Urinary System Physiology
... mechanisms • Movement of Na+ establishes electrochemical gradient and negative ions such as HCO3– and Cl– follow. • Water follows by obligatory reabsorption • Solvent drag pulls along many other solutes (as solvent moves solute concentration is changed, thus, now moves from high concentration to low ...
... mechanisms • Movement of Na+ establishes electrochemical gradient and negative ions such as HCO3– and Cl– follow. • Water follows by obligatory reabsorption • Solvent drag pulls along many other solutes (as solvent moves solute concentration is changed, thus, now moves from high concentration to low ...
Quality of Service Challenges for IP Networks
... with distance of flow. Figures 5-8 show the segment truncated and the result satisfies Darcy’s law, using equation (4) Vl can be calculated from the gradient of the curves and its ratio to the porosity of the medium gives the seepage velocity. It is interesting to note that despite the constancy of ...
... with distance of flow. Figures 5-8 show the segment truncated and the result satisfies Darcy’s law, using equation (4) Vl can be calculated from the gradient of the curves and its ratio to the porosity of the medium gives the seepage velocity. It is interesting to note that despite the constancy of ...
NEPHRON Review WS KEY - Mr. Lesiuk
... raise pH of the blood? (p. 313) As you breathe you get rid of CO2, this causes the following reaction to move to the right taking away Hydrogen ions: H+ + HCO3- H2CO3 H2O + CO2 21. Describe what affect each of the following would have on blood pH? A) If less bicarbonate ions are reabsorbed p ...
... raise pH of the blood? (p. 313) As you breathe you get rid of CO2, this causes the following reaction to move to the right taking away Hydrogen ions: H+ + HCO3- H2CO3 H2O + CO2 21. Describe what affect each of the following would have on blood pH? A) If less bicarbonate ions are reabsorbed p ...
Lab 6: Fluids and Drag - Instructional Physics Lab
... The fraction ρlv/η is called the Reynolds number, abbreviated Re. Because we got it by dividing one force by another force, the Reynolds number has no dimensions or units. When Re is much smaller than 1, viscous drag dominates; if Re is much greater than 1, pressure drag dominates. (1) We'll see Rey ...
... The fraction ρlv/η is called the Reynolds number, abbreviated Re. Because we got it by dividing one force by another force, the Reynolds number has no dimensions or units. When Re is much smaller than 1, viscous drag dominates; if Re is much greater than 1, pressure drag dominates. (1) We'll see Rey ...
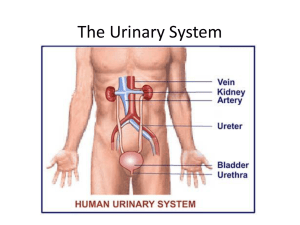
The Urinary System
... • For the most part, filtration is a passive, nonselective process in which fluids and solutes are forced through a membrane by hydrostatic pressure • Very efficient because of high permeability and high blood pressure • 55mm Hg in contrast to other capillaries in body at 18mm Hg ...
... • For the most part, filtration is a passive, nonselective process in which fluids and solutes are forced through a membrane by hydrostatic pressure • Very efficient because of high permeability and high blood pressure • 55mm Hg in contrast to other capillaries in body at 18mm Hg ...
non-invasive blood pressure
... assessing your patient’s cardiac status because a patient’s heart rate and pulse rate may vary if there is any cardiac compromise. On the Propaq monitor you can set the HR/PR tone loudness to LOW, MEDIUM, HIGH, or OFF. This does not affect the tone of the alarm if a patient exceeds an alarm limit se ...
... assessing your patient’s cardiac status because a patient’s heart rate and pulse rate may vary if there is any cardiac compromise. On the Propaq monitor you can set the HR/PR tone loudness to LOW, MEDIUM, HIGH, or OFF. This does not affect the tone of the alarm if a patient exceeds an alarm limit se ...
fluid - GEOCITIES.ws
... A device which is shaped so that the relative motion between it and a fluid produces a force perpendicular to the flow Fluid flows faster over the top surface than over the bottom. It follows that the pressure underneath is increased and that above reduced. A resultant upwards force is thus created, ...
... A device which is shaped so that the relative motion between it and a fluid produces a force perpendicular to the flow Fluid flows faster over the top surface than over the bottom. It follows that the pressure underneath is increased and that above reduced. A resultant upwards force is thus created, ...
Chapter 21 Blood Vessels
... • Vasoactive substances released from cells alter vessel diameter (K+, H+, lactic acid, nitric oxide) – systemic vessels dilate in response to low levels of O2 – pulmonary vessels constrict in response to low levels of O2 Albert Grazia, M.S., N.D. www.naturedoc.info ...
... • Vasoactive substances released from cells alter vessel diameter (K+, H+, lactic acid, nitric oxide) – systemic vessels dilate in response to low levels of O2 – pulmonary vessels constrict in response to low levels of O2 Albert Grazia, M.S., N.D. www.naturedoc.info ...
1. In which of the following fluids is the pH highest (most alkaline
... 7. A young woman is found comatose, having taken an unknown number of sleeping pills an unknown time before. An arterial blood sample yields the following values: pH HCO3PaCO2 ...
... 7. A young woman is found comatose, having taken an unknown number of sleeping pills an unknown time before. An arterial blood sample yields the following values: pH HCO3PaCO2 ...
Blood Vessels
... • Goes up as diameter is reduced • Arteriole diameter dominates • Viscosity of blood • Depends on hematocrit • Turbulence • Cause of pathological sounds ...
... • Goes up as diameter is reduced • Arteriole diameter dominates • Viscosity of blood • Depends on hematocrit • Turbulence • Cause of pathological sounds ...
Closed Conduit: Measurement Techniques
... pressure drop in a 6.35 mm I.D. pipe with a flow rate of 80 mL/s. The orifice coefficient (Korifice) is 0.6. What is the ratio of orifice diameter to pipe diameter? If the smallest pressure differential that can accurately be measured with the pressure sensor is 1 kPa, what is the smallest fl ...
... pressure drop in a 6.35 mm I.D. pipe with a flow rate of 80 mL/s. The orifice coefficient (Korifice) is 0.6. What is the ratio of orifice diameter to pipe diameter? If the smallest pressure differential that can accurately be measured with the pressure sensor is 1 kPa, what is the smallest fl ...
Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle
... Sympathetic stimulation causes increased HR and increased contractility with HR = 180-200 and C.O. = 15-20 L/min. Parasympathetic stimulation decreases HR markedly and decreases cardiac contractility slightly. Vagal fibers go mainly to atria. Fast heart rate (tachycardia) can decrease C.O. becau ...
... Sympathetic stimulation causes increased HR and increased contractility with HR = 180-200 and C.O. = 15-20 L/min. Parasympathetic stimulation decreases HR markedly and decreases cardiac contractility slightly. Vagal fibers go mainly to atria. Fast heart rate (tachycardia) can decrease C.O. becau ...
Closed conduit measurements
... pressure drop in a 6.35 mm I.D. pipe with a flow rate of 80 mL/s. The orifice coefficient (Korifice) is 0.6. What is the ratio of orifice diameter to pipe diameter? If the smallest pressure differential that can accurately be measured with the pressure sensor is 1 kPa, what is the smallest fl ...
... pressure drop in a 6.35 mm I.D. pipe with a flow rate of 80 mL/s. The orifice coefficient (Korifice) is 0.6. What is the ratio of orifice diameter to pipe diameter? If the smallest pressure differential that can accurately be measured with the pressure sensor is 1 kPa, what is the smallest fl ...
Chapter 21: Immune System
... • Speed of blood flow in cm/sec is inversely related to cross-sectional area – blood flow is slower in the arterial branches • flow in aorta is 40 cm/sec while flow in capillaries is .1 cm/sec • slow rate in capillaries allows for exchange ...
... • Speed of blood flow in cm/sec is inversely related to cross-sectional area – blood flow is slower in the arterial branches • flow in aorta is 40 cm/sec while flow in capillaries is .1 cm/sec • slow rate in capillaries allows for exchange ...
Cardiovascular Physiology MCQ`s
... a. Is >6 m/s in the Purkinje system b. Is slowest in the Bundle of His c. Is slowest through the SA and AV nodes d. Is delayed by 0.2s through the AV node 21. Regarding atrial arrhythmias which is incorrect: a. The atrial rate for flutter is 200-350/min compared with 300-500/min for fibrillation b. ...
... a. Is >6 m/s in the Purkinje system b. Is slowest in the Bundle of His c. Is slowest through the SA and AV nodes d. Is delayed by 0.2s through the AV node 21. Regarding atrial arrhythmias which is incorrect: a. The atrial rate for flutter is 200-350/min compared with 300-500/min for fibrillation b. ...
MS Word Version - Interactive Physiology
... a. The opening of voltage-gated K+ channels cause the membrane to _____________________. b. Does K+ move into or out of the cell? __________________ c. If the membrane potential becomes more negative than –70 mV, this is called _________. d. This potential is caused by what characteristic of K+ perm ...
... a. The opening of voltage-gated K+ channels cause the membrane to _____________________. b. Does K+ move into or out of the cell? __________________ c. If the membrane potential becomes more negative than –70 mV, this is called _________. d. This potential is caused by what characteristic of K+ perm ...
1 Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle
... Sympathetic stimulation causes increased HR and increased contractility with HR = 180-200 and C.O. = 15-20 L/min. Parasympathetic stimulation decreases HR markedly and decreases cardiac contractility slightly. Vagal fibers go mainly to atria. Fast heart rate (tachycardia) can decrease C.O. becau ...
... Sympathetic stimulation causes increased HR and increased contractility with HR = 180-200 and C.O. = 15-20 L/min. Parasympathetic stimulation decreases HR markedly and decreases cardiac contractility slightly. Vagal fibers go mainly to atria. Fast heart rate (tachycardia) can decrease C.O. becau ...
The Cardiac Output Curve
... Sympathetic stimulation causes increased HR and increased contractility with HR = 180-200 and C.O. = 15-20 L/min. Parasympathetic stimulation decreases HR markedly and decreases cardiac contractility slightly. Vagal fibers go mainly to atria. Fast heart rate (tachycardia) can decrease C.O. becau ...
... Sympathetic stimulation causes increased HR and increased contractility with HR = 180-200 and C.O. = 15-20 L/min. Parasympathetic stimulation decreases HR markedly and decreases cardiac contractility slightly. Vagal fibers go mainly to atria. Fast heart rate (tachycardia) can decrease C.O. becau ...
Fluid Mechanics Concepts
... An object submerged in a fluid will experience a volume stress. The magnitude of this stress will depend on the pressure of the fluid, the force that the fluid exerts on a unit area of a given surface: The SI unit for pressure is the pascal (Pa): Consider a liquid at rest in a container. If we made ...
... An object submerged in a fluid will experience a volume stress. The magnitude of this stress will depend on the pressure of the fluid, the force that the fluid exerts on a unit area of a given surface: The SI unit for pressure is the pascal (Pa): Consider a liquid at rest in a container. If we made ...
Fluid Mechanics
... closed at one end, that has been filled with mercury (ρ = 13.6 x 103 kg/m3) and then inverted in a dish of mercury. The space above the mercury column is almost a perfect vacuum. Compute the atmospheric pressure on a day when the height of mercury in a barometer is 76.0 cm. [A barometer is a device ...
... closed at one end, that has been filled with mercury (ρ = 13.6 x 103 kg/m3) and then inverted in a dish of mercury. The space above the mercury column is almost a perfect vacuum. Compute the atmospheric pressure on a day when the height of mercury in a barometer is 76.0 cm. [A barometer is a device ...
FLUID FLOW IDEAL FLUID BERNOULLI`S PRINCIPLE
... enough before the corner, and far enough after it, they are parallel and equally spaced. Consider the liquid flowing between lines 1 and 2. Its cross-sectional area decreases near the corner, so the liquid ...
... enough before the corner, and far enough after it, they are parallel and equally spaced. Consider the liquid flowing between lines 1 and 2. Its cross-sectional area decreases near the corner, so the liquid ...
Hemodynamics

Hemodynamics or hæmodynamics (hemo- + -dynamics) is the fluid dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms, much as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. Hemodynamic response continuously monitors and adjusts to conditions in the body and its environment. Thus hemodynamics explains the physical laws that govern the flow of blood in the blood vessels. The relationships can be challenging because blood vessels are complex, with many ways for blood to enter and exit under changing conditions.