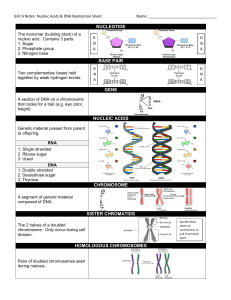
NUCLEOTIDE BASE PAIR GENE NUCLEIC ACIDS CHROMOSOME
... PURPOSE: To make an extra copy of DNA during S-Phase of the cell cycle for cellular reproduction (mitosis or meiosis). This ensures each new daughter cell has an exact copy of DNA as the original parent cell. Too much change (mutation) in the DNA sequence may result in cancer. ...
... PURPOSE: To make an extra copy of DNA during S-Phase of the cell cycle for cellular reproduction (mitosis or meiosis). This ensures each new daughter cell has an exact copy of DNA as the original parent cell. Too much change (mutation) in the DNA sequence may result in cancer. ...
The Immune System - Clark Pleasant Community School Corp
... antibodies; the single most effective protection ...
... antibodies; the single most effective protection ...
Applied Genetics
... • Genes are now known to control more than one trait • By altering/changing a single gene, multiple traits may be changed in ways we can’t predict • Human genes are only a small percentage of the information contained in DNA (5% or less)…we don’t know what most of the rest does ...
... • Genes are now known to control more than one trait • By altering/changing a single gene, multiple traits may be changed in ways we can’t predict • Human genes are only a small percentage of the information contained in DNA (5% or less)…we don’t know what most of the rest does ...
Genetic Engineering
... What is Genetic Engineering? • Basic definition: genetic engineering is the direct manipulation of an organism's genes. • Genetic Engineering is useful in many fields including food production and medicine. • While it seems promising, there is still a lot that we do not know about Genetic Engineeri ...
... What is Genetic Engineering? • Basic definition: genetic engineering is the direct manipulation of an organism's genes. • Genetic Engineering is useful in many fields including food production and medicine. • While it seems promising, there is still a lot that we do not know about Genetic Engineeri ...
Document
... Lipid: polar / non-polar molecules separate ‘self’ from ‘non-self’ regulate material flow, cell shape, compartmentalizes, etc ...
... Lipid: polar / non-polar molecules separate ‘self’ from ‘non-self’ regulate material flow, cell shape, compartmentalizes, etc ...
Lymphatic Review Sheet
... -4 cardinal signs are: _________________________________________ 3. 3rd line of defense is specific/nonspecific and is called the ___________________________. -Special about the immune system is that it acts slower/faster. -Makes two types of lymphocytes: __________________ and ____________________ ...
... -4 cardinal signs are: _________________________________________ 3. 3rd line of defense is specific/nonspecific and is called the ___________________________. -Special about the immune system is that it acts slower/faster. -Makes two types of lymphocytes: __________________ and ____________________ ...
Create the complementary strand for the following
... billion bases—accounts for the vast differences within the human race. ...
... billion bases—accounts for the vast differences within the human race. ...
DNA Replication Graphic Organizer
... REVIEW: Explain the TWO things an enzyme does in chemical reactions in the body… ...
... REVIEW: Explain the TWO things an enzyme does in chemical reactions in the body… ...
Biology Chapter 11-1
... Ex. German Sheppard’s, toy poodles, and Great Danes Hybridization- A cross between dissimilar individuals. (usually between different, but related, species.) Ex. Mules and pigs Mutagens- substances in the environment, such as radiation and chemicals, that cause mutations. Genetic engineering- a form ...
... Ex. German Sheppard’s, toy poodles, and Great Danes Hybridization- A cross between dissimilar individuals. (usually between different, but related, species.) Ex. Mules and pigs Mutagens- substances in the environment, such as radiation and chemicals, that cause mutations. Genetic engineering- a form ...
Microbiology Chapter 15 part 2
... c. Principles and Effects of Vaccination i. The injection produces the primary response of the immune system leading to the formation of antibodies and long term memory cells ii. If a second exposure is encountered the memory cells are stimulated producing a rapid response (second response is quick ...
... c. Principles and Effects of Vaccination i. The injection produces the primary response of the immune system leading to the formation of antibodies and long term memory cells ii. If a second exposure is encountered the memory cells are stimulated producing a rapid response (second response is quick ...
Introduction to Biophysics Lecture 7 Global
... evolutionary relationships between organisms. After two species diverge from each other, they begin to collect sequence mutations independently of one another. This means that two species that are closely related to each other will have DNA (or amino acid) sequences that are more similar to each oth ...
... evolutionary relationships between organisms. After two species diverge from each other, they begin to collect sequence mutations independently of one another. This means that two species that are closely related to each other will have DNA (or amino acid) sequences that are more similar to each oth ...
Genetics
... What's the center of heredity in a cell? In eukaryotic organisms it is the nucleus, in prokaryotes it is the nucleoid region. What is the genetic material? In eukaryotes & prokaryotes it is DNA, in viruses it can be either DNA or RNA. What do DNA & RNA stand for? DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid / RNA: ri ...
... What's the center of heredity in a cell? In eukaryotic organisms it is the nucleus, in prokaryotes it is the nucleoid region. What is the genetic material? In eukaryotes & prokaryotes it is DNA, in viruses it can be either DNA or RNA. What do DNA & RNA stand for? DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid / RNA: ri ...
Mark scheme - biologypost
... Difficulty of finding one gene among all the genes in the nucleus / large amounts of mRNA coding for insulin will be present in insulin producing cells / idea that mRNA will be ‘edited’ ...
... Difficulty of finding one gene among all the genes in the nucleus / large amounts of mRNA coding for insulin will be present in insulin producing cells / idea that mRNA will be ‘edited’ ...
Notes april 16 and 17 - Salmon River High School
... Example: Diabetic humans don’t produce enough insulin to control the amount of sugar in their blood. We used to harvest insulin from horses. Now, however, thanks to gene splicing we’re able to splice our genes for insulin production into bacteria. We grow the bacteria in large vats and produce larg ...
... Example: Diabetic humans don’t produce enough insulin to control the amount of sugar in their blood. We used to harvest insulin from horses. Now, however, thanks to gene splicing we’re able to splice our genes for insulin production into bacteria. We grow the bacteria in large vats and produce larg ...
DNA ends!
... Gene – a DNA region that is transcribed to RNA, and the RNA with a biological function ...
... Gene – a DNA region that is transcribed to RNA, and the RNA with a biological function ...
Microbiology Exam II - University of Evansville Faculty Web sites
... d. Plasmids e. Sex pili 8. What was one of the first and most useful microscopic tests for classifying bacteria that is still important today? a. Gram stain b. Flagella stains c. Simple stains d. Negative stain for capsule e. Metachromatic granule stain 9. Which is NOT true of virus capsids? a. They ...
... d. Plasmids e. Sex pili 8. What was one of the first and most useful microscopic tests for classifying bacteria that is still important today? a. Gram stain b. Flagella stains c. Simple stains d. Negative stain for capsule e. Metachromatic granule stain 9. Which is NOT true of virus capsids? a. They ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... Basic concepts of tumour immunology • Tumors can be initiated by environmental factors and by viruses. • Transformation involves changes in expression of normal cellular ...
... Basic concepts of tumour immunology • Tumors can be initiated by environmental factors and by viruses. • Transformation involves changes in expression of normal cellular ...
432EX2W7
... occurs at the level of the gene, an “P” for PROTEIN in boxes indicating a source of diversity that occurs at the level of the protein and an “N” for NO in boxes indicating a sources of diversity that do not exist. ...
... occurs at the level of the gene, an “P” for PROTEIN in boxes indicating a source of diversity that occurs at the level of the protein and an “N” for NO in boxes indicating a sources of diversity that do not exist. ...
2 - Blue Valley Schools
... 1. You should be familiar with the stages of the cell cycle and know the role of the nuclear membrane, centrioles, and spindle fibers in this cycle. 2. You be able to explain the enzymatic steps involved in DNA replication and know the general goal of the mitosis and the other stages of the cell cyc ...
... 1. You should be familiar with the stages of the cell cycle and know the role of the nuclear membrane, centrioles, and spindle fibers in this cycle. 2. You be able to explain the enzymatic steps involved in DNA replication and know the general goal of the mitosis and the other stages of the cell cyc ...
Exam 3 4/25/07 BISC 4A P. Sengupta Total of 7 questions, 100
... 1. Suppose that an infectious agent such as a virus or bacteria had surface antigens identical to those displayed on the surface of human cells. Would the immune system be able to detect and destroy these agents? Why or why not? 4 points No. Would not recognize them as non-self due to T-cell selecti ...
... 1. Suppose that an infectious agent such as a virus or bacteria had surface antigens identical to those displayed on the surface of human cells. Would the immune system be able to detect and destroy these agents? Why or why not? 4 points No. Would not recognize them as non-self due to T-cell selecti ...
File
... 1. DNA or RNA? 2. Write the complimentary DNA sequence 3. Write the mRNA sequence 4. Write the protein sequence. ...
... 1. DNA or RNA? 2. Write the complimentary DNA sequence 3. Write the mRNA sequence 4. Write the protein sequence. ...
No Slide Title
... colorblindness) had a child what is the percent chance that the child will be red-green colorblind and what would the sex of the child be? ...
... colorblindness) had a child what is the percent chance that the child will be red-green colorblind and what would the sex of the child be? ...
DNA vaccination

DNA vaccination is a technique for protecting an animal against disease by injecting it with genetically engineered DNA so cells directly produce an antigen, resulting in a protective immunological response. Several DNA vaccines have been released for veterinary use, and there has been promising research using the vaccines for viral, bacterial and parasitic diseases, as well as to several tumour types. Although only one DNA vaccine has been approved for human use, DNA vaccines may have a number of potential advantages over conventional vaccines, including the ability to induce a wider range of immune response types.