strawberry dna extraction lab
... Have you ever wondered what DNA looks like? You are going to break apart the cell membrane of a strawberry and separate the DNA from the nucleus. Strawberries are a good source of DNA because they have 8 copies of each type of chromosome. This large number of chromosomes will filter out of your solu ...
... Have you ever wondered what DNA looks like? You are going to break apart the cell membrane of a strawberry and separate the DNA from the nucleus. Strawberries are a good source of DNA because they have 8 copies of each type of chromosome. This large number of chromosomes will filter out of your solu ...
DNA Test Study Guide
... Human cells have ________chromosomes, or two sets of _________. One set came from the ___________ and one from the ___________. Body cells we also call ________________Because our body cells’ chromosomes are found in pairs, we call them ___________. When arranged on a karyotype, you can see that the ...
... Human cells have ________chromosomes, or two sets of _________. One set came from the ___________ and one from the ___________. Body cells we also call ________________Because our body cells’ chromosomes are found in pairs, we call them ___________. When arranged on a karyotype, you can see that the ...
chapter 12 test review key
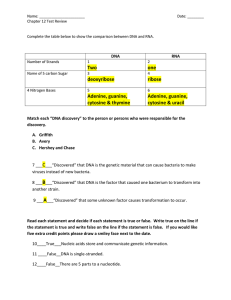
... 7 ___C___“Discovered” that DNA is the genetic material that can cause bacteria to make viruses instead of new bacteria. 8 ___B___“Discovered” that DNA is the factor that caused one bacterium to transform into another strain. 9 ___A___“Discovered” that some unknown factor causes transformation to occ ...
... 7 ___C___“Discovered” that DNA is the genetic material that can cause bacteria to make viruses instead of new bacteria. 8 ___B___“Discovered” that DNA is the factor that caused one bacterium to transform into another strain. 9 ___A___“Discovered” that some unknown factor causes transformation to occ ...
GE & Profiling iQuiz
... artificially alter the genetic information in the chromosome of an organism? Gene therapy ...
... artificially alter the genetic information in the chromosome of an organism? Gene therapy ...
DNA Biology
... Transcription – first stage of gene expression. A messenger RNA (mRNA) is synthesized from a gene within DNA. Translation – second stage – mRNA is used to direct production of a protein. ...
... Transcription – first stage of gene expression. A messenger RNA (mRNA) is synthesized from a gene within DNA. Translation – second stage – mRNA is used to direct production of a protein. ...
Allele: One of the variant forms of the DNA sequence at a particular
... chromosome. Different alleles can produce variation on inherited characteristics such as hair or eye color. One form of the allele (the dominant one) may be expressed more than the other form (the recessive one). Some alleles may have no direct affect (silent) but may tag genes or other nearby allel ...
... chromosome. Different alleles can produce variation on inherited characteristics such as hair or eye color. One form of the allele (the dominant one) may be expressed more than the other form (the recessive one). Some alleles may have no direct affect (silent) but may tag genes or other nearby allel ...
biology quiz chapter 12
... Answer the following questions on a separate sheet of paper. 1. What are the three types of RNA? 2. What are the three differences between DNA and RNA 3. What is a Codon? 4. If there are 64 possible codons and only 20 amino acids what has to be true? 5. Why does mRNA have to carry DNA’s message to t ...
... Answer the following questions on a separate sheet of paper. 1. What are the three types of RNA? 2. What are the three differences between DNA and RNA 3. What is a Codon? 4. If there are 64 possible codons and only 20 amino acids what has to be true? 5. Why does mRNA have to carry DNA’s message to t ...
Electrophoresis literally means “the condition of
... A segment of DNA has two restriction sites–I and II. When incubated with restriction enzymes I and II, three fragments will be formed–a, b, and c. Which of the following gels produced by electrophoresis would represent the separation and identity of these fragments? ...
... A segment of DNA has two restriction sites–I and II. When incubated with restriction enzymes I and II, three fragments will be formed–a, b, and c. Which of the following gels produced by electrophoresis would represent the separation and identity of these fragments? ...
Intro to Strawberry DNA Extraction Lab
... Where have you heard of genes before? What do genes have to do with DNA? Gene = Segments of DNA that control the production of protein ...
... Where have you heard of genes before? What do genes have to do with DNA? Gene = Segments of DNA that control the production of protein ...
Honors Biology Final Exam-‐Part 2-‐Semester 2
... 1. The process of cell division which produces cells identical to the original cell is: 2. The purpose of meiosis is to produce ____________ . 3. Body cells are 2n or ________________ . 4. Ga ...
... 1. The process of cell division which produces cells identical to the original cell is: 2. The purpose of meiosis is to produce ____________ . 3. Body cells are 2n or ________________ . 4. Ga ...
a copy of the Candy DNA Replication
... project (or a movie if you know how) that depicts all of the steps of DNA replication. Take photographs of each step and be sure they are easy to see on the Powerpoint. Include labels, arrows, captions, titles where necessary. The following steps below should help you organize your project: 1. Assem ...
... project (or a movie if you know how) that depicts all of the steps of DNA replication. Take photographs of each step and be sure they are easy to see on the Powerpoint. Include labels, arrows, captions, titles where necessary. The following steps below should help you organize your project: 1. Assem ...
AP BIO Unit 6 Review Ch. 14,15,16,18,19 Westbrook Gene
... What must happen for transcription to be initiated? (many steps) Eukaryotes have regulatory proteins which have two distinct binding domains that allows for “control from a distance.” What are those binding domains called? What is the sequence of three tRNA nucleotides that is complementary to and b ...
... What must happen for transcription to be initiated? (many steps) Eukaryotes have regulatory proteins which have two distinct binding domains that allows for “control from a distance.” What are those binding domains called? What is the sequence of three tRNA nucleotides that is complementary to and b ...
Genetic Engineering
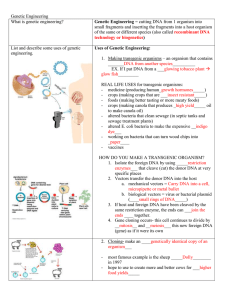
... 1. Isolate the foreign DNA by using _____restriction enzymes___ that cleave (cut) the donor DNA at very specific places 2. Vectors transfer the donor DNA into the host a. mechanical vectors = Carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid (____ ...
... 1. Isolate the foreign DNA by using _____restriction enzymes___ that cleave (cut) the donor DNA at very specific places 2. Vectors transfer the donor DNA into the host a. mechanical vectors = Carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid (____ ...
Chapter 11: Organization of DNA in Eukaryotes 11.2: mtDNA
... chloroplasts, allowing these (believed to be) prokaryotes to reside inside of the cytoplasm in a symbiotic relationship. After some time, these mitochondria and chloroplast could no longer live on their own outside of the eukaryote. How large is mtDNA in humans? About 16,000 base pairs, or 16 kilobi ...
... chloroplasts, allowing these (believed to be) prokaryotes to reside inside of the cytoplasm in a symbiotic relationship. After some time, these mitochondria and chloroplast could no longer live on their own outside of the eukaryote. How large is mtDNA in humans? About 16,000 base pairs, or 16 kilobi ...
Vocabulary Quiz Key Terms
... An enzyme that breaks the hydrogen bonds holding the base pairs together as it unwinds and unzips the double helix, allowing new nucleotides to bind to the 2 single strands by base pairing. An enzyme that adds complementary nucleotides to the template strand of the unzipped double helix until the en ...
... An enzyme that breaks the hydrogen bonds holding the base pairs together as it unwinds and unzips the double helix, allowing new nucleotides to bind to the 2 single strands by base pairing. An enzyme that adds complementary nucleotides to the template strand of the unzipped double helix until the en ...
2013 DNA, Repl, Trans and Transl Review
... 6. What 3 things are found on RNA, but are not found on DNA molecules? 7. What do tRNA anticodons match during translation? 8. What is a codon & where are they found? 9. Where do you find rRNA? 10. What organelle is made of rRNA? Where is this organelle synthesized, organelle? 11. What bases pair wi ...
... 6. What 3 things are found on RNA, but are not found on DNA molecules? 7. What do tRNA anticodons match during translation? 8. What is a codon & where are they found? 9. Where do you find rRNA? 10. What organelle is made of rRNA? Where is this organelle synthesized, organelle? 11. What bases pair wi ...
doc - Let`s Get Healthy!
... finally discovered as the molecule that mediates heredity though most people were skeptical of these findings until 1952 when scientists used labeled bacteriophages to demonstrate this conclusively. ...
... finally discovered as the molecule that mediates heredity though most people were skeptical of these findings until 1952 when scientists used labeled bacteriophages to demonstrate this conclusively. ...
From Genetics to Epigenetics
... finally discovered as the molecule that mediates heredity though most people were skeptical of these findings until 1952 when scientists used labeled bacteriophages to demonstrate this conclusively. ...
... finally discovered as the molecule that mediates heredity though most people were skeptical of these findings until 1952 when scientists used labeled bacteriophages to demonstrate this conclusively. ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.