a REVIEW
... 8. The amino acid ________________________ is represented by ACA. 9. __________ and __________ are mRNA codons for phenylalanine. 10. The genetic code is said to be universal because a codon represents the same ____________________________ in all organisms. ...
... 8. The amino acid ________________________ is represented by ACA. 9. __________ and __________ are mRNA codons for phenylalanine. 10. The genetic code is said to be universal because a codon represents the same ____________________________ in all organisms. ...
DNA in classifying species
... Biochemical similarities can be used to identify closely related organisms. Proteins such as enzymes and haemoglobin (found in red blood cells) have more differences in their amino acid sequences as organisms become more distantly related. ...
... Biochemical similarities can be used to identify closely related organisms. Proteins such as enzymes and haemoglobin (found in red blood cells) have more differences in their amino acid sequences as organisms become more distantly related. ...
Name
... A) turns on the genes necessary for synthesis of proteins. B) serves as a master control gene that functions during embryonic development by controlling the developmental fate of groups of cells. C) represses gene transcription and promotes mRNA translation. D) produces a product that controls the t ...
... A) turns on the genes necessary for synthesis of proteins. B) serves as a master control gene that functions during embryonic development by controlling the developmental fate of groups of cells. C) represses gene transcription and promotes mRNA translation. D) produces a product that controls the t ...
They are the offspring of these two people They are the
... Every organism exhibits one or more of the traits of their grandparents. Your description could involve; via the people who married into the family, by the expression of a recessive trait, via mutation. The children share more traits with parents than the grandchildren share. The children share more ...
... Every organism exhibits one or more of the traits of their grandparents. Your description could involve; via the people who married into the family, by the expression of a recessive trait, via mutation. The children share more traits with parents than the grandchildren share. The children share more ...
Biology Final Exam
... _____________, or the Central Dogma of Biology. 4. During DNA replication, complementary strands of DNA are made from the original DNA strands. Using this template (original strand of DNA) and the base-pairing rules, give the complementary strand: TACCCCGAGAGG 5. What would be the complementary sequ ...
... _____________, or the Central Dogma of Biology. 4. During DNA replication, complementary strands of DNA are made from the original DNA strands. Using this template (original strand of DNA) and the base-pairing rules, give the complementary strand: TACCCCGAGAGG 5. What would be the complementary sequ ...
DNA and RNA Notes
... Discovery of DNA _____________ - pneumonia causing bacteria and mice. (Determined…) _____________ - process of one bacteria changing its DNA from the addition of another. Avery- DNA is the nucleic acid that ___________ and __________ genetic information from one generation to the next. Hersh ...
... Discovery of DNA _____________ - pneumonia causing bacteria and mice. (Determined…) _____________ - process of one bacteria changing its DNA from the addition of another. Avery- DNA is the nucleic acid that ___________ and __________ genetic information from one generation to the next. Hersh ...
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis: Power Point presentation
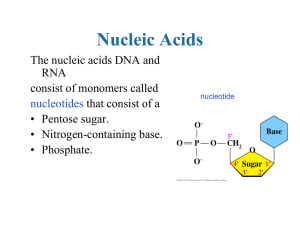
... Nucleic Acids The nucleic acids DNA and RNA consist of monomers called nucleotides that consist of a • Pentose sugar. • Nitrogen-containing base. • Phosphate. ...
... Nucleic Acids The nucleic acids DNA and RNA consist of monomers called nucleotides that consist of a • Pentose sugar. • Nitrogen-containing base. • Phosphate. ...
DNA as Videotape: Introductory Fact Sheet
... • DNA can be edited--for example, we can take DNA containing one gene from an animal (for example, the gene for insulin from humans) and splice it biologically into the DNA of a bacterium. • That bacterium can multiply, and its offspring will contain the insulin gene. • Those bacteria can make the i ...
... • DNA can be edited--for example, we can take DNA containing one gene from an animal (for example, the gene for insulin from humans) and splice it biologically into the DNA of a bacterium. • That bacterium can multiply, and its offspring will contain the insulin gene. • Those bacteria can make the i ...
Chapter 10 Structure and Function of DNA
... Okazaki Fragments What is significant about the 3’-OH Why do chromosomes get shorter and shorter every round of replication? What are telomeres? What is telomerase? What happens if there is a mistake? What is the role of single-stranded binding proteins Protein Synthesis Central Dogma DNA -> mRNA -> ...
... Okazaki Fragments What is significant about the 3’-OH Why do chromosomes get shorter and shorter every round of replication? What are telomeres? What is telomerase? What happens if there is a mistake? What is the role of single-stranded binding proteins Protein Synthesis Central Dogma DNA -> mRNA -> ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.