Term: Definition: The Prismaflex® 5.1 System is a fully integrated
... 1. Verify that all connections are secure to the patient to prevent leakage, blood loss, air embolism and clots. CLAMP any lines that are not in use or have a flow rate of ZERO. 2. Verify that Prismaflex tubing is inserted into the air detector. 3. Record date and time CRRT is initiated. 4. After in ...
... 1. Verify that all connections are secure to the patient to prevent leakage, blood loss, air embolism and clots. CLAMP any lines that are not in use or have a flow rate of ZERO. 2. Verify that Prismaflex tubing is inserted into the air detector. 3. Record date and time CRRT is initiated. 4. After in ...
Document
... other substances around the body 3. Lymphatic system picks up fluid (lymph) leaked from blood, filters it, and returns it to the blood via network of vessels ...
... other substances around the body 3. Lymphatic system picks up fluid (lymph) leaked from blood, filters it, and returns it to the blood via network of vessels ...
Kidneys- complete!
... Now we will back up a bit, and look at filtrate entering the thin segment. The thin segment is right next to the thick segment, and they share peritubular space. Remember that the thin segment is highly permeable to water. Fluid entering the thin segment is suddenly thrown into highly hypertonic su ...
... Now we will back up a bit, and look at filtrate entering the thin segment. The thin segment is right next to the thick segment, and they share peritubular space. Remember that the thin segment is highly permeable to water. Fluid entering the thin segment is suddenly thrown into highly hypertonic su ...
BODY FLUIDS and ELECTROLYTES
... 3. Kidney excretion of H+ (Urinary system) H+ ions are actively transported in nephron to adjust body pH in exchange for Na+ III. Acid-base imbalances normal blood pH range is narrow 7.35–7.45 more acid - acidosis 7.35 – 6.20 (low O2 transport) more basic – alkalosis 7.45 – 8.00 usually these chang ...
... 3. Kidney excretion of H+ (Urinary system) H+ ions are actively transported in nephron to adjust body pH in exchange for Na+ III. Acid-base imbalances normal blood pH range is narrow 7.35–7.45 more acid - acidosis 7.35 – 6.20 (low O2 transport) more basic – alkalosis 7.45 – 8.00 usually these chang ...
Suffix for
... Hydro/philic: be able to dissolve more readily in water hemophilia: Hemophilia is a rare, inherited bleeding disorder in which your blood doesn’t clot normally. If you have hemophilia, you may bleed for a longer time than others after an injury. You also may bleed internally, especially in your knee ...
... Hydro/philic: be able to dissolve more readily in water hemophilia: Hemophilia is a rare, inherited bleeding disorder in which your blood doesn’t clot normally. If you have hemophilia, you may bleed for a longer time than others after an injury. You also may bleed internally, especially in your knee ...
Interpreting Clinical and Laboratory Data
... • The threshold for blood transfusion typically is a hematocrit of 21% or a hemoglobin of 7.0 g/dl. ...
... • The threshold for blood transfusion typically is a hematocrit of 21% or a hemoglobin of 7.0 g/dl. ...
cardiovascular project
... presentation, but remember your primary objective: to learn how blood circulates through the body. For each circulatory pathway, you only have to use the blood vessels listed when constructing your diagram. It’s fine to assign certain pathways to certain people in the group, but allow each other tim ...
... presentation, but remember your primary objective: to learn how blood circulates through the body. For each circulatory pathway, you only have to use the blood vessels listed when constructing your diagram. It’s fine to assign certain pathways to certain people in the group, but allow each other tim ...
File
... with Glucose level why ? , Lipid Profile (checking your cholesterol level) is done on all patients. ...
... with Glucose level why ? , Lipid Profile (checking your cholesterol level) is done on all patients. ...
Name: Period: Anatomy and Physiology Blood Blood has several
... Blood has several functions, according to its components: red blood cells (rbc’s) carry _________________________________, white blood cells (wbc’s) protect against/fight _________________________________, and platelets promote _________________________________. ...
... Blood has several functions, according to its components: red blood cells (rbc’s) carry _________________________________, white blood cells (wbc’s) protect against/fight _________________________________, and platelets promote _________________________________. ...
Human Physiology Study Questions-3
... c. When would the production of dilute urine be biologically important? d. What CNS created sensation should not accompany the production of dilute urine? 10. Explain why a nephron lacking a loop of Henle could help restore osmotic balance to an organism with low blood osmolarity (too much water in ...
... c. When would the production of dilute urine be biologically important? d. What CNS created sensation should not accompany the production of dilute urine? 10. Explain why a nephron lacking a loop of Henle could help restore osmotic balance to an organism with low blood osmolarity (too much water in ...
Nerve and humoral regulation of heart activity
... signals through sympathetic fibers to heart to increase its rate and contractility. Vasodilator area is located bilaterally in ventromedial of reticular substance in upper medulla oblongata and lower pons. Its neurons inhibit dorsolateral portion and decrease blood pressure. It transmits also inhibi ...
... signals through sympathetic fibers to heart to increase its rate and contractility. Vasodilator area is located bilaterally in ventromedial of reticular substance in upper medulla oblongata and lower pons. Its neurons inhibit dorsolateral portion and decrease blood pressure. It transmits also inhibi ...
Lec 8Aviation, High-Altitude by Prof. Saboohi
... in normal air are used, with four times as much nitrogen as oxygen and a total pressure of 760 mm Hg. The presence of nitrogen in the mixture greatly diminishes the likelihood of fire and explosion. It also protects against development of local patches of lung atelectasis that often occur when breat ...
... in normal air are used, with four times as much nitrogen as oxygen and a total pressure of 760 mm Hg. The presence of nitrogen in the mixture greatly diminishes the likelihood of fire and explosion. It also protects against development of local patches of lung atelectasis that often occur when breat ...
You can
... Each time the ventricles contract (systole), they send a surge of blood into arteries. The force exerted by this blood against the vessel walls creates systolic blood pressure. When the ventricles relax (diastole), the pressure drops to its lowest level. This lowest pressure mark is referred to dias ...
... Each time the ventricles contract (systole), they send a surge of blood into arteries. The force exerted by this blood against the vessel walls creates systolic blood pressure. When the ventricles relax (diastole), the pressure drops to its lowest level. This lowest pressure mark is referred to dias ...
Musculoskeletal system - Responses to exercise PPT
... – Works harder (beats more often and with larger amount of blood in each beat) to provide the Oxygen and Nutrients to the skeletal muscle via the blood, and get rid of the Waste products of exercise (Carbon Dioxide, Water and Heat). ...
... – Works harder (beats more often and with larger amount of blood in each beat) to provide the Oxygen and Nutrients to the skeletal muscle via the blood, and get rid of the Waste products of exercise (Carbon Dioxide, Water and Heat). ...
Introduction to Body Function
... Correction of blood pressure in this situation is an example of a negative feedback process because the initial change (decreased blood pressure) is corrected by the response (increased blood pressure) which reveres the direction of the initial change. When you stand up, gravity causes blood to sett ...
... Correction of blood pressure in this situation is an example of a negative feedback process because the initial change (decreased blood pressure) is corrected by the response (increased blood pressure) which reveres the direction of the initial change. When you stand up, gravity causes blood to sett ...
Fluid Dynamics
... So far, we have considered ideal fluids: • They coast along with no difference in pressure • An ideal milk shake would be as easy to drink as a watery soda ...
... So far, we have considered ideal fluids: • They coast along with no difference in pressure • An ideal milk shake would be as easy to drink as a watery soda ...
Blood culture bottles incubation period, 5 days or more?
... In general, adult patients with bacteremia are likely to have low quantities of bacteria in the blood, even in the setting of severe clinical symptoms. In addition, bacteremia in adults is generally intermittent. For this reason, multiple blood cultures, each containing large volumes of blood, are r ...
... In general, adult patients with bacteremia are likely to have low quantities of bacteria in the blood, even in the setting of severe clinical symptoms. In addition, bacteremia in adults is generally intermittent. For this reason, multiple blood cultures, each containing large volumes of blood, are r ...
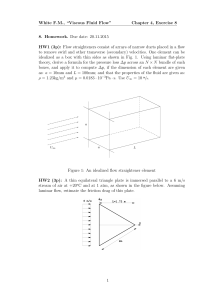
White FM, “Viscous Fluid Flow”
... to remove swirl and other transverse (secondary) velocities. One element can be idealized as a box with thin sides as shown in Fig. 1. Using laminar flat-plate theory, derive a formula for the pressure loss ∆p across an N × N bundle of such boxes, and apply it to compute ∆p, if the dimension of each ...
... to remove swirl and other transverse (secondary) velocities. One element can be idealized as a box with thin sides as shown in Fig. 1. Using laminar flat-plate theory, derive a formula for the pressure loss ∆p across an N × N bundle of such boxes, and apply it to compute ∆p, if the dimension of each ...
Control of arterial blood pressure
... HP > OP & so fluid passes from capillaries into the tissues At venous end of the capillaries: HP < OP & so fluid passes from the tissues into the capillaries Some heart diseases: Tachycardia: Abnormally fast heart rate (More than 100 beats/min) Bradycardia: Abnormally slow heart rate (Less than ...
... HP > OP & so fluid passes from capillaries into the tissues At venous end of the capillaries: HP < OP & so fluid passes from the tissues into the capillaries Some heart diseases: Tachycardia: Abnormally fast heart rate (More than 100 beats/min) Bradycardia: Abnormally slow heart rate (Less than ...
systolic blood pressure
... [STAT PLOT] window. If the normal probability plot is approximately linear, and the boxplot shows no outliers, we can use the method outlined in section 9.4 of our book. a) At the 0.005 significance level can we conclude that captopril is effective in lowering systolic blood pressure? Note: the stat ...
... [STAT PLOT] window. If the normal probability plot is approximately linear, and the boxplot shows no outliers, we can use the method outlined in section 9.4 of our book. a) At the 0.005 significance level can we conclude that captopril is effective in lowering systolic blood pressure? Note: the stat ...
1 Physiology week 9 – Cardiovascular (flow/BP)
... Important to differentiate between velocity (displacement per unit time) and flow (volume per unit time) Velocity V=Flow (Q) / cross sectional area (A) Therefore slow in capillaries because much higher cross-sectional area Poiseuille-Hagen Formula Describes basic factors which determine rate of flow ...
... Important to differentiate between velocity (displacement per unit time) and flow (volume per unit time) Velocity V=Flow (Q) / cross sectional area (A) Therefore slow in capillaries because much higher cross-sectional area Poiseuille-Hagen Formula Describes basic factors which determine rate of flow ...
Physiology (L09) Slides#58 + #59 :
... -The amount of oxygen in pulmonary vein and in radial artery is the same, what differs is the amount of oxygen in the artery and the vein of one structure because between we have a capillary where exchange of materials occur. -Pre-capillary center is within the arteriol that comes from the heart. -T ...
... -The amount of oxygen in pulmonary vein and in radial artery is the same, what differs is the amount of oxygen in the artery and the vein of one structure because between we have a capillary where exchange of materials occur. -Pre-capillary center is within the arteriol that comes from the heart. -T ...
Major Concepts of Anatomy and Physiology
... Baroreceptors: Pressure-sensitive receptors in the arteries that signal the CV center to control the carotid sinus reflex and the aortic reflex – also regulates the baroreflexes. Chemoreceptors: Sensors in the aorta and the carotid sinus of the brain that detect changes in blood oxygen, carbon dioxi ...
... Baroreceptors: Pressure-sensitive receptors in the arteries that signal the CV center to control the carotid sinus reflex and the aortic reflex – also regulates the baroreflexes. Chemoreceptors: Sensors in the aorta and the carotid sinus of the brain that detect changes in blood oxygen, carbon dioxi ...
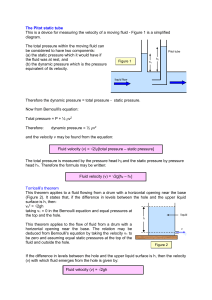
Pitot and Toricelli
... The total pressure is measured by the pressure head h2 and the static pressure by pressure head h1. Therefore the formula may be written: Fluid velocity (v) = √2g[h2 – h1] Torricelli’s theorem This theorem applies to a fluid flowing from a drum with a horizontal opening near the base (Figure 2). It ...
... The total pressure is measured by the pressure head h2 and the static pressure by pressure head h1. Therefore the formula may be written: Fluid velocity (v) = √2g[h2 – h1] Torricelli’s theorem This theorem applies to a fluid flowing from a drum with a horizontal opening near the base (Figure 2). It ...
Hemodynamics

Hemodynamics or hæmodynamics (hemo- + -dynamics) is the fluid dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms, much as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. Hemodynamic response continuously monitors and adjusts to conditions in the body and its environment. Thus hemodynamics explains the physical laws that govern the flow of blood in the blood vessels. The relationships can be challenging because blood vessels are complex, with many ways for blood to enter and exit under changing conditions.