2. Physiology_Respiratory_System
... fashion at a frequency of 1000-1500 cycles per minute. ♦ The ciliary mechanism is capable of moving particles away from the lungs at a rate of at least 16mm/min. Particles less than 2µm in diameter generally reach the alveoli, where they are ingested by the macrophages ♦ When ciliary motility is def ...
... fashion at a frequency of 1000-1500 cycles per minute. ♦ The ciliary mechanism is capable of moving particles away from the lungs at a rate of at least 16mm/min. Particles less than 2µm in diameter generally reach the alveoli, where they are ingested by the macrophages ♦ When ciliary motility is def ...
The Normal Pleura
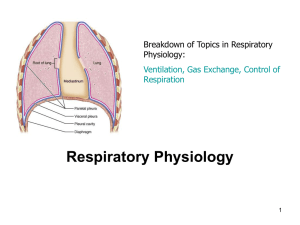
... The lung is covered with visceral pleura The adjacent surfaces of the mediastinum, chest wall, and diaphragm are lined by parietal pleura. These layers are in continuity both at the hilum and below, where they form the pulmonary ligament. The visceral and parietal pleura are separated by a p ...
... The lung is covered with visceral pleura The adjacent surfaces of the mediastinum, chest wall, and diaphragm are lined by parietal pleura. These layers are in continuity both at the hilum and below, where they form the pulmonary ligament. The visceral and parietal pleura are separated by a p ...
Paediatric shock
... 60% body weight. Of this, about two thirds is intracellular and the rest - about 20% body weight normally – extracellular. Extracellular water is further divided into interstitial and intravascular (or plasma) compartments. Plasma volume is typically one third of extracellular water and is therefore ...
... 60% body weight. Of this, about two thirds is intracellular and the rest - about 20% body weight normally – extracellular. Extracellular water is further divided into interstitial and intravascular (or plasma) compartments. Plasma volume is typically one third of extracellular water and is therefore ...
Challenges in teaching the mechanics of breathing to
... two components. Now let’s turn briefly to dynamics, which has to do with pressures and flows. I do not spend a lot of time on the diagrams shown in Fig. 8 because laminar and turbulent flow are dealt with extensively by the cardiovascular section later in the course. However, it is important for stu ...
... two components. Now let’s turn briefly to dynamics, which has to do with pressures and flows. I do not spend a lot of time on the diagrams shown in Fig. 8 because laminar and turbulent flow are dealt with extensively by the cardiovascular section later in the course. However, it is important for stu ...
AHF 2203 AVIATION HUMAN FACTORS
... circulation of blood arriving at the cells. • An arm or leg going to sleep because the blood flow has accidentally been shut off is one form of stagnant hypoxia. ...
... circulation of blood arriving at the cells. • An arm or leg going to sleep because the blood flow has accidentally been shut off is one form of stagnant hypoxia. ...
Viscous flow in pipe
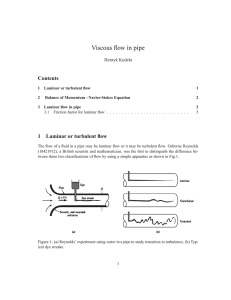
... V D/ν the ratio of the inertia to viscous effects in the flow. Hence, the term flowrate should be replaced by Reynolds number, where V is the average velocity in the pipe. That is, the flow in a pipe is laminar, transitional, or turbulent provided the Reynolds number is small enough, intermediate, o ...
... V D/ν the ratio of the inertia to viscous effects in the flow. Hence, the term flowrate should be replaced by Reynolds number, where V is the average velocity in the pipe. That is, the flow in a pipe is laminar, transitional, or turbulent provided the Reynolds number is small enough, intermediate, o ...
The impact of debris flows on structures
... The understanding and quantification of mudflow and debris flow – structure interactions in terms of modification of the incident flow and impact force applied to the obstacle are of paramount importance for the conception and design of structural countermeasures. In this context, the present study ...
... The understanding and quantification of mudflow and debris flow – structure interactions in terms of modification of the incident flow and impact force applied to the obstacle are of paramount importance for the conception and design of structural countermeasures. In this context, the present study ...
11 Respiratory physiology
... • Lung Compliance is how much the lung volume changes when the pressure changes. • Compliance can be considered the opposite of stiffness. • A low lung compliance would mean that the lungs would need a greater than average change in pressure to change the volume of the lungs. Instead of needing only ...
... • Lung Compliance is how much the lung volume changes when the pressure changes. • Compliance can be considered the opposite of stiffness. • A low lung compliance would mean that the lungs would need a greater than average change in pressure to change the volume of the lungs. Instead of needing only ...
American Journal of Physics, Vol. 71, Nº 1, 46-48 (2003).
... cylindrical tube as a function of the variation in pressure at the two ends of the tube is calculated by applying the Navier-Stokes equation. With the use of the Navier-Stokes equation many problems involving flow through tubes can be solved.1,2 Nevertheless, to avoid difficult mathematics (involvin ...
... cylindrical tube as a function of the variation in pressure at the two ends of the tube is calculated by applying the Navier-Stokes equation. With the use of the Navier-Stokes equation many problems involving flow through tubes can be solved.1,2 Nevertheless, to avoid difficult mathematics (involvin ...
Saladin 5e Extended Outline
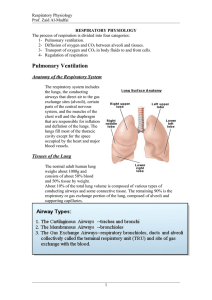
... mammals have lungs with 150 million little sacs, the alveoli, that provide about 70 m2 of surface for gas exchange. b. Thin, broad cells called squamous (type I) alveolar cells cover about 95% of the alveolar surface area. c. The other 5% is covered by round to cuboidal great (type II) alveolar cell ...
... mammals have lungs with 150 million little sacs, the alveoli, that provide about 70 m2 of surface for gas exchange. b. Thin, broad cells called squamous (type I) alveolar cells cover about 95% of the alveolar surface area. c. The other 5% is covered by round to cuboidal great (type II) alveolar cell ...
Laboratory Exercise 10: Physiology of Ventilation (Breathing)
... breathing muscles relax, the thoracic cage recoils, pressure gradients are reversed. The greater intrathoracic pressure causes air to be expired. A breathing cycle (one breath) includes inspiration and expiration. A normal breathing rate at rest for an adult is 12-18 breaths/minute. This called eupn ...
... breathing muscles relax, the thoracic cage recoils, pressure gradients are reversed. The greater intrathoracic pressure causes air to be expired. A breathing cycle (one breath) includes inspiration and expiration. A normal breathing rate at rest for an adult is 12-18 breaths/minute. This called eupn ...
The Relation between the Coefficient of Friction and Pressure Drop
... move from the high-pressure area to the low area. The fluid speed directly proportional to the amount of pressure drop depends on the dimensions and shape of the space passing through the fluid [1]. Therefore two-phase flows are widely used in most of the engineering disciplines. Researchers at the ...
... move from the high-pressure area to the low area. The fluid speed directly proportional to the amount of pressure drop depends on the dimensions and shape of the space passing through the fluid [1]. Therefore two-phase flows are widely used in most of the engineering disciplines. Researchers at the ...
Flow Measurement
... substantial obstruction into the flow path to measure the flow. For this reason, these devices are used only when an obstruction does not cause any unwanted reaction on the flow system ...
... substantial obstruction into the flow path to measure the flow. For this reason, these devices are used only when an obstruction does not cause any unwanted reaction on the flow system ...
Fick Principle - 911 Training Concepts
... Perfusion Needs of Tissues: The heart demands a constant supply of blood. The brain and spinal cord can survive for 4 to 6 ...
... Perfusion Needs of Tissues: The heart demands a constant supply of blood. The brain and spinal cord can survive for 4 to 6 ...
Pressure
... the fluid would have to be moving to the right, left, or back & forth, which doesn’t happen with a fluid in equilibrium. Imagine submersing a container of water in the shape of a rectangular prism (a box). ...
... the fluid would have to be moving to the right, left, or back & forth, which doesn’t happen with a fluid in equilibrium. Imagine submersing a container of water in the shape of a rectangular prism (a box). ...
Fluid Mechanics II
... Relating high and low pressures down and top of the wing creates a secondary flow called trailing vortex (TV) This vortex reduces the net lift force More heavy the aircraft more powerful these vortices These vortices creates two line of water vapor in the sky These vortices may exist up to 10 miles ...
... Relating high and low pressures down and top of the wing creates a secondary flow called trailing vortex (TV) This vortex reduces the net lift force More heavy the aircraft more powerful these vortices These vortices creates two line of water vapor in the sky These vortices may exist up to 10 miles ...
Respiratory physiology
... lymphatics and evaporation The pulmonary circulation receives the entire output of the right heart, but vascular pressures are considerably lower than in systemic vessels. Lung vessels lack high resistance arterioles, which accounts for their low resistance to blood flow. However, the lack of arteri ...
... lymphatics and evaporation The pulmonary circulation receives the entire output of the right heart, but vascular pressures are considerably lower than in systemic vessels. Lung vessels lack high resistance arterioles, which accounts for their low resistance to blood flow. However, the lack of arteri ...
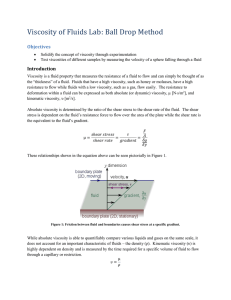
Viscosity of Fluids Lab (Ball Drop Method)
... the “thickness” of a fluid. Fluids that have a high viscosity, such as honey or molasses, have a high resistance to flow while fluids with a low viscosity, such as a gas, flow easily. The resistance to deformation within a fluid can be expressed as both absolute (or dynamic) viscosity, µ [Ns/m2], a ...
... the “thickness” of a fluid. Fluids that have a high viscosity, such as honey or molasses, have a high resistance to flow while fluids with a low viscosity, such as a gas, flow easily. The resistance to deformation within a fluid can be expressed as both absolute (or dynamic) viscosity, µ [Ns/m2], a ...
Understanding Our Circulatory System
... 2. How did it smell? Where do you think this odor came from? __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 3. ...
... 2. How did it smell? Where do you think this odor came from? __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 3. ...
Cal State LA - Instructional Web Server
... Force transducer behind model senses lift, drag and pitching moment directly. Motor-controlled mechanism adjusts the model’s angle of attack. ...
... Force transducer behind model senses lift, drag and pitching moment directly. Motor-controlled mechanism adjusts the model’s angle of attack. ...
Physiology of urinary system
... (GFR) The rate of glomerular filtration is a function of the - net filtration pressure, - the permeability of the filtration membrane, - the surface area available for filtration. The measured GFR reflects these factors, and the total number of functioning nephrons. Average GFR is 125 ml/min for a h ...
... (GFR) The rate of glomerular filtration is a function of the - net filtration pressure, - the permeability of the filtration membrane, - the surface area available for filtration. The measured GFR reflects these factors, and the total number of functioning nephrons. Average GFR is 125 ml/min for a h ...
Principal technical particulars <
... There are, besides these, other types of fans with special characteristics. The fans can obviously gather more then one of the described characteristics. ...
... There are, besides these, other types of fans with special characteristics. The fans can obviously gather more then one of the described characteristics. ...
Renal Physiology - e-safe
... limb, which is impermeable to water which therefore cannot follow. Deep in the medulla, Na+ and Cl- leave by passive diffusion, however this passive diffusion is not sufficient to maintain such a steep gradient, so in the thick ascending limb sodium is actively pumped out into the interstitium. Wate ...
... limb, which is impermeable to water which therefore cannot follow. Deep in the medulla, Na+ and Cl- leave by passive diffusion, however this passive diffusion is not sufficient to maintain such a steep gradient, so in the thick ascending limb sodium is actively pumped out into the interstitium. Wate ...
MAE 3130: Fluid Mechanics Lecture 4: Bernoulli Equation
... Swiss mathematician, son of Johann Bernoulli, who showed that as the velocity of a fluid increases, the pressure decreases, a statement known as the Bernoulli principle. He won the annual prize of the French Academy ten times for work on vibrating strings, ocean tides, and the kinetic theory of gase ...
... Swiss mathematician, son of Johann Bernoulli, who showed that as the velocity of a fluid increases, the pressure decreases, a statement known as the Bernoulli principle. He won the annual prize of the French Academy ten times for work on vibrating strings, ocean tides, and the kinetic theory of gase ...
The Diagnosis of Uterine Rupture with VBAC
... Heparin Pharmacokinetics during Pregnancy • Shorter time to peak heparin ...
... Heparin Pharmacokinetics during Pregnancy • Shorter time to peak heparin ...
Hemodynamics

Hemodynamics or hæmodynamics (hemo- + -dynamics) is the fluid dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms, much as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. Hemodynamic response continuously monitors and adjusts to conditions in the body and its environment. Thus hemodynamics explains the physical laws that govern the flow of blood in the blood vessels. The relationships can be challenging because blood vessels are complex, with many ways for blood to enter and exit under changing conditions.