File
... • Delivery of O2 and nutrients to, and removal of wastes from, tissue cells • Gas exchange (lungs) • Absorption of nutrients (digestive tract) • Urine formation (kidneys) • Rate of flow is precisely the right amount to provide for proper function Velocity of Blood Flow • Changes as it travels throug ...
... • Delivery of O2 and nutrients to, and removal of wastes from, tissue cells • Gas exchange (lungs) • Absorption of nutrients (digestive tract) • Urine formation (kidneys) • Rate of flow is precisely the right amount to provide for proper function Velocity of Blood Flow • Changes as it travels throug ...
BDS Ist YEAR EXAMINATION 2008-09
... Note: 1. Attempt all questions and return this part of the question paper to the invigilator after 20 Minutes. 2. Please tick (√) correct one only. Cutting, overwriting or any other marking are not allowed. 3. For answering please use Ball- pen only. c) CO d) NO2 Q.1 Renal plasma flow can be measure ...
... Note: 1. Attempt all questions and return this part of the question paper to the invigilator after 20 Minutes. 2. Please tick (√) correct one only. Cutting, overwriting or any other marking are not allowed. 3. For answering please use Ball- pen only. c) CO d) NO2 Q.1 Renal plasma flow can be measure ...
MCAT Fluid dynamics
... 5:-Mechanics is concerned with motion of the bodies under the action of forces. 6:-When a body is moving with terminal velocity then it has zero acceleration. 7:-At terminal velocity fluid friction is maximum. 8:-At terminal velocity the net force acting on the body is zero. 9:-Terminal velocity of ...
... 5:-Mechanics is concerned with motion of the bodies under the action of forces. 6:-When a body is moving with terminal velocity then it has zero acceleration. 7:-At terminal velocity fluid friction is maximum. 8:-At terminal velocity the net force acting on the body is zero. 9:-Terminal velocity of ...
Bellwork - OnCourse
... quickly, I’ll use the quadratic equation. 2) I’m looking at a graph with one x-intercept, so it must be the graph of a linear equation? 3) I obtained -17 for the discriminant, so there are two imaginary solutions. 4) When I use the square root property to determine the length of a right triangles si ...
... quickly, I’ll use the quadratic equation. 2) I’m looking at a graph with one x-intercept, so it must be the graph of a linear equation? 3) I obtained -17 for the discriminant, so there are two imaginary solutions. 4) When I use the square root property to determine the length of a right triangles si ...
1-Acute Control of Local Blood Flow
... 1-By decrease vascularity : if the metabolism is decreased. 2-Formation of new vessels(angiogenesis): deficiency of tissue oxygen or other nutrients, leads to formation of the vascular growth factors (also called "angiogenic factors").They cause new vessels to sprout from other small vessels. So oxy ...
... 1-By decrease vascularity : if the metabolism is decreased. 2-Formation of new vessels(angiogenesis): deficiency of tissue oxygen or other nutrients, leads to formation of the vascular growth factors (also called "angiogenic factors").They cause new vessels to sprout from other small vessels. So oxy ...
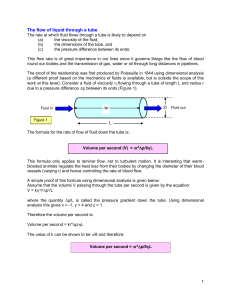
Flow of liquid through a tube
... The proof of the relationship was first produced by Poiseuille in 1844 using dimensional analysis (a different proof based on the mechanics of fluids is available, but is outside the scope of this work at this level). Consider a fluid of viscosity flowing through a tube of length L and radius r du ...
... The proof of the relationship was first produced by Poiseuille in 1844 using dimensional analysis (a different proof based on the mechanics of fluids is available, but is outside the scope of this work at this level). Consider a fluid of viscosity flowing through a tube of length L and radius r du ...
The Circulatory System
... • Arteries – carry oxygenated blood to the body • Veins – carry unoxygenated blood to the lungs • Capillaries – where O2 and CO2 change; connect arteries to veins. ...
... • Arteries – carry oxygenated blood to the body • Veins – carry unoxygenated blood to the lungs • Capillaries – where O2 and CO2 change; connect arteries to veins. ...
Arterial blood pressure
... Factors that determine the blood pressure: 1- Cardiac output (CO). 2- Total peripheral resistance (PR). 3- Elasticity of the aorta and large arteries. 4- Blood volume and circulatory capacity. ...
... Factors that determine the blood pressure: 1- Cardiac output (CO). 2- Total peripheral resistance (PR). 3- Elasticity of the aorta and large arteries. 4- Blood volume and circulatory capacity. ...
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21
... - Short Term (aimed at ↑BP and ↑flow: blood flow to brain kept constant while other systems adjust, can compensate for ~20% blood loss) 1. ↑C.O., trigger peripheral vasoconstriction to ↑BP 2. Venoconstrict to mobilize venous reserve to ↑blood volume 3. Release NE, ADH, Angiotensin II to ↑BP ...
... - Short Term (aimed at ↑BP and ↑flow: blood flow to brain kept constant while other systems adjust, can compensate for ~20% blood loss) 1. ↑C.O., trigger peripheral vasoconstriction to ↑BP 2. Venoconstrict to mobilize venous reserve to ↑blood volume 3. Release NE, ADH, Angiotensin II to ↑BP ...
THE PHYSIOLOGICAL PRINCIPLE OF MINIMUMI WORK. I. THE
... No one can escape the impression of a physiological determinism as exemplified by the narrowness of the "physiological range;" but the hypothesis of the constancy of the internal environment, being in effect a denial of adaptive change, holds out no hope whatever of interpreting quantitatively the p ...
... No one can escape the impression of a physiological determinism as exemplified by the narrowness of the "physiological range;" but the hypothesis of the constancy of the internal environment, being in effect a denial of adaptive change, holds out no hope whatever of interpreting quantitatively the p ...
Blood Pressure Controls
... Physical Chemistry States that for a fluid-filled rigid system there is a reciprocal relationship between pressure and volume: if the volume decreases, pressure increases if volume increases, pressure decreases: P1V1 = P2V2. So, it should be possible to decrease blood pressure by increasing the vol ...
... Physical Chemistry States that for a fluid-filled rigid system there is a reciprocal relationship between pressure and volume: if the volume decreases, pressure increases if volume increases, pressure decreases: P1V1 = P2V2. So, it should be possible to decrease blood pressure by increasing the vol ...
7- Introduction and functional anatomy of vascular physiology
... 3- Capillaries: The arterioles divide into smaller muscle-walled vessels called metarterioles and these in turn feed into capillaries. The openings of the capillaries are surrounded by minute smooth muscle (precapillary sphincters). The capillaries are thin-walled structures which are about 1 μm thi ...
... 3- Capillaries: The arterioles divide into smaller muscle-walled vessels called metarterioles and these in turn feed into capillaries. The openings of the capillaries are surrounded by minute smooth muscle (precapillary sphincters). The capillaries are thin-walled structures which are about 1 μm thi ...
The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels
... Flow, Pressure, and Resistance Blood flow (F) is directly proportional to the difference in blood pressure (P) between two points in the circulation and inversely proportional to the peripheral resistance (R) in the systemic flow. Therefore: F = DP R ...
... Flow, Pressure, and Resistance Blood flow (F) is directly proportional to the difference in blood pressure (P) between two points in the circulation and inversely proportional to the peripheral resistance (R) in the systemic flow. Therefore: F = DP R ...
Physiology of blood system. Red blood cells. Respiratory pigments
... takes place in the cells of the reticuloendothelian tissues, especially those in the spleen, the liver, and the bone marrow. ...
... takes place in the cells of the reticuloendothelian tissues, especially those in the spleen, the liver, and the bone marrow. ...
Lecture 12. Physiology of blood system. Red blood cells.Respiratory
... takes place in the cells of the reticuloendothelian tissues, especially those in the spleen, the liver, and the bone marrow. ...
... takes place in the cells of the reticuloendothelian tissues, especially those in the spleen, the liver, and the bone marrow. ...
Function of plasma proteins
... proteins play a special role in providing the body with immunity. 5- Fibrinogen other plasma proteins are concerned with blood clotting ...
... proteins play a special role in providing the body with immunity. 5- Fibrinogen other plasma proteins are concerned with blood clotting ...
Cardiovascular Dynamics, part 1 File
... Physiology of Circulation: Definition of Terms • Blood flow – Volume of blood flowing through a vessel, an organ, or the entire circulation in a given period • Measured as ml/min • Equivalent to cardiac output (CO) for entire vascular system • Relatively constant when at rest • Varies widely throug ...
... Physiology of Circulation: Definition of Terms • Blood flow – Volume of blood flowing through a vessel, an organ, or the entire circulation in a given period • Measured as ml/min • Equivalent to cardiac output (CO) for entire vascular system • Relatively constant when at rest • Varies widely throug ...
Blood Vessels
... • Blood flow (ml/min) – Amount of blood moving at a given time – Equivalent to cardiac output (CO) – Constant at rest; varies w/organ needs ...
... • Blood flow (ml/min) – Amount of blood moving at a given time – Equivalent to cardiac output (CO) – Constant at rest; varies w/organ needs ...
PP Chapter 19-Blood Vessels
... Blood will pass through either: – Metarteriole straight through to the venule via a thoroughfare channel (shunt) – True capillaries to outer tissue areas ...
... Blood will pass through either: – Metarteriole straight through to the venule via a thoroughfare channel (shunt) – True capillaries to outer tissue areas ...
File
... 3) List and describe the protective structures found in the CNS. 4) Describe the pathway of light through the eyeball and the process of light refraction. 5) Explain the meaning of an "odor snapshot" and its relevance to human beings. 6) Discuss the age-related disorders presbyopia and presbycusis. ...
... 3) List and describe the protective structures found in the CNS. 4) Describe the pathway of light through the eyeball and the process of light refraction. 5) Explain the meaning of an "odor snapshot" and its relevance to human beings. 6) Discuss the age-related disorders presbyopia and presbycusis. ...
Hematologic System
... • Blood makes up about 7% of body weight (about 5.6 liters in a 72 Kg man). This proportion is less in women, while in children is greater (gradually decreasing until the adult level is reached). ...
... • Blood makes up about 7% of body weight (about 5.6 liters in a 72 Kg man). This proportion is less in women, while in children is greater (gradually decreasing until the adult level is reached). ...
circ and homeo
... • The transport medium in this system is blood which is pumped throughout an organism through a closed circuit of blood vessels. • This closed system keeps blood contained as it passes through various “circulations” of the body. ...
... • The transport medium in this system is blood which is pumped throughout an organism through a closed circuit of blood vessels. • This closed system keeps blood contained as it passes through various “circulations” of the body. ...
2-Arterial Blood pressure
... The arterial blood flow is pulsatile in character (due to cardiac ejection) and become steady in the capillaries because of large surface area so the exchange of diffusible substance occur between blood and tissue. *The heart is an extremely complication pump. *The blood vessels are multi branched e ...
... The arterial blood flow is pulsatile in character (due to cardiac ejection) and become steady in the capillaries because of large surface area so the exchange of diffusible substance occur between blood and tissue. *The heart is an extremely complication pump. *The blood vessels are multi branched e ...
Circulatory System as a Circuit
... Of course, to get any farther, we need to determine what Rk is, and we will do this by arguing what Lk and ak are: i.e., the length and radius of the vessels, respectively. (f) Assume that the blood in one vessel is approximately destined for all locations in the body which are within a distance of ...
... Of course, to get any farther, we need to determine what Rk is, and we will do this by arguing what Lk and ak are: i.e., the length and radius of the vessels, respectively. (f) Assume that the blood in one vessel is approximately destined for all locations in the body which are within a distance of ...
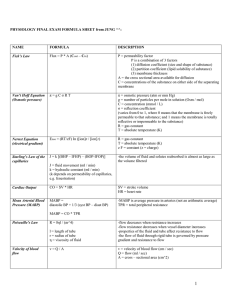
Cumulative Formula Sheet
... Q = flow (ml / min) ∆P = pressure difference (mm Hg) R = resistance (mm Hg / ml / min) Reynold’s number ...
... Q = flow (ml / min) ∆P = pressure difference (mm Hg) R = resistance (mm Hg / ml / min) Reynold’s number ...
Hemodynamics

Hemodynamics or hæmodynamics (hemo- + -dynamics) is the fluid dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms, much as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. Hemodynamic response continuously monitors and adjusts to conditions in the body and its environment. Thus hemodynamics explains the physical laws that govern the flow of blood in the blood vessels. The relationships can be challenging because blood vessels are complex, with many ways for blood to enter and exit under changing conditions.