Third Semester M.Sc. Degree Examination (CSS)
... Describe the factors affecting immunogenicity. Explain the role of MHC proteins in cell mediated lysis. Give an account on the applications of monoclonal antibodies. Describe the role of cytokines in immunogenic reactions. Explain the immune responses shown to viral, bacterial and parasitic infectio ...
... Describe the factors affecting immunogenicity. Explain the role of MHC proteins in cell mediated lysis. Give an account on the applications of monoclonal antibodies. Describe the role of cytokines in immunogenic reactions. Explain the immune responses shown to viral, bacterial and parasitic infectio ...
consumer perceptions of food biotechnology
... Molecular biology Study of genes and gene replication, mutation and expression Genome is the collection of all base pairs within the cell Human Genome project started in 1980s ...
... Molecular biology Study of genes and gene replication, mutation and expression Genome is the collection of all base pairs within the cell Human Genome project started in 1980s ...
Structure and Role of DNA Genetic and DNA Genetics
... Chromosomes and Genes Chromosomes(contain genetic information) wraps around proteins and become tightly coiled Every species has a characteristic number of chromosomes in its cells Traits are dertermined by small parts of chromosomes Gene-section of a chromosome that codes for a trait o EX: ...
... Chromosomes and Genes Chromosomes(contain genetic information) wraps around proteins and become tightly coiled Every species has a characteristic number of chromosomes in its cells Traits are dertermined by small parts of chromosomes Gene-section of a chromosome that codes for a trait o EX: ...
Chapter 19 Organization and Control of Eukaryotic Genomes
... with the Nucleosome that forms folds that are 30 nm in size Looped domains—30nm fiber folds and attaches on to nonhistone protein scafold. When Chromatin is condensed into chromosomes the looped domains coil and form a tightly packed Chromosome. ...
... with the Nucleosome that forms folds that are 30 nm in size Looped domains—30nm fiber folds and attaches on to nonhistone protein scafold. When Chromatin is condensed into chromosomes the looped domains coil and form a tightly packed Chromosome. ...
Lecture VII
... Naturally - transplacental transfer of maternal IgG Abs to developing fetus; transfer of IgG + IgA Abs in milk during breast-feeding of newborn Medically - injection of immune globulin Performed prophylactically, either after diagnosis of exposure to toxin/virus or as a short term preventive procedu ...
... Naturally - transplacental transfer of maternal IgG Abs to developing fetus; transfer of IgG + IgA Abs in milk during breast-feeding of newborn Medically - injection of immune globulin Performed prophylactically, either after diagnosis of exposure to toxin/virus or as a short term preventive procedu ...
Chapter 12-1 Skeleton Notes
... Labeled the protein coat with a radioactive sulfur isotope and the DNA with a radioactive phosphorous isotope so that they may follow where each part goes after the infection Mixed solution of bacteriophage and solution of bacteria together and let virus work After a time, put mixture into a blende ...
... Labeled the protein coat with a radioactive sulfur isotope and the DNA with a radioactive phosphorous isotope so that they may follow where each part goes after the infection Mixed solution of bacteriophage and solution of bacteria together and let virus work After a time, put mixture into a blende ...
ABO Blood Type: An Example of Genetic Variation
... ABO Blood Type: An Example of Genetic Variation • In others this enzyme has a structure that causes it to make B type carbohydrates. • In others they may have copies of both enzyme structures. • In still others this enzyme has a structure that makes in nonfunctional so no carbohydrate is made. ...
... ABO Blood Type: An Example of Genetic Variation • In others this enzyme has a structure that causes it to make B type carbohydrates. • In others they may have copies of both enzyme structures. • In still others this enzyme has a structure that makes in nonfunctional so no carbohydrate is made. ...
Biotechnoloy :Guides for Exam 2
... C. defective protein defective beta globin D. defective muscle protein. 3. Sickle-cell disease is due to a defective beta globin. A. True. B. False. 4. In US any clinical trial for human gene therapy must be approved by A. the RAC committee B. EPA committee C. Biotechnology committee D. Ethic cleara ...
... C. defective protein defective beta globin D. defective muscle protein. 3. Sickle-cell disease is due to a defective beta globin. A. True. B. False. 4. In US any clinical trial for human gene therapy must be approved by A. the RAC committee B. EPA committee C. Biotechnology committee D. Ethic cleara ...
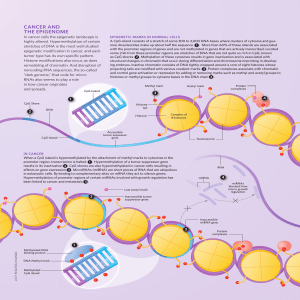
CaNCer aND THe ePIGeNOMe
... epigenetic modification in cancer, and each tumor type has its own specific pattern. Histone modifications also occur, as does remodeling of chromatin. And disruption of noncoding RNA sequences, the so-called “dark genome,” that code for microRNAs also seems to play a role in how cancer originates a ...
... epigenetic modification in cancer, and each tumor type has its own specific pattern. Histone modifications also occur, as does remodeling of chromatin. And disruption of noncoding RNA sequences, the so-called “dark genome,” that code for microRNAs also seems to play a role in how cancer originates a ...
Nucleic acid review sheet
... What is the material in each cell that contains a set of instructions that controls all genetic traits? ...
... What is the material in each cell that contains a set of instructions that controls all genetic traits? ...
DNA Discovery - Biology Junction
... mechanisms of protein synthesis, including the structure of DNA and its discovery. ...
... mechanisms of protein synthesis, including the structure of DNA and its discovery. ...
DNA notes File
... Mutations in the _____________ may not be as serious Mutations in _____________ mean that the mutation is permanent. Mutations bring ___________ to a species. Mutations can be ________________ and _____________ ...
... Mutations in the _____________ may not be as serious Mutations in _____________ mean that the mutation is permanent. Mutations bring ___________ to a species. Mutations can be ________________ and _____________ ...
Chapter 10 Study Guide Know the definitions for: Cross
... mRNA – transcription of DNA sequence that can move from the nucleus to cytoplasm to site of ribosomes. tRNA – translation of mRNA sequence carried from the nucleus by carrying appropriate amino acids to construct polypeptide sequence (protein). rRNA – ribosomes are composed of rRNA and protein that ...
... mRNA – transcription of DNA sequence that can move from the nucleus to cytoplasm to site of ribosomes. tRNA – translation of mRNA sequence carried from the nucleus by carrying appropriate amino acids to construct polypeptide sequence (protein). rRNA – ribosomes are composed of rRNA and protein that ...
Recombinant and Synthetic Nucleic Acid Activity Registration
... Consist entirely of DNA segments from a single nonchromosomal or viral DNA source, though one or more of the segments may be a synthetic equivalent. Consist entirely of DNA from a prokaryotic host including its indigenous plasmids or viruses when propagated only in that host (or a closely related st ...
... Consist entirely of DNA segments from a single nonchromosomal or viral DNA source, though one or more of the segments may be a synthetic equivalent. Consist entirely of DNA from a prokaryotic host including its indigenous plasmids or viruses when propagated only in that host (or a closely related st ...
TEKS 5C – describe the roles of DNA, ribonucleic acid (RNA), and
... (RNA), and environmental factors in cell differentiation 1. Unicellular organisms carry out all the necessary life processes in one cell. In multicellular organisms, each cell is specialized to perform a specific function. How do the cells in multicellular organisms become specialized? A A single nu ...
... (RNA), and environmental factors in cell differentiation 1. Unicellular organisms carry out all the necessary life processes in one cell. In multicellular organisms, each cell is specialized to perform a specific function. How do the cells in multicellular organisms become specialized? A A single nu ...
Extra Credit DNA Study Guide
... 11. What do they have in common? 12. List the types of RNA and the job of each 13. What is the end product of transcription and the end product of translation? 14. What are introns and exons? 15. If there are 6 codons, how many amino acids will there be? 16. If there are 6 codons, how many nucleotid ...
... 11. What do they have in common? 12. List the types of RNA and the job of each 13. What is the end product of transcription and the end product of translation? 14. What are introns and exons? 15. If there are 6 codons, how many amino acids will there be? 16. If there are 6 codons, how many nucleotid ...
7.1 DNA Structure
... DNA Structure • How are the two strands of nucleotides connected? • Two strands arrange themselves so that the Nbases are in the center • N-bases complementary bond with each other using hydrogen bonds ▫ Cytosine – Guanine (C-G) ▫ Adenine – Thymine (A-T) ...
... DNA Structure • How are the two strands of nucleotides connected? • Two strands arrange themselves so that the Nbases are in the center • N-bases complementary bond with each other using hydrogen bonds ▫ Cytosine – Guanine (C-G) ▫ Adenine – Thymine (A-T) ...
What is DNA?
... An organism that is genetically identical to the organism from which it is produced. What is a clone? ...
... An organism that is genetically identical to the organism from which it is produced. What is a clone? ...
DNA vaccination

DNA vaccination is a technique for protecting an animal against disease by injecting it with genetically engineered DNA so cells directly produce an antigen, resulting in a protective immunological response. Several DNA vaccines have been released for veterinary use, and there has been promising research using the vaccines for viral, bacterial and parasitic diseases, as well as to several tumour types. Although only one DNA vaccine has been approved for human use, DNA vaccines may have a number of potential advantages over conventional vaccines, including the ability to induce a wider range of immune response types.