GLU in urine
... 1- one of them : First, it triggers dilation of the renal afferent arteriole, decreasing afferent arteriole resistance and, thus, offsetting the decrease in glomerular hydrostatic pressure caused by the drop in blood pressure. ,, Second, macula densa cells release prostaglandins, which triggers gran ...
... 1- one of them : First, it triggers dilation of the renal afferent arteriole, decreasing afferent arteriole resistance and, thus, offsetting the decrease in glomerular hydrostatic pressure caused by the drop in blood pressure. ,, Second, macula densa cells release prostaglandins, which triggers gran ...
Unit 8 * Organism Regulation, Physiology and Development
... – Ex: Response to toxins • interferes with specific metabolic pathways or cause cell damage ...
... – Ex: Response to toxins • interferes with specific metabolic pathways or cause cell damage ...
Homeostasis
... – Ex: Response to toxins • interferes with specific metabolic pathways or cause cell damage ...
... – Ex: Response to toxins • interferes with specific metabolic pathways or cause cell damage ...
Exam2 - Purdue Engineering
... without circulation. If sufficient circulation is a added to make the max velocity 3 times free stream, the lift coefficient would be closest to a. 0 b. 2 c. 4 d. 6 e. 8 7) In a two-D laminar Channel flow (Poiseuille flow), the velocity in the x direction is given by u=3*y*(2-y). The upper wall (at ...
... without circulation. If sufficient circulation is a added to make the max velocity 3 times free stream, the lift coefficient would be closest to a. 0 b. 2 c. 4 d. 6 e. 8 7) In a two-D laminar Channel flow (Poiseuille flow), the velocity in the x direction is given by u=3*y*(2-y). The upper wall (at ...
unit 8 - blood / lymphatic / cardiovascular systems
... The largest artery in the body extends from the left ventricle and is called the _______________. The first branch feeds the myocardium with blood and are the ___________________________. The next branch ________________________________________takes blood into the right arm and the right side of the ...
... The largest artery in the body extends from the left ventricle and is called the _______________. The first branch feeds the myocardium with blood and are the ___________________________. The next branch ________________________________________takes blood into the right arm and the right side of the ...
Solids and Fluids
... depend on the density of 1) helium 2) air or 3) the weight of the rubber skin? Compute the magnitude of the buoyant force on the balloon. ρair = 1.29 kg/m3 and ρHe = 0.18 kg/m3. If the rubber skin of the balloon has mass of 1.2 kg, find the balloon’s initial acceleration when released if it carr ...
... depend on the density of 1) helium 2) air or 3) the weight of the rubber skin? Compute the magnitude of the buoyant force on the balloon. ρair = 1.29 kg/m3 and ρHe = 0.18 kg/m3. If the rubber skin of the balloon has mass of 1.2 kg, find the balloon’s initial acceleration when released if it carr ...
Blood Vessels
... • Blood flow • Volume of blood flowing through a vessel, an organ, or the entire circulation in a given period • Measured as ml/min • Equivalent to cardiac output (CO) for entire vascular system • Relatively constant when at rest • Varies widely through individual organs, based on needs ...
... • Blood flow • Volume of blood flowing through a vessel, an organ, or the entire circulation in a given period • Measured as ml/min • Equivalent to cardiac output (CO) for entire vascular system • Relatively constant when at rest • Varies widely through individual organs, based on needs ...
Diastolic pressure
... Pressure and Resistance • An Overview of Cardiovascular Pressures • Systolic pressure • Peak arterial pressure during ventricular systole ...
... Pressure and Resistance • An Overview of Cardiovascular Pressures • Systolic pressure • Peak arterial pressure during ventricular systole ...
07 Blood Press Vital Sign LQ
... Mean arterial pressure (MAP) is not a simple average of the two pressures, because the duration of diastole is twice that of systole. MAP is used by emergency room and intensive care unit personnel as a measure of the adequacy of blood supplied to vital tissues (such as the brain, heart, and kidneys ...
... Mean arterial pressure (MAP) is not a simple average of the two pressures, because the duration of diastole is twice that of systole. MAP is used by emergency room and intensive care unit personnel as a measure of the adequacy of blood supplied to vital tissues (such as the brain, heart, and kidneys ...
Sample Paper
... (a) The centerline velocity increases monotonically with the streamwise coordinate (b) The developing length increases as the Reynolds number increases provided that the flow remains laminar (c) The developing length reduces if the flow transits to turbulence (d) The pressure gradient in the develop ...
... (a) The centerline velocity increases monotonically with the streamwise coordinate (b) The developing length increases as the Reynolds number increases provided that the flow remains laminar (c) The developing length reduces if the flow transits to turbulence (d) The pressure gradient in the develop ...
Hydraulic Systems- Questions
... 4. Hydraulic systems work due to the pressure of liquids. 5. Pressure in liquids is transmitted along a continuous and enclosed system until something moves or bulges. 6. The balloon bulger is an example of a simple hydraulic system. 7. Hydraulics work because liquids exert pressure. 8. In a hydraul ...
... 4. Hydraulic systems work due to the pressure of liquids. 5. Pressure in liquids is transmitted along a continuous and enclosed system until something moves or bulges. 6. The balloon bulger is an example of a simple hydraulic system. 7. Hydraulics work because liquids exert pressure. 8. In a hydraul ...
13/mhso2/015 course code: phs212 physiology of
... mercury) with the ischiocavernosus muscles (rigid –erection phase) The angle of the erect penis is determined by its size and its attachment to the puboischial rami (the crura) and the anterior surface of the pubic bone (the suspensory and funiform ligaments). In the men with a long heavy penis or a ...
... mercury) with the ischiocavernosus muscles (rigid –erection phase) The angle of the erect penis is determined by its size and its attachment to the puboischial rami (the crura) and the anterior surface of the pubic bone (the suspensory and funiform ligaments). In the men with a long heavy penis or a ...
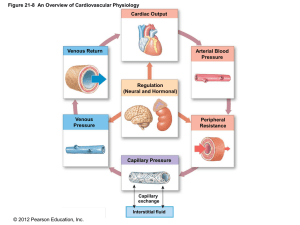
8 Renal Physo Overview Flashcards
... bloodstream? 71. What effect will the above hormone have on water reabsorption? 72. What condition can cause low sodium levels? 73. What hormone is released when the bloodstream needs more water? 74. What is another name for this hormone? 75. What effect do Aldosterone and ADH have on BP and blood v ...
... bloodstream? 71. What effect will the above hormone have on water reabsorption? 72. What condition can cause low sodium levels? 73. What hormone is released when the bloodstream needs more water? 74. What is another name for this hormone? 75. What effect do Aldosterone and ADH have on BP and blood v ...
Review for Medical Physiology
... positive-feedback increase in sodium permeability caused by the transient opening of voltage-gated sodium channels. At almost the same time, the permeability to potassium decreases as certain potassium channels close, which contributes to the membrane depolarization. These potassium channels remain ...
... positive-feedback increase in sodium permeability caused by the transient opening of voltage-gated sodium channels. At almost the same time, the permeability to potassium decreases as certain potassium channels close, which contributes to the membrane depolarization. These potassium channels remain ...
Numerical Simulation of Blood Flow in Centrifugal Heart
... damages by determining theareas of circulation flow and high pressure gradient and shear stress, although the amount of damage is not realized. Therefore, the possible damages can be reduced by evaluating the locations in which return flow or vertex occurs or disturbance is higher than other areas a ...
... damages by determining theareas of circulation flow and high pressure gradient and shear stress, although the amount of damage is not realized. Therefore, the possible damages can be reduced by evaluating the locations in which return flow or vertex occurs or disturbance is higher than other areas a ...
Cardiovascular System: Vessels
... The factors that determine the resistance of a blood vessel to blood flow are expressed by Poiseuille’s (pwä-zwēz) Law: ...
... The factors that determine the resistance of a blood vessel to blood flow are expressed by Poiseuille’s (pwä-zwēz) Law: ...
m5zn_dc4109a43372373
... feedback. When a blood vessel is ruptured and a clot begins to form, multiple enzymes called clotting factors are activated within the clot itself. Some of these enzymes act on other unactivated enzymes of the immediately adjacent blood, thus causing more blood clotting. This process continues until ...
... feedback. When a blood vessel is ruptured and a clot begins to form, multiple enzymes called clotting factors are activated within the clot itself. Some of these enzymes act on other unactivated enzymes of the immediately adjacent blood, thus causing more blood clotting. This process continues until ...
07 Blood Press Vital Sign kj - Region 11 Math And Science Teacher
... Mean arterial pressure (MAP) is not a simple average of the two pressures, because the duration of diastole is twice that of systole. MAP is used by emergency room and intensive care unit personnel as a measure of the adequacy of blood supplied to vital tissues (such as the brain, heart, and kidneys ...
... Mean arterial pressure (MAP) is not a simple average of the two pressures, because the duration of diastole is twice that of systole. MAP is used by emergency room and intensive care unit personnel as a measure of the adequacy of blood supplied to vital tissues (such as the brain, heart, and kidneys ...
Document
... Throbbing sensation is felt - Pulse Pulse rate should = the heart rate Pulse rate is the number of pulsations felt in a minute. Pulse usually = diastolic pressure ...
... Throbbing sensation is felt - Pulse Pulse rate should = the heart rate Pulse rate is the number of pulsations felt in a minute. Pulse usually = diastolic pressure ...
Division of physiology
... 114. Pain. Types of pain. Pain receptors. Dual pathways for transmission of pain signals into the CNS. 115. Pain suppression system. Referred pain. Visceral pain. Headache. 116. Visual system. Optics of the eye. Accommodation. Presbyopia. Errors of refraction. Control of accommodation and pupillary ...
... 114. Pain. Types of pain. Pain receptors. Dual pathways for transmission of pain signals into the CNS. 115. Pain suppression system. Referred pain. Visceral pain. Headache. 116. Visual system. Optics of the eye. Accommodation. Presbyopia. Errors of refraction. Control of accommodation and pupillary ...
Fluid Terms
... The buoyant force is equal to the weight of the liquid displaced by the object… …the buoyant force is equal to the weight of the body of fluid whose volume equals the volume of the original submerged object Objects appear to weigh less when submerged in a fluid ...
... The buoyant force is equal to the weight of the liquid displaced by the object… …the buoyant force is equal to the weight of the body of fluid whose volume equals the volume of the original submerged object Objects appear to weigh less when submerged in a fluid ...
16 Renal Physo Overview Flashcards
... 25. If the plasma if too dilute, is the osmotic pressure high or low? 26. What does it mean when plasma is too dilute? 27. What condition can cause low osmotic pressure? 28. If a person is over-hydrated what will it cause the blood pressure to do? 29. When plasma osmotic pressure is too low, what wi ...
... 25. If the plasma if too dilute, is the osmotic pressure high or low? 26. What does it mean when plasma is too dilute? 27. What condition can cause low osmotic pressure? 28. If a person is over-hydrated what will it cause the blood pressure to do? 29. When plasma osmotic pressure is too low, what wi ...
13a Renal Physo Overview Flashcards
... 25. If the plasma if too dilute, is the osmotic pressure high or low? 26. What does it mean when plasma is too dilute? 27. What condition can cause low osmotic pressure? 28. If a person is over-hydrated what will it cause the blood pressure to do? 29. When plasma osmotic pressure is too low, what wi ...
... 25. If the plasma if too dilute, is the osmotic pressure high or low? 26. What does it mean when plasma is too dilute? 27. What condition can cause low osmotic pressure? 28. If a person is over-hydrated what will it cause the blood pressure to do? 29. When plasma osmotic pressure is too low, what wi ...
07 Blood Press Vital Sign
... Mean arterial pressure (MAP) is not a simple average of the two pressures, because the duration of diastole is twice that of systole. MAP is used by emergency room and intensive care unit personnel as a measure of the adequacy of blood supplied to vital tissues (such as the brain, heart, and kidneys ...
... Mean arterial pressure (MAP) is not a simple average of the two pressures, because the duration of diastole is twice that of systole. MAP is used by emergency room and intensive care unit personnel as a measure of the adequacy of blood supplied to vital tissues (such as the brain, heart, and kidneys ...
File - Wk 1-2
... to bind with O2. Conversely, as the blood pH ↑’s, the Hb has an ↑’d ability to bind to O2. The effect of pH (H+ ions) on the O2-Hb dissociation curve is called the Bohr Effect. ↑ PCO2 → ↓ ability of Hb to bind to O2 due to the effect of Co2 on pH. As CO2 levels ↑, more H+ ions are produced → ↓ pH. A ...
... to bind with O2. Conversely, as the blood pH ↑’s, the Hb has an ↑’d ability to bind to O2. The effect of pH (H+ ions) on the O2-Hb dissociation curve is called the Bohr Effect. ↑ PCO2 → ↓ ability of Hb to bind to O2 due to the effect of Co2 on pH. As CO2 levels ↑, more H+ ions are produced → ↓ pH. A ...
Hemodynamics

Hemodynamics or hæmodynamics (hemo- + -dynamics) is the fluid dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms, much as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. Hemodynamic response continuously monitors and adjusts to conditions in the body and its environment. Thus hemodynamics explains the physical laws that govern the flow of blood in the blood vessels. The relationships can be challenging because blood vessels are complex, with many ways for blood to enter and exit under changing conditions.