Fluid Mechanics
... closed at one end, that has been filled with mercury (ρ = 13.6 x 103 kg/m3) and then inverted in a dish of mercury. The space above the mercury column is almost a perfect vacuum. Compute the atmospheric pressure on a day when the height of mercury in a barometer is 76.0 cm. [A barometer is a device ...
... closed at one end, that has been filled with mercury (ρ = 13.6 x 103 kg/m3) and then inverted in a dish of mercury. The space above the mercury column is almost a perfect vacuum. Compute the atmospheric pressure on a day when the height of mercury in a barometer is 76.0 cm. [A barometer is a device ...
Which pressures and where
... Experiment: Arterial pressure after heart arrest This is determining the filling of right ventricle = venous return kvs7e16.ppt ...
... Experiment: Arterial pressure after heart arrest This is determining the filling of right ventricle = venous return kvs7e16.ppt ...
Anatomy And Physiology Of The kidney
... Drugs affecting GFR, hormones, osmolarity or electrolytes also could alter the response of these functions. An example of this alteration is found in diuretics. They can affect kidney function in five ways (Figure 14) by: 1. Increasing the blood supply to the kidney such that (a) aminophyllin causes ...
... Drugs affecting GFR, hormones, osmolarity or electrolytes also could alter the response of these functions. An example of this alteration is found in diuretics. They can affect kidney function in five ways (Figure 14) by: 1. Increasing the blood supply to the kidney such that (a) aminophyllin causes ...
Mechanical Rate - U
... Drag increases with speed. When turbulence is created, pressure drag increases more rapidly than friction drag. Viscosity is the property of a fluid that describes its internal friction. The SI units of viscosity are Pa • s. Stokes’ law can be used to calculate the drag force on a sphere moving at c ...
... Drag increases with speed. When turbulence is created, pressure drag increases more rapidly than friction drag. Viscosity is the property of a fluid that describes its internal friction. The SI units of viscosity are Pa • s. Stokes’ law can be used to calculate the drag force on a sphere moving at c ...
Lymphatic
... Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System consists of tissues and organs that help to release the body of toxins and other harmful materials. The number one function of the system is the transport Lymph throughout the body. o Lymph is a fluid which holds white blood cells for fighting against infect ...
... Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System consists of tissues and organs that help to release the body of toxins and other harmful materials. The number one function of the system is the transport Lymph throughout the body. o Lymph is a fluid which holds white blood cells for fighting against infect ...
Changes in renal physiology
... Special attention should be given when interpreting the results of plasma concentrations to guide therapeutic efficacy as most labs report total plasma concentration (bound and unbound) A fall in plasma concentrations does not reflect a fall in free drug Ideally, free drug concentrations should be m ...
... Special attention should be given when interpreting the results of plasma concentrations to guide therapeutic efficacy as most labs report total plasma concentration (bound and unbound) A fall in plasma concentrations does not reflect a fall in free drug Ideally, free drug concentrations should be m ...
Slide 1 - OCCC.edu
... Since O2 is carried in such high reserves and saturation, it has little effect on the rate of ventilation CO2 concentration and pH do significantly change and have an immediate effect on ventilation ...
... Since O2 is carried in such high reserves and saturation, it has little effect on the rate of ventilation CO2 concentration and pH do significantly change and have an immediate effect on ventilation ...
Renal Physiology
... Glomerular filtration follows the same principles that govern filtration in other capillaries. ...
... Glomerular filtration follows the same principles that govern filtration in other capillaries. ...
Dear Notetaker:
... - 1) Bohr Effect: Right of Left shift in the curve in response to change circulation levels of: o 1. PCO2 o 2. H+ (pH) Right Shift: Tissue capillaries ↑ PCO2 ↑ H2CO3 ↑ H+ ↓ pH .`. ↓ O2 Binding Left Shift: Pulmonary capillaries ...
... - 1) Bohr Effect: Right of Left shift in the curve in response to change circulation levels of: o 1. PCO2 o 2. H+ (pH) Right Shift: Tissue capillaries ↑ PCO2 ↑ H2CO3 ↑ H+ ↓ pH .`. ↓ O2 Binding Left Shift: Pulmonary capillaries ...
Blood Pressure:
... Shivering until body temperature is extremely low Pale, cool, and puffy skin Impaired muscle coordination Listlessness Bradycardia and bradypnea Irregular heart rhythm Decreased ability to think coherently and use goodjudgment Diminished ability to feel pain or other sensations Clients with severe h ...
... Shivering until body temperature is extremely low Pale, cool, and puffy skin Impaired muscle coordination Listlessness Bradycardia and bradypnea Irregular heart rhythm Decreased ability to think coherently and use goodjudgment Diminished ability to feel pain or other sensations Clients with severe h ...
Cardiovascular Physiology 2016
... Cardiac contractility is a measure the heart’s intrinsic ability to generate force (pressure) for a given fiber length (preload) Contractility is determined by a number of variables Contractility is approximated by several means such as dP/dt, ejection velocity, and ESPVR (End Systolic Pressure Volu ...
... Cardiac contractility is a measure the heart’s intrinsic ability to generate force (pressure) for a given fiber length (preload) Contractility is determined by a number of variables Contractility is approximated by several means such as dP/dt, ejection velocity, and ESPVR (End Systolic Pressure Volu ...
ME 101
... Ratio between the inertia (density related) and viscous forces (viscosity related) acting within a fluid – When fluid moves quickly or is not very viscous or dense, Re large, inertia disrupts the flow – turbulent ...
... Ratio between the inertia (density related) and viscous forces (viscosity related) acting within a fluid – When fluid moves quickly or is not very viscous or dense, Re large, inertia disrupts the flow – turbulent ...
Urinary Physiology - El Camino College
... 1. Primary function is to generate a ________ gradient that enables the collecting duct to concentrate the urine and conserve water 2. The __________ thin segment allows _______ to flow out to surrounding peritubular capillaries (or vasa recta) 3. The __________ thick segment is impermeable to water ...
... 1. Primary function is to generate a ________ gradient that enables the collecting duct to concentrate the urine and conserve water 2. The __________ thin segment allows _______ to flow out to surrounding peritubular capillaries (or vasa recta) 3. The __________ thick segment is impermeable to water ...
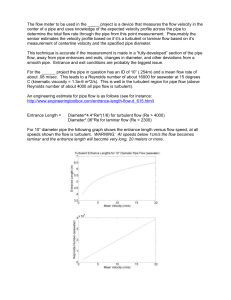
The flow meter to be used in the _____ project is a device that
... C (kinematic viscosity = 1.3e-6 m^2/s). This is well in the turbulent region for pipe flow (above Reynolds number of about 4000 all pipe flow is turbulent). An engineering estimate for pipe flow is as follows (see for instance: http://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/entrance-length-flow-d_615.html) ...
... C (kinematic viscosity = 1.3e-6 m^2/s). This is well in the turbulent region for pipe flow (above Reynolds number of about 4000 all pipe flow is turbulent). An engineering estimate for pipe flow is as follows (see for instance: http://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/entrance-length-flow-d_615.html) ...
Types of Flow
... When a fluid is flowing in pipe, the countless small particles get together and form a flowing stream. These particles, while moving, group themselves in a variety of ways, e.g., they move in a regular formation, just as disciplined soldiers do; or they may swirl, like the individuals, in a disorder ...
... When a fluid is flowing in pipe, the countless small particles get together and form a flowing stream. These particles, while moving, group themselves in a variety of ways, e.g., they move in a regular formation, just as disciplined soldiers do; or they may swirl, like the individuals, in a disorder ...
Slide 1
... Nonviscous flow means that viscosity is negligible. Viscosity produces drag, and retards fluid flow. Incompressible flow means that the fluid’s density is constant. This is generally true for liquids, but not ...
... Nonviscous flow means that viscosity is negligible. Viscosity produces drag, and retards fluid flow. Incompressible flow means that the fluid’s density is constant. This is generally true for liquids, but not ...
Hypovolemic Shock
... cause of hypovolemia. Vomiting and diarrhea from gastroenteritis is a second common cause. The signs and symptoms of hypovolemic shock vary with the amount, duration, and timing of fluid loss. As intravascular volume is further compromised by ongoing fluid losses (such as profuse diarrhea), the chil ...
... cause of hypovolemia. Vomiting and diarrhea from gastroenteritis is a second common cause. The signs and symptoms of hypovolemic shock vary with the amount, duration, and timing of fluid loss. As intravascular volume is further compromised by ongoing fluid losses (such as profuse diarrhea), the chil ...
10.7 Buoyancy and Archimedes Principle 10.8 Fluids in Motion
... 1. Students will explain the principles associated to Archimedes Principle. 2. Students will relate the various flow rates to forces and motion. 3. Students will explain how Bernoulli’s equation is applied. 4. Students will relate viscosity to flow in tubes. ...
... 1. Students will explain the principles associated to Archimedes Principle. 2. Students will relate the various flow rates to forces and motion. 3. Students will explain how Bernoulli’s equation is applied. 4. Students will relate viscosity to flow in tubes. ...
turbulent flow - SNS Courseware
... 1. According to the equation of continuity when water falls its speed increases, while it’s cross sectional area 1. increases 2. decreases 3. remain same 4. different 2. If the layers of the fluid has frictional force between them then it is known as 1. viscous 2. non-viscous 3. incompressible 4. in ...
... 1. According to the equation of continuity when water falls its speed increases, while it’s cross sectional area 1. increases 2. decreases 3. remain same 4. different 2. If the layers of the fluid has frictional force between them then it is known as 1. viscous 2. non-viscous 3. incompressible 4. in ...
NVCC Bio 212 - gserianne.com
... About 125 ml/minute (180 L/day) of the total 1200 ml/min of blood that passes through the glomerulus becomes filtrate • Glomerular Filtration (GF) *Adds to volume of urine produced • substances move from blood to glomerular ...
... About 125 ml/minute (180 L/day) of the total 1200 ml/min of blood that passes through the glomerulus becomes filtrate • Glomerular Filtration (GF) *Adds to volume of urine produced • substances move from blood to glomerular ...
Pressure in a fluid
... how the speed of flow in a tube depends on the tube’s size. • how viscous flow and turbulent flow differ from ideal flow. © 2016 Pearson Education Inc. ...
... how the speed of flow in a tube depends on the tube’s size. • how viscous flow and turbulent flow differ from ideal flow. © 2016 Pearson Education Inc. ...
Fluids
... A Fluid can easily deform to any shape. It is defined as any substance that deforms continuously under a shear. If you think about a piece of ice (solid water), unless the ice melts, no amount of pushing on the ice will cause it to deform enough to let your finger inside until it reaches its breakin ...
... A Fluid can easily deform to any shape. It is defined as any substance that deforms continuously under a shear. If you think about a piece of ice (solid water), unless the ice melts, no amount of pushing on the ice will cause it to deform enough to let your finger inside until it reaches its breakin ...
Modeling the Cardiovascular System using STELLA A module for
... Thus far, we have considered the delivery of blood to the vicinity of cells throughout the body. The blood must return to the heart to complete the circulation. On the return journey, blood travels through conduits called veins . The veins connected directly to the capillaries are small ones called ...
... Thus far, we have considered the delivery of blood to the vicinity of cells throughout the body. The blood must return to the heart to complete the circulation. On the return journey, blood travels through conduits called veins . The veins connected directly to the capillaries are small ones called ...
Physiology – spinal anesthesia MGMC
... higher than motor ( may be 6 also ?) Sensory level of T3 – complete sympathetic block ...
... higher than motor ( may be 6 also ?) Sensory level of T3 – complete sympathetic block ...
2 Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle
... Intra- and extracellular ion concentrations must be maintained for normal heart function ...
... Intra- and extracellular ion concentrations must be maintained for normal heart function ...
Hemodynamics

Hemodynamics or hæmodynamics (hemo- + -dynamics) is the fluid dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms, much as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. Hemodynamic response continuously monitors and adjusts to conditions in the body and its environment. Thus hemodynamics explains the physical laws that govern the flow of blood in the blood vessels. The relationships can be challenging because blood vessels are complex, with many ways for blood to enter and exit under changing conditions.