
capillaries - Human Anatomy and Physiology
... Principles of Blood Flow • blood supply to a tissue can be expressed in terms of flow and perfusion – blood flow – the amount of blood flowing through an organ, tissue, or blood vessel in a given time (ml/min) – perfusion – the flow per given volume or mass of tissue in a given time (ml/min/g) ...
... Principles of Blood Flow • blood supply to a tissue can be expressed in terms of flow and perfusion – blood flow – the amount of blood flowing through an organ, tissue, or blood vessel in a given time (ml/min) – perfusion – the flow per given volume or mass of tissue in a given time (ml/min/g) ...
phy221 tutorial kit - Covenant University
... place much more rigidly. This cohesion plays an important roll in the viscosity of liquids. Increasing the temperature of a liquid reduces the cohesive forces and increases the molecular interchange. Reducing cohesive forces reduces shear stress, while increasing molecular interchange increases she ...
... place much more rigidly. This cohesion plays an important roll in the viscosity of liquids. Increasing the temperature of a liquid reduces the cohesive forces and increases the molecular interchange. Reducing cohesive forces reduces shear stress, while increasing molecular interchange increases she ...
flowing fluids and pressure variation!
... 2) All fluid particles keep their temperature, but the velocity u brings a new particle to x0 which has a different temperature:! ...
... 2) All fluid particles keep their temperature, but the velocity u brings a new particle to x0 which has a different temperature:! ...
Cardio110-ExercisePhysI
... Increasing the workload further will NOT increase O2 consumption. Anaerobic metabolism helps out at this point to allow you to exercise a little harder. VO2 isn’t measured clinically. Workload is measured because there’s a linear relationship between the 2 until the maximum point. B. Cardiac Outpu ...
... Increasing the workload further will NOT increase O2 consumption. Anaerobic metabolism helps out at this point to allow you to exercise a little harder. VO2 isn’t measured clinically. Workload is measured because there’s a linear relationship between the 2 until the maximum point. B. Cardiac Outpu ...
Hydrostatics and Bernoulli`s Principle Slide Notes
... opposed to solid body analysis: a. Fluid – A substance in the liquid or gas phase b. Steady – No change at a point in time i. This is important because it defines a state of consistency that allows for basic calculations under normal parameters. Analysis becomes incredibly more difficult under ...
... opposed to solid body analysis: a. Fluid – A substance in the liquid or gas phase b. Steady – No change at a point in time i. This is important because it defines a state of consistency that allows for basic calculations under normal parameters. Analysis becomes incredibly more difficult under ...
Chapter 16 - Dr. Dorena Rode
... The respiratory system regulates the process of breathing and monitors the movements of oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) gases in the body. The thoracic cavity is the ideal sealed enclosure for the lungs (and the heart, in between) playing an important role in the mechanics of breathing. Of prim ...
... The respiratory system regulates the process of breathing and monitors the movements of oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) gases in the body. The thoracic cavity is the ideal sealed enclosure for the lungs (and the heart, in between) playing an important role in the mechanics of breathing. Of prim ...
Department of Mechanical Eng.
... point only. This point is called the minimum pressure point or the point of maximum suction. Evaluation the lower critical Mach number for airfoil with Cpimin=-0.7 . The characteristic Mach number at point of maximum suction when the airfoil is traveling at M cr1 is equal 1.0 i.e λ c = 1.0, from Cr ...
... point only. This point is called the minimum pressure point or the point of maximum suction. Evaluation the lower critical Mach number for airfoil with Cpimin=-0.7 . The characteristic Mach number at point of maximum suction when the airfoil is traveling at M cr1 is equal 1.0 i.e λ c = 1.0, from Cr ...
Does an increase in filtration always cause edema? NO NO NO
... There is less pressure to act as a retaining force in the capillary, so fluid leaves the vessels for the interstitial spaces This increases the tissue pressure significantly above its normal level of about zero mm/Hg Lymphatics try to remove the excessive filtration out of the circulation alon ...
... There is less pressure to act as a retaining force in the capillary, so fluid leaves the vessels for the interstitial spaces This increases the tissue pressure significantly above its normal level of about zero mm/Hg Lymphatics try to remove the excessive filtration out of the circulation alon ...
solutions
... airconditioning units from which these came. What is that assumption and does it seem likely to be true in this case? The population is normally distributed. Not likely - the sample is skewed right with a large outlier – perhaps the population is similarly skewed. ...
... airconditioning units from which these came. What is that assumption and does it seem likely to be true in this case? The population is normally distributed. Not likely - the sample is skewed right with a large outlier – perhaps the population is similarly skewed. ...
Renal physiology for the Primary FRCA
... ADH produce urine volumes of 1.5l/day, with an osmolality of 300500mosmol/kgH2O. When no ADH is present (diabetes insipidus) urine volumes are 23l/day with osmolality of 60mosmol/kgH2O. Adrenal steroids must be present for ADH to have its maximum effect on water permeability. Regulation of fluid and ...
... ADH produce urine volumes of 1.5l/day, with an osmolality of 300500mosmol/kgH2O. When no ADH is present (diabetes insipidus) urine volumes are 23l/day with osmolality of 60mosmol/kgH2O. Adrenal steroids must be present for ADH to have its maximum effect on water permeability. Regulation of fluid and ...
View the PowerPoint
... A “gold” statue weighs 147 N in vacuum and 139 N when immersed in salt water of density 1024 kg m-3 . What is the density of the “gold”? ...
... A “gold” statue weighs 147 N in vacuum and 139 N when immersed in salt water of density 1024 kg m-3 . What is the density of the “gold”? ...
View the PowerPoint
... A “gold” statue weighs 147 N in vacuum and 139 N when immersed in salt water of density 1024 kg m-3 . What is the density of the “gold”? ...
... A “gold” statue weighs 147 N in vacuum and 139 N when immersed in salt water of density 1024 kg m-3 . What is the density of the “gold”? ...
PPT - gserianne.com
... capillary, and the shared basement membrane between them Mechanisms that prevent alveoli from filling with fluid: 1) cells of alveolar wall are tightly joined together 2) the relatively high osmotic pressure of the interstitial fluid draws water out of them 3) there is low pressure in the pulmonary ...
... capillary, and the shared basement membrane between them Mechanisms that prevent alveoli from filling with fluid: 1) cells of alveolar wall are tightly joined together 2) the relatively high osmotic pressure of the interstitial fluid draws water out of them 3) there is low pressure in the pulmonary ...
File - The Physics Doctor
... at a fixed height close to the ground. The density of the cold air is 1.4kgm-3. The total mass of the balloon’s fabric gondola, fuel, burners and occupants is 700kg and it’s volume is 2500m3 ...
... at a fixed height close to the ground. The density of the cold air is 1.4kgm-3. The total mass of the balloon’s fabric gondola, fuel, burners and occupants is 700kg and it’s volume is 2500m3 ...
cardiac output
... cardiovascular system attempting to increase oxygen delivery to the working muscles. However, blood pressure greater than 250/115 mmHg is an indication to terminate exercise (hypertensive response). ...
... cardiovascular system attempting to increase oxygen delivery to the working muscles. However, blood pressure greater than 250/115 mmHg is an indication to terminate exercise (hypertensive response). ...
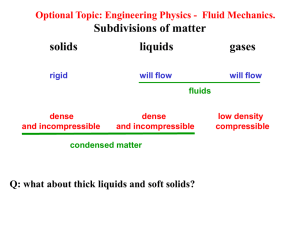
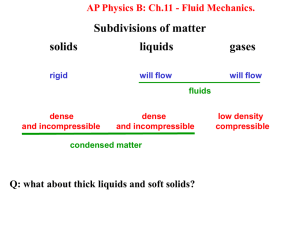
9 – Fluids
... There is a boundary between solids and fluids since solids have crystal lattice and fluids not. On the contrary, liquids can be made gases without crossing any boundary. ...
... There is a boundary between solids and fluids since solids have crystal lattice and fluids not. On the contrary, liquids can be made gases without crossing any boundary. ...
Chapter 3 - Martinos Center
... to maintain the ability to perfuse all of the tissues throughout the body. Intuitively, this is no different than maintaining water pressure throughout a large town. Many of the same issues apply: • Consumers’ needs vary with time of day and with their activity level • Water is consumed at different ...
... to maintain the ability to perfuse all of the tissues throughout the body. Intuitively, this is no different than maintaining water pressure throughout a large town. Many of the same issues apply: • Consumers’ needs vary with time of day and with their activity level • Water is consumed at different ...
GFR - ISpatula
... of both kidneys per minute. • The volume of fluid filtered daily through all the corpuscles of both kidneys per day = 180 L • Hence, GFR= 180 L/24hours * (1000 ml/ L)*(1hour/60 min)= 125 ml/min (Males) • For 125ml/min; renal plasma flow = 625ml/min FF * PF=GFR, PF= 125/(20%)=625 ml/min • 55% of bloo ...
... of both kidneys per minute. • The volume of fluid filtered daily through all the corpuscles of both kidneys per day = 180 L • Hence, GFR= 180 L/24hours * (1000 ml/ L)*(1hour/60 min)= 125 ml/min (Males) • For 125ml/min; renal plasma flow = 625ml/min FF * PF=GFR, PF= 125/(20%)=625 ml/min • 55% of bloo ...
L 15 Fluids [4] Bernoulli`s principle WIND
... The ball is rotating clockwise. The layer of air adjacent to the ball is dragged along by the rotation, causing the flow speed to be higher on the top side. The higher pressure on the bottom causes the ball to curve upward. ...
... The ball is rotating clockwise. The layer of air adjacent to the ball is dragged along by the rotation, causing the flow speed to be higher on the top side. The higher pressure on the bottom causes the ball to curve upward. ...
There are several equations useful in understanding hydraulics and
... tranquil flow give way to rapid it occurs in an smooth transition. When rapid flow suddenly decreases to a tranquil flow, there is an abrupt change known as Hydraulic jump (a sudden increase in depth accompanied by much turbulence, smoke). ...
... tranquil flow give way to rapid it occurs in an smooth transition. When rapid flow suddenly decreases to a tranquil flow, there is an abrupt change known as Hydraulic jump (a sudden increase in depth accompanied by much turbulence, smoke). ...
Fluids, elasticity
... 1. the weight of the body. 2. the weight of the fluid displaced by the body. 3. the difference between the weights of the body and the displaced fluid. 4. the average pressure of the fluid times the surface area of the body. ...
... 1. the weight of the body. 2. the weight of the fluid displaced by the body. 3. the difference between the weights of the body and the displaced fluid. 4. the average pressure of the fluid times the surface area of the body. ...
L15
... The layer of air adjacent to the ball is dragged along by the rotation, causing the flow speed to be higher on the top side. The higher pressure on the bottom causes the ball to curve upward. ...
... The layer of air adjacent to the ball is dragged along by the rotation, causing the flow speed to be higher on the top side. The higher pressure on the bottom causes the ball to curve upward. ...
[j26] Chapter 14#
... The last chapter introduced the blood, the structure and function of the heart and the blood vessels. Logically, this chapter follows these concepts with descriptions of how the many complex factors in the cardiovascular system specifically operate to control the work of the heart (cardiac output) a ...
... The last chapter introduced the blood, the structure and function of the heart and the blood vessels. Logically, this chapter follows these concepts with descriptions of how the many complex factors in the cardiovascular system specifically operate to control the work of the heart (cardiac output) a ...
Hemodynamics

Hemodynamics or hæmodynamics (hemo- + -dynamics) is the fluid dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms, much as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. Hemodynamic response continuously monitors and adjusts to conditions in the body and its environment. Thus hemodynamics explains the physical laws that govern the flow of blood in the blood vessels. The relationships can be challenging because blood vessels are complex, with many ways for blood to enter and exit under changing conditions.

















![L 15 Fluids [4] Bernoulli`s principle WIND](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016758540_1-efd75f7a7777372eeb0885c6e88a0e4b-300x300.png)



![[j26] Chapter 14#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000367221_1-b8dd3faa03e0a519508f460a9af94122-300x300.png)