Genetic Engineering
... • It can be used for gene discovery or expression analysis • Immediate PCR Amplification of known genes • Verification of genetic mutation • Comparison of a specific gene between different tissues • Analysis of mRNA alternative splicing • Gene cloning and target sequencing ...
... • It can be used for gene discovery or expression analysis • Immediate PCR Amplification of known genes • Verification of genetic mutation • Comparison of a specific gene between different tissues • Analysis of mRNA alternative splicing • Gene cloning and target sequencing ...
Answer Key
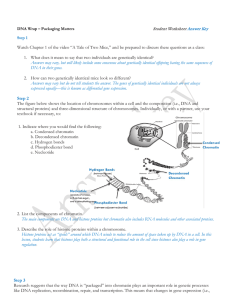
... The main components are DNA and histone proteins but chromatin also includes RNA molecules and other associated proteins. 3. Describe the role of histone proteins within a chromosome. Histone proteins act as “spools” around which DNA winds to reduce the amount of space taken up by DNA in a cell. In ...
... The main components are DNA and histone proteins but chromatin also includes RNA molecules and other associated proteins. 3. Describe the role of histone proteins within a chromosome. Histone proteins act as “spools” around which DNA winds to reduce the amount of space taken up by DNA in a cell. In ...
DNA RNA
... So what is a telomere anyway? • A telomere is a repeating DNA sequence (for example, TTAGGG) at the end of the body's chromosomes. • The telomere can reach a length of 15,000 base pairs. • Telomeres function by preventing chromosomes from losing base pair sequences at their ends. They also stop chr ...
... So what is a telomere anyway? • A telomere is a repeating DNA sequence (for example, TTAGGG) at the end of the body's chromosomes. • The telomere can reach a length of 15,000 base pairs. • Telomeres function by preventing chromosomes from losing base pair sequences at their ends. They also stop chr ...
Loading Complete Instructions: Choose the best answer for each
... A) must have the resource competition from the other wren species. B) eat different foods found in and on the tree. C) have different natural enemies. D) breed at different times. 21) Which of the following statements BEST describes how mutations are related to evolution? A) There is not a strong re ...
... A) must have the resource competition from the other wren species. B) eat different foods found in and on the tree. C) have different natural enemies. D) breed at different times. 21) Which of the following statements BEST describes how mutations are related to evolution? A) There is not a strong re ...
Beyond the double helix
... which in turn coils up like an overtwisted string into globular chromosomes. Over the past few years, researchers have come to realize that chromosomes, which seem to be carefully arranged in the nucleus, may be positioned so that those that are most important to the cell gain preferential spots. We ...
... which in turn coils up like an overtwisted string into globular chromosomes. Over the past few years, researchers have come to realize that chromosomes, which seem to be carefully arranged in the nucleus, may be positioned so that those that are most important to the cell gain preferential spots. We ...
Plasmid Isolation Using Alkaline Lysis
... free the plasmid DNA from the cell, leaving behind the E. coli chromosomal DNA with cell wall debris. The protocol described involves three basic steps: growth of bacteria and amplification of the plasmid; harvesting and lysis of the bacteria; and purification of the plasmid DNA. These purification ...
... free the plasmid DNA from the cell, leaving behind the E. coli chromosomal DNA with cell wall debris. The protocol described involves three basic steps: growth of bacteria and amplification of the plasmid; harvesting and lysis of the bacteria; and purification of the plasmid DNA. These purification ...
Recitation Notes for RDM Day 1 1. Module Overview –
... There are normally 4-5 components in a given reaction. 1- DNA which will be digested. Must have specific site for enzyme. Also needs to be free of contaminants such as phenol, alcohol, excessive salts, which interfere with enzyme activity. 2- the enzyme- RE are fragile! Need to be treated carefully ...
... There are normally 4-5 components in a given reaction. 1- DNA which will be digested. Must have specific site for enzyme. Also needs to be free of contaminants such as phenol, alcohol, excessive salts, which interfere with enzyme activity. 2- the enzyme- RE are fragile! Need to be treated carefully ...
Genome Structure - Pennsylvania State University
... • Genetics: study of inherited phenotypes • Genomics: study of genomes • Biochemistry: study of the chemistry of living organisms and/or cells • Revolution lauched by full genome sequencing – Many biological problems now have finite (albeit complex) solutions. – New era will see an even greater inte ...
... • Genetics: study of inherited phenotypes • Genomics: study of genomes • Biochemistry: study of the chemistry of living organisms and/or cells • Revolution lauched by full genome sequencing – Many biological problems now have finite (albeit complex) solutions. – New era will see an even greater inte ...
File
... • Takes place in the nucleus. • A specific gene of DNA is transcribed into mRNA by RNA polymerase. • The instructions for making a protein are transferred from the nucleus to the ribosome. ...
... • Takes place in the nucleus. • A specific gene of DNA is transcribed into mRNA by RNA polymerase. • The instructions for making a protein are transferred from the nucleus to the ribosome. ...
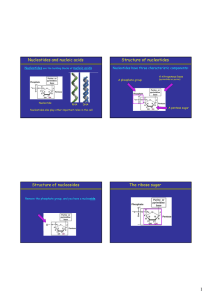
Nucleic Acids - Structure and Replication
... For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ ...
... For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ ...
AP Biology: Unit 3A Homework
... 3. What is transformation? 4. If a species has 35% adenine in its DNA, what are the percents of the other three bases? 5. Describe the basic structure of DNA. Be detailed! Include base pairing. 6. What is the advantage of the double stranded aspect of DNA? 7. What are the three models of DNA replica ...
... 3. What is transformation? 4. If a species has 35% adenine in its DNA, what are the percents of the other three bases? 5. Describe the basic structure of DNA. Be detailed! Include base pairing. 6. What is the advantage of the double stranded aspect of DNA? 7. What are the three models of DNA replica ...
Lecture 15 Biol302 Spring 2011
... ratios of total purines to total pyrimidines were not far from 1. More should not be read into these figures.’’ Later in 1950, apparently as a last-minute insertion in the paper, Chargaff wrote ‘‘It is noteworthy – whether this is more than accidental, cannot yet be said – that in all desoxypentose ...
... ratios of total purines to total pyrimidines were not far from 1. More should not be read into these figures.’’ Later in 1950, apparently as a last-minute insertion in the paper, Chargaff wrote ‘‘It is noteworthy – whether this is more than accidental, cannot yet be said – that in all desoxypentose ...
Checkpoints
... Square: arrest with MBC, release and X-ray Triangle: arrest with MBC, x-ray and hold in MBC for 4 hr ...
... Square: arrest with MBC, release and X-ray Triangle: arrest with MBC, x-ray and hold in MBC for 4 hr ...
Nucleic Acid Biotechnology Techniques
... This project is funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community Based Job Training Grant as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration (CB-15-162-06-60). NCC is an equal opportunity employer and does not discriminate on the following basis: against ...
... This project is funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community Based Job Training Grant as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration (CB-15-162-06-60). NCC is an equal opportunity employer and does not discriminate on the following basis: against ...
frontiers of genetics chap13
... B. Regulation of Genes in Eukaryotes 1. Transcription factors- proteins that regulate transcription by binding to those promoters or to RNA polymerases; are activated and deactivated by chemical signals in the cell 2. Gene expression- the transcription and translation of genes into proteins ...
... B. Regulation of Genes in Eukaryotes 1. Transcription factors- proteins that regulate transcription by binding to those promoters or to RNA polymerases; are activated and deactivated by chemical signals in the cell 2. Gene expression- the transcription and translation of genes into proteins ...
1) The function of the cell cycle is to produce daughter cells that: (A
... (B.) The protein would be several amino acids shorter (C.) The protein would be the same except for one amino acid substitution (D.) The mRNA would change but the protein would be unaffected (E.) none of the above 37) The type of mutation described in #36 is known as a: (A.) nonsense mutation (B.) f ...
... (B.) The protein would be several amino acids shorter (C.) The protein would be the same except for one amino acid substitution (D.) The mRNA would change but the protein would be unaffected (E.) none of the above 37) The type of mutation described in #36 is known as a: (A.) nonsense mutation (B.) f ...
Provincial Exam Questions
... A. single helix, ribose, guanine B. double helix, ribose, adenine C. single helix, deoxyribose, uracil D. double helix, deoxyribose, thymine ...
... A. single helix, ribose, guanine B. double helix, ribose, adenine C. single helix, deoxyribose, uracil D. double helix, deoxyribose, thymine ...
Genetics Terminology List - Arabian Horse Association
... Genetic code - the instructions in a gene that tell the cell how to function. Genetic marker - a gene or other identifiable portion of DNA whose inheritance can be followed. Heterozygote - an individual having two different alleles of a particular gene; the individual can pass either allele to their ...
... Genetic code - the instructions in a gene that tell the cell how to function. Genetic marker - a gene or other identifiable portion of DNA whose inheritance can be followed. Heterozygote - an individual having two different alleles of a particular gene; the individual can pass either allele to their ...
1) Lecture notes: mechanisms of gene activation
... The synthesis of a complementary RNA strand, that matches the sequence of the DNA strand. This is the process where most regulation occurs, during gene expression. This will be illustrated with some very simple examples of this process. ...
... The synthesis of a complementary RNA strand, that matches the sequence of the DNA strand. This is the process where most regulation occurs, during gene expression. This will be illustrated with some very simple examples of this process. ...
KlenTherm™ DNA Polymerase
... more KlenTherm than Taq protein if the nucleic acid incorporation is more than 500 bp. KlenTherm™ DNA polymerase is shipped at higher (10 u/µl) concentration, so that it can easily incorporate 2 kb, if the same quantity is used as for full-length Taq. The use of KlenTherm™ is espacially recomended f ...
... more KlenTherm than Taq protein if the nucleic acid incorporation is more than 500 bp. KlenTherm™ DNA polymerase is shipped at higher (10 u/µl) concentration, so that it can easily incorporate 2 kb, if the same quantity is used as for full-length Taq. The use of KlenTherm™ is espacially recomended f ...
Ch. 13 Genetic Engineering
... which takes advantage of naturally occurring genetic variation in plants, animals, and other organisms, to pass desired traits on to the next generation of organisms ...
... which takes advantage of naturally occurring genetic variation in plants, animals, and other organisms, to pass desired traits on to the next generation of organisms ...
History of Genetics
... Century • 1900: rediscovery of Mendel’s work by Robert Correns, Hugo de Vries, and Erich von Tschermak . • 1902: Archibald Garrod discovers that alkaptonuria, a human disease, has a genetic basis. • 1904: Gregory Bateson discovers linkage between genes. Also coins the word “genetics”. • 1910: Thomas ...
... Century • 1900: rediscovery of Mendel’s work by Robert Correns, Hugo de Vries, and Erich von Tschermak . • 1902: Archibald Garrod discovers that alkaptonuria, a human disease, has a genetic basis. • 1904: Gregory Bateson discovers linkage between genes. Also coins the word “genetics”. • 1910: Thomas ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.