Transfusion Packed Red Blood Cells, Not Actively
... Blood bank uses the same fin # . STAT, T;N, Type: Blood Comments: Good for 3 days of draw, best if done the day before needed. Blood bank uses the same fin # . Before blood products can be transfused, place a TYPE and Crossmatch order below.(NOTE)* Crossmatch Units from Type and Screen Routine, T;N, ...
... Blood bank uses the same fin # . STAT, T;N, Type: Blood Comments: Good for 3 days of draw, best if done the day before needed. Blood bank uses the same fin # . Before blood products can be transfused, place a TYPE and Crossmatch order below.(NOTE)* Crossmatch Units from Type and Screen Routine, T;N, ...
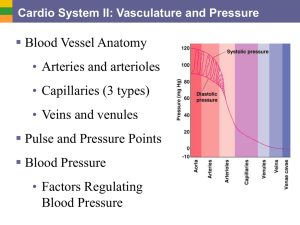
3b CardioII-Vasculature
... • Volume of blood flowing through a vessel, an organ, or the entire circulation in a given period, measured in ml/min Blood pressure (BP) • Force per unit area exerted on the wall of a blood vessel by the blood, expressed in mm Hg • Measured as systemic arterial BP in large arteries near heart P ...
... • Volume of blood flowing through a vessel, an organ, or the entire circulation in a given period, measured in ml/min Blood pressure (BP) • Force per unit area exerted on the wall of a blood vessel by the blood, expressed in mm Hg • Measured as systemic arterial BP in large arteries near heart P ...
Potential Essay Questions For Final
... Potential Essay Questions for the Final Exam: Sem. 2, 2007-08 Question Tell the story of a red blood cell as it travels up the inferior vena cava, through the heart/lung system, out through the aorta, to some particular tissue, and back to the heart. Tell the story of all of the anatomical structure ...
... Potential Essay Questions for the Final Exam: Sem. 2, 2007-08 Question Tell the story of a red blood cell as it travels up the inferior vena cava, through the heart/lung system, out through the aorta, to some particular tissue, and back to the heart. Tell the story of all of the anatomical structure ...
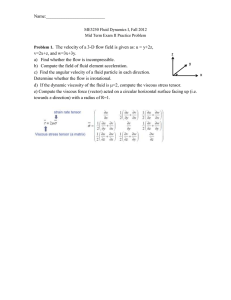
Problem 1. Water flows steadily from a large closed tank as shown in
... Solution. Solution of the Navier-Stokes equation for flow between the parallel plates looks like that: ...
... Solution. Solution of the Navier-Stokes equation for flow between the parallel plates looks like that: ...
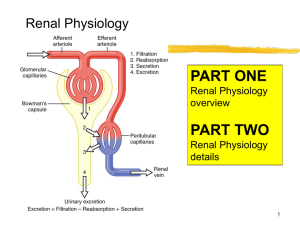
Glomerular Filtration
... three basic processes; glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption and tubular secretion. • Define GFR and quote normal value. • Identify and describe the factors controlling GFR in terms of starling forces, permeability with respect to size, shape and electrical charges and ultra-filtration coeffic ...
... three basic processes; glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption and tubular secretion. • Define GFR and quote normal value. • Identify and describe the factors controlling GFR in terms of starling forces, permeability with respect to size, shape and electrical charges and ultra-filtration coeffic ...
Derive from first principles the Poiseuille equation for
... pressure and does not depend upon the absolute magnitude of the pressure itself. In other words, even if the pressure in the tube is very large, there will be no motion of the fluid if there is no difference in pressure between the two ends and the motion will be in the direction of the positive pre ...
... pressure and does not depend upon the absolute magnitude of the pressure itself. In other words, even if the pressure in the tube is very large, there will be no motion of the fluid if there is no difference in pressure between the two ends and the motion will be in the direction of the positive pre ...
Unit 1 Lecture 3
... veins. They are composed of the same three layers as arteries except that the tunica interna and tunica media are thinner and the tunica externa is thicker than those found in arteries. Veins in the limbs contain valves that prevent the backflow of blood. Veins and venules serve as the main blood re ...
... veins. They are composed of the same three layers as arteries except that the tunica interna and tunica media are thinner and the tunica externa is thicker than those found in arteries. Veins in the limbs contain valves that prevent the backflow of blood. Veins and venules serve as the main blood re ...
Blood Cross matching Activity Guide Equipment: • 6 x Salad
... Our blood type depends on the presence of certain antigens on our red blood cells. These are substances that cause our immune system to produce antibodies. An antibody is a protein produced by the body’s immune system in response to a foreign substance such as a bacterium or virus. Each antibody is ...
... Our blood type depends on the presence of certain antigens on our red blood cells. These are substances that cause our immune system to produce antibodies. An antibody is a protein produced by the body’s immune system in response to a foreign substance such as a bacterium or virus. Each antibody is ...
Regional Vascular Systems
... Regional circulations The resting cardiac output is 5-6 litres per minute and this may be divided up between the various organs in the systemic circulation. Flow is determined by the pressure change divided by the resistance. From this we know can derive that the percentage of each organ blood flow ...
... Regional circulations The resting cardiac output is 5-6 litres per minute and this may be divided up between the various organs in the systemic circulation. Flow is determined by the pressure change divided by the resistance. From this we know can derive that the percentage of each organ blood flow ...
13 Renal Clearance overview
... The hypothalamus monitors the concentration of water in the plasma. If the plasma is too concentrated (high osmotic pressure), it means there are many electrolytes and not enough water inside the blood vessels (the person is dehydrated, and blood pressure will drop). Since water goes to the ar ...
... The hypothalamus monitors the concentration of water in the plasma. If the plasma is too concentrated (high osmotic pressure), it means there are many electrolytes and not enough water inside the blood vessels (the person is dehydrated, and blood pressure will drop). Since water goes to the ar ...
Complex Geometries and Higher Reynolds Numbers
... • Flow must be accompanied by a pressure gradient and hence the pressure must be lower at the outlet • The pressure and density are related through an ideal gas law of the form P = r/3 in this model • Densities at the input and output must be different • If the velocity boundaries on each end of the ...
... • Flow must be accompanied by a pressure gradient and hence the pressure must be lower at the outlet • The pressure and density are related through an ideal gas law of the form P = r/3 in this model • Densities at the input and output must be different • If the velocity boundaries on each end of the ...
Models of Cheyne-Stokes Respiration with Cardiovascular
... EXPIRATION OF CO2 TO THE ATMOSPHERE is removed from the lungs by breathing, at a rate proportional to the difference in partial pressures between the alveoli and the atmosphere, and proportional to the ventilation rate ...
... EXPIRATION OF CO2 TO THE ATMOSPHERE is removed from the lungs by breathing, at a rate proportional to the difference in partial pressures between the alveoli and the atmosphere, and proportional to the ventilation rate ...
BIO 202 Human Anatomy and Physiology II
... Anatomy laboratory Power Point Presentations Blackboard & other online tutorial/practice ...
... Anatomy laboratory Power Point Presentations Blackboard & other online tutorial/practice ...
BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
... middle muscle layer and a smooth lining. The difference between the two is that the muscle layer is much thicker in the artery than in the vein. The artery requires a thick muscular wall so that it can assist in pumping blood around the body. The vein is soft so that blood can be squeezed along it b ...
... middle muscle layer and a smooth lining. The difference between the two is that the muscle layer is much thicker in the artery than in the vein. The artery requires a thick muscular wall so that it can assist in pumping blood around the body. The vein is soft so that blood can be squeezed along it b ...
Human homeostasis
... For instance, heart failure may occur when negative feedback mechanisms become overwhelmed and destructive positive feedback mechanisms take over.[3] Other diseases which result from a homeostatic imbalance include diabetes, dehydration, hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia, gout and any disease caused by th ...
... For instance, heart failure may occur when negative feedback mechanisms become overwhelmed and destructive positive feedback mechanisms take over.[3] Other diseases which result from a homeostatic imbalance include diabetes, dehydration, hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia, gout and any disease caused by th ...
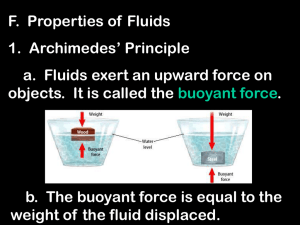
Fluid statics and dynamics
... perpendicular to the surface. The length of the cylinder above water is 2.0 cm. What is the cylinder’s mass density? ...
... perpendicular to the surface. The length of the cylinder above water is 2.0 cm. What is the cylinder’s mass density? ...
Effects Of Microgravity on the Circulatory System
... • Is felt when Standing and Sitting too fast • Baroreceptors are trying to re-adapt • When an astronaut returns to Earth and blood rushes to his/her legs, the vessels might respond not by constricting, to force the blood back up, but by dilating further resulting in less blood in the astronaut’s upp ...
... • Is felt when Standing and Sitting too fast • Baroreceptors are trying to re-adapt • When an astronaut returns to Earth and blood rushes to his/her legs, the vessels might respond not by constricting, to force the blood back up, but by dilating further resulting in less blood in the astronaut’s upp ...
Sample problems
... Problem 4 Water with density and dynamic viscosity flows down an inclined pipe with radius R. The flow is in steady state and fully developed. The angle between the pipe and the ground is 30. There is no axial (z-direction) pressure gradient. a) Write down the Navier-Stokes equation in the axia ...
... Problem 4 Water with density and dynamic viscosity flows down an inclined pipe with radius R. The flow is in steady state and fully developed. The angle between the pipe and the ground is 30. There is no axial (z-direction) pressure gradient. a) Write down the Navier-Stokes equation in the axia ...
Unit 8 Class Notes
... Angle of Impact: The angle at which a blood droplet strikes a surface. Parent Drop: The droplet from which a satellite spatter originates. Satellite Spatters: Small drops of blood that break of from the parent spatter when the blood droplet hits a surface. Spines: The pointed edges of a stain that r ...
... Angle of Impact: The angle at which a blood droplet strikes a surface. Parent Drop: The droplet from which a satellite spatter originates. Satellite Spatters: Small drops of blood that break of from the parent spatter when the blood droplet hits a surface. Spines: The pointed edges of a stain that r ...
States of Matter Part 3
... a. As the velocity of a fluid increases, the pressure exerted by the fluid decreases. lower pressure oncoming air ...
... a. As the velocity of a fluid increases, the pressure exerted by the fluid decreases. lower pressure oncoming air ...
19 - FacultyWeb Support Center
... Physiology of Circulation: Definition of Terms • Blood flow • Volume of blood flowing through a vessel, an organ, or the entire circulation in a given period • Measured as ml/min • Equivalent to cardiac output (CO) for entire vascular system • Relatively constant when at rest • Varies widely through ...
... Physiology of Circulation: Definition of Terms • Blood flow • Volume of blood flowing through a vessel, an organ, or the entire circulation in a given period • Measured as ml/min • Equivalent to cardiac output (CO) for entire vascular system • Relatively constant when at rest • Varies widely through ...
The Heart, Day 4 (Professor Powerpoint)
... ♦ Resistance of blood vessel walls • Small diameter = ↑ BP • Blood flow is proportional to the radius of the “pipe” ...
... ♦ Resistance of blood vessel walls • Small diameter = ↑ BP • Blood flow is proportional to the radius of the “pipe” ...
Fluid Friction in Pipes
... typically conveyed through pipelines, in which viscous action. Such friction is normally overcome either by means of the pressure generated by a pump or by the fluid falling under gravity from a higher to a lower elevation. In both cases it is necessary to know what flow rate or velocity can be ...
... typically conveyed through pipelines, in which viscous action. Such friction is normally overcome either by means of the pressure generated by a pump or by the fluid falling under gravity from a higher to a lower elevation. In both cases it is necessary to know what flow rate or velocity can be ...
Cardiovascular Physiology
... wall Blood moves through vessels because of blood pressure Measured by listening for Korotkoff sounds produced by turbulent flow in arteries as pressure released from blood pressure cuff ...
... wall Blood moves through vessels because of blood pressure Measured by listening for Korotkoff sounds produced by turbulent flow in arteries as pressure released from blood pressure cuff ...
Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology, 3rd
... 18. Osmotic pressure—Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration, with the aim of equalizing the solute concentrations on the two sides. Osmotic pressure is the pressure that needs to be applied to a solution to p ...
... 18. Osmotic pressure—Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration, with the aim of equalizing the solute concentrations on the two sides. Osmotic pressure is the pressure that needs to be applied to a solution to p ...
Hemodynamics

Hemodynamics or hæmodynamics (hemo- + -dynamics) is the fluid dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms, much as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. Hemodynamic response continuously monitors and adjusts to conditions in the body and its environment. Thus hemodynamics explains the physical laws that govern the flow of blood in the blood vessels. The relationships can be challenging because blood vessels are complex, with many ways for blood to enter and exit under changing conditions.