Chapter 2 - CP Physics
... Application – Vascular Flutter • The artery is constricted as a result of accumulated plaque on its inner walls • To maintain a constant flow rate, the blood must travel faster than normal • If the speed is high enough, the blood pressure is low and the artery may collapse Section 9.8 ...
... Application – Vascular Flutter • The artery is constricted as a result of accumulated plaque on its inner walls • To maintain a constant flow rate, the blood must travel faster than normal • If the speed is high enough, the blood pressure is low and the artery may collapse Section 9.8 ...
PAC01 Pulmonary Physiology
... The oxygen saturation curve is NOT a linear relationship. It represents the percent saturation as compared to partial pressure. We have the PO2 100= 97.5% saturation. At PO2 40 (veins), we get 75% saturation (15ml of O2). The AV O2 difference is the difference in mL between venous and arterial blood ...
... The oxygen saturation curve is NOT a linear relationship. It represents the percent saturation as compared to partial pressure. We have the PO2 100= 97.5% saturation. At PO2 40 (veins), we get 75% saturation (15ml of O2). The AV O2 difference is the difference in mL between venous and arterial blood ...
The formation of urine
... pass through the walls of the glomerulus into the Bowman’s capsule moving from highlow pressure • The following are too large to move through the walls of the glomerulus: plasma proteins, erythrocytes, platelets ...
... pass through the walls of the glomerulus into the Bowman’s capsule moving from highlow pressure • The following are too large to move through the walls of the glomerulus: plasma proteins, erythrocytes, platelets ...
Regulation of Water
... Primary Active Transport • From there it moves to peritubular capillaries due to: – Low hydrostatic pressure – High osmotic pressure of the blood ...
... Primary Active Transport • From there it moves to peritubular capillaries due to: – Low hydrostatic pressure – High osmotic pressure of the blood ...
Flume handout
... Lab demonstration: flow of water at the seafloor Animals and plants continually interact with the living and non-living features of their surroundings. In benthic ecology, water flow is an especially important part of the physical environment. Due to physical properties of fluids in contact with ‘so ...
... Lab demonstration: flow of water at the seafloor Animals and plants continually interact with the living and non-living features of their surroundings. In benthic ecology, water flow is an especially important part of the physical environment. Due to physical properties of fluids in contact with ‘so ...
Urine Concentration and Dilution
... Vasa recta branches off the efferent arteriole and surround the loop of Henley in its entirety. It provides blood flow to the medulla and papilla. Vasa recta is a capillary blood system and as such the exchange taking place across the membranes is purely passive. The other purpose of the vasa recta ...
... Vasa recta branches off the efferent arteriole and surround the loop of Henley in its entirety. It provides blood flow to the medulla and papilla. Vasa recta is a capillary blood system and as such the exchange taking place across the membranes is purely passive. The other purpose of the vasa recta ...
Introduction to the cardiovascular system
... veins. Pressure is a measure of the force that the blood exerts against the vessel walls as it moves the blood through the vessels. Like all fluids, blood flows from a high pressure area to a region with lower pressure. Blood flows in the same direction as the decreasing pressure gradient: arteries ...
... veins. Pressure is a measure of the force that the blood exerts against the vessel walls as it moves the blood through the vessels. Like all fluids, blood flows from a high pressure area to a region with lower pressure. Blood flows in the same direction as the decreasing pressure gradient: arteries ...
Transvascular and Intrastitial Transport File
... Vascular permeability • Capacity of a blood vessel wall to allow for the flow of small molecules (ions, water, nutrients) or even whole cells (lymphocytes on their way to the site of inflammation) in and out of the vessel. • Flux across membrane J=P*S*∆C – J= rate of mass flow kg/s (not kg/m2*s) – ...
... Vascular permeability • Capacity of a blood vessel wall to allow for the flow of small molecules (ions, water, nutrients) or even whole cells (lymphocytes on their way to the site of inflammation) in and out of the vessel. • Flux across membrane J=P*S*∆C – J= rate of mass flow kg/s (not kg/m2*s) – ...
Renal Physiology
... Fluid Processing in the Kidneys 180 liters of blood fluid processes each day 1.5 liters of urine produced each day ...
... Fluid Processing in the Kidneys 180 liters of blood fluid processes each day 1.5 liters of urine produced each day ...
Capillaries and Exchange of Materials
... Plasma and Tissue fluid Plasma is a watery yellow fluid containing dissolved substances such as glucose, amino acids, blood cells, platelets and plasma proteins Blood arriving at the arteriole end of a capillary bed is at a higher pressure than blood in the capillaries As blood is forced into the ...
... Plasma and Tissue fluid Plasma is a watery yellow fluid containing dissolved substances such as glucose, amino acids, blood cells, platelets and plasma proteins Blood arriving at the arteriole end of a capillary bed is at a higher pressure than blood in the capillaries As blood is forced into the ...
sugar
... involved in below are low, answer the following questions. I-1 (1.0 point) What is the unit of C ? (in terms of SI units:kg, s, m.) I-2 (1.5 points) Following problem I-1, consider a dust particle of radius, R = 3.0×10-6 m, falls in air at 20°C. The numerical value of C for this particle in the air ...
... involved in below are low, answer the following questions. I-1 (1.0 point) What is the unit of C ? (in terms of SI units:kg, s, m.) I-2 (1.5 points) Following problem I-1, consider a dust particle of radius, R = 3.0×10-6 m, falls in air at 20°C. The numerical value of C for this particle in the air ...
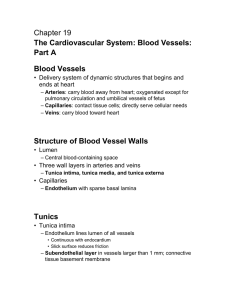
Blood Vessels
... Blood Vessels • Delivery system of dynamic structures that begins and ends at heart – Arteries: carry blood away from heart; oxygenated except for pulmonary circulation and umbilical vessels of fetus – Capillaries: contact tissue cells; directly serve cellular needs – Veins: carry blood toward heart ...
... Blood Vessels • Delivery system of dynamic structures that begins and ends at heart – Arteries: carry blood away from heart; oxygenated except for pulmonary circulation and umbilical vessels of fetus – Capillaries: contact tissue cells; directly serve cellular needs – Veins: carry blood toward heart ...
Physics 2053C – Fall 2001
... F = P x A = (1.20x105 N/m2)(20.0 m)(11.60 m) = 2.79x107 N 3. What will be the pressure against the side of the pool near the bottom? The pressure near the bottom is the same as on the bottom P = 1.20x105 N/m2 ...
... F = P x A = (1.20x105 N/m2)(20.0 m)(11.60 m) = 2.79x107 N 3. What will be the pressure against the side of the pool near the bottom? The pressure near the bottom is the same as on the bottom P = 1.20x105 N/m2 ...
Which of the following is an example of a positive feedback loop
... During a race, the body temperature of a runner increases. The runner responds by perspiring, which lowers body temperature. This process is an example of ...
... During a race, the body temperature of a runner increases. The runner responds by perspiring, which lowers body temperature. This process is an example of ...
Pulse
... Pulse rate is the number of pulsations felt in a minute. Pulse usually = diastolic pressure ...
... Pulse rate is the number of pulsations felt in a minute. Pulse usually = diastolic pressure ...
changes in oxygen delivery to muscle during exercise
... For example, during low-intensity exercise, a relatively small number of motor units will be recruited into action resulting in a relatively small demand for blood flow to these active muscle fibers. In contrast. high-intensity exercise would result in the recruitment of a large number of motor ...
... For example, during low-intensity exercise, a relatively small number of motor units will be recruited into action resulting in a relatively small demand for blood flow to these active muscle fibers. In contrast. high-intensity exercise would result in the recruitment of a large number of motor ...
Movement of Fluids and Electrolytes
... A dynamic relationship exists between the extracellular and intracellular fluid compartments. This relationship maintains cellular homeostasis through the exchange of fluids and electrolytes. The compartments are kept separate by the structural and functional integrity of cell membranes. Both passiv ...
... A dynamic relationship exists between the extracellular and intracellular fluid compartments. This relationship maintains cellular homeostasis through the exchange of fluids and electrolytes. The compartments are kept separate by the structural and functional integrity of cell membranes. Both passiv ...
A Preliminary Investigation into Retrospective Calculation of In
... • Alfazil and Anderson, JAT, 32:511; 2008 – Loss of 19.9% of cocaine in dried blood spots on filter paper in one month at room temperature – blood matrix was prepared by diluting packed cells with isotonic saline ...
... • Alfazil and Anderson, JAT, 32:511; 2008 – Loss of 19.9% of cocaine in dried blood spots on filter paper in one month at room temperature – blood matrix was prepared by diluting packed cells with isotonic saline ...
Modeling Your Circulatory System
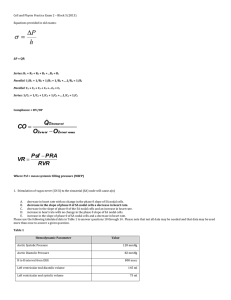
... He found that the flow rate of a fluid undergoing laminar flow in a cylindrical tube is: Flow Rate = π * pressure * (radius)4 / (8 * viscosity* length) ...
... He found that the flow rate of a fluid undergoing laminar flow in a cylindrical tube is: Flow Rate = π * pressure * (radius)4 / (8 * viscosity* length) ...
Blood - El Camino College
... D. Blood ______ - watery portion of blood, composes 55% of blood; consists of about 90% ______ and 10% solutes. _______ include: 1. Plasma __________ - 7% of solutes; 3 major types produced by the ________ are: a. ___________ (60%) - small protein that makes blood viscous to maintain blood _________ ...
... D. Blood ______ - watery portion of blood, composes 55% of blood; consists of about 90% ______ and 10% solutes. _______ include: 1. Plasma __________ - 7% of solutes; 3 major types produced by the ________ are: a. ___________ (60%) - small protein that makes blood viscous to maintain blood _________ ...
D - VCOMcc
... A. Autoregulation becomes impaired at low cerebral arterial pressures. B. Increased NO production by perivascular glial cells increases the local effects of chronic cerebral hypertension. C. The autoregulatory range is adjusted downward by VSM atrophy. D. The autoregulatory range is adjusted downwar ...
... A. Autoregulation becomes impaired at low cerebral arterial pressures. B. Increased NO production by perivascular glial cells increases the local effects of chronic cerebral hypertension. C. The autoregulatory range is adjusted downward by VSM atrophy. D. The autoregulatory range is adjusted downwar ...
MS Word
... Here is an engineer's sketch of the blood circulation system of a human body. The circulatory system can be thought of as a closed-loop circulation system with two pumps. One-way valves keep the flow uni-directional through the pumps. The pressures are indicated in mm of Hg where 1 atmosphere of pre ...
... Here is an engineer's sketch of the blood circulation system of a human body. The circulatory system can be thought of as a closed-loop circulation system with two pumps. One-way valves keep the flow uni-directional through the pumps. The pressures are indicated in mm of Hg where 1 atmosphere of pre ...
ENT 211 Week 1 - Introduction to Thermal-Fluid
... Blood plasma shows viscosity only, while whole blood shows viscous and elastic. Viscosity - Energy dissipated during flow due to sliding and deformation of red blood cell and its ...
... Blood plasma shows viscosity only, while whole blood shows viscous and elastic. Viscosity - Energy dissipated during flow due to sliding and deformation of red blood cell and its ...
Gastrointestinal Bleeding - Western Maryland Health System
... Nuclear Medicine Nuclear medicine, gastrointestinal blood loss imaging tagged red blood cell scan Ultrasonography Ultrasound, abdomen ...
... Nuclear Medicine Nuclear medicine, gastrointestinal blood loss imaging tagged red blood cell scan Ultrasonography Ultrasound, abdomen ...
Hemodynamics

Hemodynamics or hæmodynamics (hemo- + -dynamics) is the fluid dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms, much as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. Hemodynamic response continuously monitors and adjusts to conditions in the body and its environment. Thus hemodynamics explains the physical laws that govern the flow of blood in the blood vessels. The relationships can be challenging because blood vessels are complex, with many ways for blood to enter and exit under changing conditions.