Secretion
... • The juxtaglomerular cells are cells that synthesize, store, and secrete the enzyme renin. • Specialized smooth muscle cells in the wall of the afferent arteriole that are in contact with distal tubule. • Have mechano-receptors for blood pressure • The macula densa is an area of closely packed spec ...
... • The juxtaglomerular cells are cells that synthesize, store, and secrete the enzyme renin. • Specialized smooth muscle cells in the wall of the afferent arteriole that are in contact with distal tubule. • Have mechano-receptors for blood pressure • The macula densa is an area of closely packed spec ...
A quick summary: The skeletal system is made up of
... through the lungs by way of the circulation. The waste products combine with the blood (after the blood has delivered its load of oxygen) and then this blood is pumped back to the lungs. As mentioned previously, at that point, these waste products move from the blood into the alveoli and they are re ...
... through the lungs by way of the circulation. The waste products combine with the blood (after the blood has delivered its load of oxygen) and then this blood is pumped back to the lungs. As mentioned previously, at that point, these waste products move from the blood into the alveoli and they are re ...
Fundamentals II
... Cyanosis - bluish tinge caused by decrease in O2 in RBC. Cyanosis is assessed by checking the mucous membranes of the conjunctiva (lower eyelids), under the tongue and inside the mouth..should be pink not pale or bluish ...
... Cyanosis - bluish tinge caused by decrease in O2 in RBC. Cyanosis is assessed by checking the mucous membranes of the conjunctiva (lower eyelids), under the tongue and inside the mouth..should be pink not pale or bluish ...
PowerPoint Notes for Blood Vessels
... and cohesive with a high resistance to flow. Increased pressure is required to move a viscous substance. Normally, blood viscosity remains fairly constant as plasma and formed elements remain within normal ranges. ...
... and cohesive with a high resistance to flow. Increased pressure is required to move a viscous substance. Normally, blood viscosity remains fairly constant as plasma and formed elements remain within normal ranges. ...
Circulatory system I: Blood Circulatory system I: Blood
... • Flow of blood depends on pressure difference at both ends of the blood vessels • Change in pressure (ΔP) = P1-P2 = 100-0 = 100mm Hg • Blood flow – directly proportional to ΔP – inversely proportional to frictional resistance – resistance depends on: • 1. Length of the vessel • 2. Viscosity of bloo ...
... • Flow of blood depends on pressure difference at both ends of the blood vessels • Change in pressure (ΔP) = P1-P2 = 100-0 = 100mm Hg • Blood flow – directly proportional to ΔP – inversely proportional to frictional resistance – resistance depends on: • 1. Length of the vessel • 2. Viscosity of bloo ...
Physiology en
... 6. The students will sit down and breathe naturally. Check that the stopwatch is reset. After regular exhalation the students will hold his breath, and the instructor will press the "start" button on the stopwatch at the same time. Each student should make an effort and continue to hold his/her brea ...
... 6. The students will sit down and breathe naturally. Check that the stopwatch is reset. After regular exhalation the students will hold his breath, and the instructor will press the "start" button on the stopwatch at the same time. Each student should make an effort and continue to hold his/her brea ...
Unit Four Essential Questions
... quickly depleted, causing muscles to remain contracted. It can take 10 minutes to hours to occur, with maximum stiffness 12-24 hours after death. Eventually tissue decays and lysosomal enzymes leak and cause muscles to relax. ...
... quickly depleted, causing muscles to remain contracted. It can take 10 minutes to hours to occur, with maximum stiffness 12-24 hours after death. Eventually tissue decays and lysosomal enzymes leak and cause muscles to relax. ...
derived along a fluid flow streamline is often called the
... and was one of the many prominent mathematicians in the Bernoulli family. He is particularly remembered for his applications of mathematics to mechanics, especially fluid mechanics, and for his pioneering work in probability and statistics. Bernoulli's work is still studied at length by many schools ...
... and was one of the many prominent mathematicians in the Bernoulli family. He is particularly remembered for his applications of mathematics to mechanics, especially fluid mechanics, and for his pioneering work in probability and statistics. Bernoulli's work is still studied at length by many schools ...
Bernoulli - Cloudfront.net
... • To accelerate a fluid as it goes into the constriction, the pushing force in the large diameter area must be greater than the pushing force in the constriction. At point B, the pushing force in the x direction ...
... • To accelerate a fluid as it goes into the constriction, the pushing force in the large diameter area must be greater than the pushing force in the constriction. At point B, the pushing force in the x direction ...
Instructor`s Answer Key Chapter 16: Respiratory Physiology
... part of the compensatory response, the levels of hemoglobin concentration also increase at high elevation, as does the number of red blood cells (rise in hematocrit). However on the negative side, polycythemia leads to increases the viscosity of blood, which can lead to pulmonary hypertension, ventr ...
... part of the compensatory response, the levels of hemoglobin concentration also increase at high elevation, as does the number of red blood cells (rise in hematocrit). However on the negative side, polycythemia leads to increases the viscosity of blood, which can lead to pulmonary hypertension, ventr ...
Exercise and High Blood Pressure
... Start slowly. If you haven't exercised much lately, try walking at a relaxed pace for 20 minutes. Exercise at least three times each week. Warm up by walking slowly or stretching for five minutes, then exercise for 25 to 30 minutes and cool down with five more minutes of light activity. Aim for your ...
... Start slowly. If you haven't exercised much lately, try walking at a relaxed pace for 20 minutes. Exercise at least three times each week. Warm up by walking slowly or stretching for five minutes, then exercise for 25 to 30 minutes and cool down with five more minutes of light activity. Aim for your ...
CfE Higher Human Biology Unit 2 Physiology and Health
... that those affected have high levels of cholesterol in their blood. I can identify issues created with elevated blood glucose levels, including damage to the retina, renal failure or peripheral nerve problems. I can describe the regulation of blood glucose levels through the hormones insulin and glu ...
... that those affected have high levels of cholesterol in their blood. I can identify issues created with elevated blood glucose levels, including damage to the retina, renal failure or peripheral nerve problems. I can describe the regulation of blood glucose levels through the hormones insulin and glu ...
MMV211, March 9, 2005 P1. The figure below shows a vane with a
... and outlet are equal, it follows from the Bernoulli equation along a streamline that the (absolute) fluid velocities at section 1 and 2 are equal as well, V2 = V1 = V − U. Mass flow rate, ṁ = ρA(V − U), i.e., ...
... and outlet are equal, it follows from the Bernoulli equation along a streamline that the (absolute) fluid velocities at section 1 and 2 are equal as well, V2 = V1 = V − U. Mass flow rate, ṁ = ρA(V − U), i.e., ...
Management of Spontaneous ICH
... Hold VKA, give IV vit K, correct INR (I,C) PCCs are faster and fewer side effects (IIb, B) rFVIIa not recommended (III, C) ...
... Hold VKA, give IV vit K, correct INR (I,C) PCCs are faster and fewer side effects (IIb, B) rFVIIa not recommended (III, C) ...
Tripura Bojjawar BIEN 501 Physiological
... d) None of the above Q7)The equation below represents momentum flux distribution for steady incompressible flow in an annulus When κ is made zero it reduces to Trz = (((P0 – Pl)R)/2L) [(r/R)-((1- κ²)/(2ln(1/ κ))(R/r)] a) equation of flow for a falling film b) equation of flow for a circular tube c) ...
... d) None of the above Q7)The equation below represents momentum flux distribution for steady incompressible flow in an annulus When κ is made zero it reduces to Trz = (((P0 – Pl)R)/2L) [(r/R)-((1- κ²)/(2ln(1/ κ))(R/r)] a) equation of flow for a falling film b) equation of flow for a circular tube c) ...
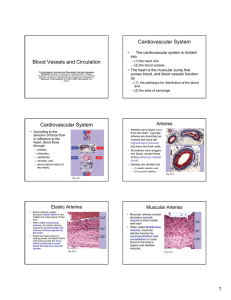
Cardiovascular System Part 2
... layer, squamous epithelium surrounded by connective tissue membrane • tunica media: middle layer, smooth muscle, provides support and ability to regulate blood flow ...
... layer, squamous epithelium surrounded by connective tissue membrane • tunica media: middle layer, smooth muscle, provides support and ability to regulate blood flow ...
Edema, Hyperemia and Congestion
... Exudate: extravascular fluid collection that is rich in protein and/or cells. Fluid appears grossly cloudy. Transudate: extravascular fluid collection that is basically an ultrafiltrate of plasma with little protein and few or no cells. Fluid ...
... Exudate: extravascular fluid collection that is rich in protein and/or cells. Fluid appears grossly cloudy. Transudate: extravascular fluid collection that is basically an ultrafiltrate of plasma with little protein and few or no cells. Fluid ...
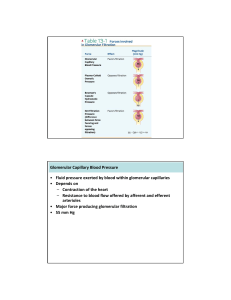
Lecture 16: The Nephron
... 1. Discuss results of each GROUP in 5 graphs that display the AVERAGE values for EACH GROUP collected during the lab. 2. Clearly connect each group’s data to exactly what is happening in the kidney. Tie in as many aspects of kidney function as you can. Your answers should refer to the graphs as ev ...
... 1. Discuss results of each GROUP in 5 graphs that display the AVERAGE values for EACH GROUP collected during the lab. 2. Clearly connect each group’s data to exactly what is happening in the kidney. Tie in as many aspects of kidney function as you can. Your answers should refer to the graphs as ev ...
Slide 1
... MAP – Mean Arterial Pressure = Average effective pressure driving blood flow through the systemic organs ...
... MAP – Mean Arterial Pressure = Average effective pressure driving blood flow through the systemic organs ...
Chapter-9 The Behavior of Fluids
... gave him the means to solve the problem. He was so excited that he ran naked through the streets of Syracuse shouting "Eureka! eureka!" (I have found it!). The fraudulent goldsmith was brought to justice. ...
... gave him the means to solve the problem. He was so excited that he ran naked through the streets of Syracuse shouting "Eureka! eureka!" (I have found it!). The fraudulent goldsmith was brought to justice. ...
29 - Kentucky Department of Education
... Blood flow – the volume of blood flowing through a vessel Pressure – force per unit area exerted against a vessel containing blood (mm Hg.) Resistance – opposition to flow as the blood passes through the vessels (viscosity, length and diameter) ...
... Blood flow – the volume of blood flowing through a vessel Pressure – force per unit area exerted against a vessel containing blood (mm Hg.) Resistance – opposition to flow as the blood passes through the vessels (viscosity, length and diameter) ...
File
... Plasma and Tissue fluid Plasma is a watery yellow fluid containing dissolved substances such as glucose, amino acids, blood cells, platelets and plasma proteins Blood arriving at the arteriole end of a capillary bed is at a higher pressure than blood in the capillaries As blood is forced into the ...
... Plasma and Tissue fluid Plasma is a watery yellow fluid containing dissolved substances such as glucose, amino acids, blood cells, platelets and plasma proteins Blood arriving at the arteriole end of a capillary bed is at a higher pressure than blood in the capillaries As blood is forced into the ...
Hemodynamics

Hemodynamics or hæmodynamics (hemo- + -dynamics) is the fluid dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms, much as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. Hemodynamic response continuously monitors and adjusts to conditions in the body and its environment. Thus hemodynamics explains the physical laws that govern the flow of blood in the blood vessels. The relationships can be challenging because blood vessels are complex, with many ways for blood to enter and exit under changing conditions.