Genetics 1
... physical and mental traits of their parents or ancestors i.e. certain traits are transmitted from one generation to the next. Genetic information is carried on the DNA molecule as a gene. Gene: is the unit of heredity found on a chromosome, and is an instruction (code) to the cell to make a particul ...
... physical and mental traits of their parents or ancestors i.e. certain traits are transmitted from one generation to the next. Genetic information is carried on the DNA molecule as a gene. Gene: is the unit of heredity found on a chromosome, and is an instruction (code) to the cell to make a particul ...
Unit 4 Resources - Schoolwires.net
... __________________________ . 8. The amino acid __________________________ is represented by the mRNA codon ACA. 9. ________________________ and ________________________ are mRNA codons for phenylalanine. 10. There can be more than one __________________________ for the same amino acid. 11. For any o ...
... __________________________ . 8. The amino acid __________________________ is represented by the mRNA codon ACA. 9. ________________________ and ________________________ are mRNA codons for phenylalanine. 10. There can be more than one __________________________ for the same amino acid. 11. For any o ...
Chapter 11: DNA
... DNA Replication… • The process by which DNA makes a copy of itself • Occurs during interphase, before cell division • Semi-conservative: half of the original strand is always conserved to make the new strand • Enzymes are involved: – DNA helicase: separates the strands of the DNA molecule by breaki ...
... DNA Replication… • The process by which DNA makes a copy of itself • Occurs during interphase, before cell division • Semi-conservative: half of the original strand is always conserved to make the new strand • Enzymes are involved: – DNA helicase: separates the strands of the DNA molecule by breaki ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis Notes Organizer
... 18. Mutations that occur in somatic cells are ____________ passed on to the next generation. 19. Mutations that occur in sex cells are passed on and will be present in ______________ cell in the offspring. 20. Point mutations involve the changing of ________________ nitrogen base. a. Substitution: ...
... 18. Mutations that occur in somatic cells are ____________ passed on to the next generation. 19. Mutations that occur in sex cells are passed on and will be present in ______________ cell in the offspring. 20. Point mutations involve the changing of ________________ nitrogen base. a. Substitution: ...
Nucleic Acids Placemat
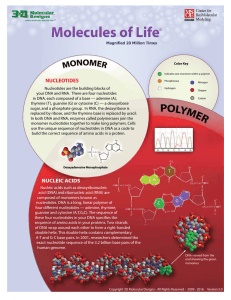
... NUCLEIC ACIDS Nucleic acids such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA ...
... NUCLEIC ACIDS Nucleic acids such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA ...
DNA cr.eu updated plg latest
... form of chromatin (DNA, RNA and protein) that is rich in gene concentration, and is often under active transcription. • Unlike heterochromatin, it is found in both cells with nuclei (eukaryotes) and cells without nuclei (prokaryotes). • Euchromatin comprises the most active portion of the genome wit ...
... form of chromatin (DNA, RNA and protein) that is rich in gene concentration, and is often under active transcription. • Unlike heterochromatin, it is found in both cells with nuclei (eukaryotes) and cells without nuclei (prokaryotes). • Euchromatin comprises the most active portion of the genome wit ...
DNA: The Secret of Life
... Inheritance, but we did not always know this fact. • Inheritance is easy to observe ...
... Inheritance, but we did not always know this fact. • Inheritance is easy to observe ...
DNA-Polymerase
... 4. Microwave until it turns clear and all Agarose is in solution. (roughly 40 seconds-CAUTION: It bubbles quickly so do 10 second intervals) 5. Add 2.5 ml of 10x TAE buffer, then add 20 ml ethidium bromide (EtBr). 6. Gently pour solution into gel tray, remove bubbles and let it sit for 20 minutes. ...
... 4. Microwave until it turns clear and all Agarose is in solution. (roughly 40 seconds-CAUTION: It bubbles quickly so do 10 second intervals) 5. Add 2.5 ml of 10x TAE buffer, then add 20 ml ethidium bromide (EtBr). 6. Gently pour solution into gel tray, remove bubbles and let it sit for 20 minutes. ...
DNA Technology
... phage DNA that has been clipped by restriction enzymes. In either case, gene cloning results when the foreign genes replicate inside the host bacterium or other host cell. Although bacteria are the most common host organisms for cloning, DNA can be introduced directly into certain eukaryotic cells a ...
... phage DNA that has been clipped by restriction enzymes. In either case, gene cloning results when the foreign genes replicate inside the host bacterium or other host cell. Although bacteria are the most common host organisms for cloning, DNA can be introduced directly into certain eukaryotic cells a ...
E. coli
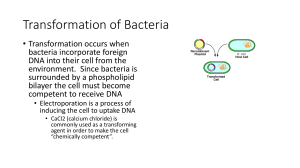
... environment. Since bacteria is surrounded by a phospholipid bilayer the cell must become competent to receive DNA • Electroporation is a process of inducing the cell to uptake DNA • CaCl2 (calcium chloride) is commonly used as a transforming agent in order to make the cell ...
... environment. Since bacteria is surrounded by a phospholipid bilayer the cell must become competent to receive DNA • Electroporation is a process of inducing the cell to uptake DNA • CaCl2 (calcium chloride) is commonly used as a transforming agent in order to make the cell ...
Restriction Analysis of pARA and pKAN-R
... The tangle is a portion of a single DNA molecule containing over 4.6 million base pairs encoding approximately 4,300 genes. The small circlets are plasmids. (Courtesy of Huntington Potter and David Dressler, Harvard Medical School.) ...
... The tangle is a portion of a single DNA molecule containing over 4.6 million base pairs encoding approximately 4,300 genes. The small circlets are plasmids. (Courtesy of Huntington Potter and David Dressler, Harvard Medical School.) ...
Life Science Vocabulary.xlsx
... an organism that always produces an offspring with the same form of a trait as the purebred parent trait a characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes allele the different forms of a gene Rosalind Franklin famous woman scientist who used x-rays to photograph DNA mo ...
... an organism that always produces an offspring with the same form of a trait as the purebred parent trait a characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes allele the different forms of a gene Rosalind Franklin famous woman scientist who used x-rays to photograph DNA mo ...
Word Definition Synonym 1 DNA replication the
... an organism that always produces an offspring with the same form of a trait as the purebred parent trait a characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes allele the different forms of a gene Rosalind Franklin famous woman scientist who used x-rays to photograph DNA mo ...
... an organism that always produces an offspring with the same form of a trait as the purebred parent trait a characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes allele the different forms of a gene Rosalind Franklin famous woman scientist who used x-rays to photograph DNA mo ...
CST Review PowerPoint
... contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and some viruses. -The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in regulating the use of this genetic in ...
... contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and some viruses. -The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in regulating the use of this genetic in ...
the nucleic acids - Y11-Biology-SG
... the two strands together are the H bonds that form between complementary bases. ...
... the two strands together are the H bonds that form between complementary bases. ...
Biotechnology Genetic Engineering and Recombinant DNA
... 5e.* Students know how exogenous DNA can be inserted into bacterial cells to alter their genetic makeup and support expression of new protein products. ...
... 5e.* Students know how exogenous DNA can be inserted into bacterial cells to alter their genetic makeup and support expression of new protein products. ...
Biotechnology
... 5e.* Students know how exogenous DNA can be inserted into bacterial cells to alter their genetic makeup and support expression of new protein products. ...
... 5e.* Students know how exogenous DNA can be inserted into bacterial cells to alter their genetic makeup and support expression of new protein products. ...
How can PCR be used to mutagenize DNA or to introduce novel
... Mutate gene by site-specific in vitro mutagenesis----using PCR the point : using siutable primers containing ...
... Mutate gene by site-specific in vitro mutagenesis----using PCR the point : using siutable primers containing ...
DNA
... Guanine must pair with Cytosine Their amounts in a given DNA molecule will be about the same. ...
... Guanine must pair with Cytosine Their amounts in a given DNA molecule will be about the same. ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.