Review for Post Exam 10 on iLearn
... 1. What differences in DNA gives each organism its own unique look? 2. Why is DNA called a universal code? 3. What macromolecule is DNA and RNA? 4. How are genes coded for in DNA 5. Why does DNA replicate? 6. How is DNA inherited? 7. Describe how DNA replicates? (makes a copy of itself) Using the wo ...
... 1. What differences in DNA gives each organism its own unique look? 2. Why is DNA called a universal code? 3. What macromolecule is DNA and RNA? 4. How are genes coded for in DNA 5. Why does DNA replicate? 6. How is DNA inherited? 7. Describe how DNA replicates? (makes a copy of itself) Using the wo ...
drugs and meds answers antivirals
... Block the virus from entering cell, alter host dna so virus can’t use to replicate, block cells enzymes so viruses can’t replicate, block reproduced viruses from leaving cell 3) What is HIV and what is AIDS? human immunodeficiency virus, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome 4) State reasons why effect ...
... Block the virus from entering cell, alter host dna so virus can’t use to replicate, block cells enzymes so viruses can’t replicate, block reproduced viruses from leaving cell 3) What is HIV and what is AIDS? human immunodeficiency virus, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome 4) State reasons why effect ...
03-Chapter-8-supplement
... It is a control protein that is required to prevent apoptosis The cells remain alive so long as Bcl-2 is present (i.e., rescues lymphocytes from apoptosis) When a CTL delivers a death signal to an infected cell, Bcl-2 expression is turned off, resulting in the cell’s death EBV encodes BHRF1, a Bcl-2 ...
... It is a control protein that is required to prevent apoptosis The cells remain alive so long as Bcl-2 is present (i.e., rescues lymphocytes from apoptosis) When a CTL delivers a death signal to an infected cell, Bcl-2 expression is turned off, resulting in the cell’s death EBV encodes BHRF1, a Bcl-2 ...
Basic Immunology - Pipestone Veterinary Services
... We often are faced with many options to help control disease. Adequate nutrition, sanitation, isolation and treatment of sick animals are often means that help control or minimize disease. Furthermore, some diseases lend themselves to control by vaccination. In the next few paragraphs we will take a ...
... We often are faced with many options to help control disease. Adequate nutrition, sanitation, isolation and treatment of sick animals are often means that help control or minimize disease. Furthermore, some diseases lend themselves to control by vaccination. In the next few paragraphs we will take a ...
DNA fingerprinting Cell Specialization Cells differentiate because of
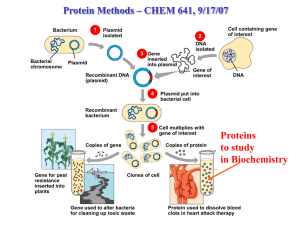
... The bacteria can then produce the desired product Ex. Insulin ...
... The bacteria can then produce the desired product Ex. Insulin ...
14-3 Human Molecular Genetics
... These are specific DNA base sequences that detect the complementary base sequences found in the disease- causing allele ...
... These are specific DNA base sequences that detect the complementary base sequences found in the disease- causing allele ...
1133693644_460426
... • Antigen presenting cells (APCs) – Macrophages and dendritic cells kill microbes – Present intruding microorganisms to T cells ...
... • Antigen presenting cells (APCs) – Macrophages and dendritic cells kill microbes – Present intruding microorganisms to T cells ...
Reproductive cloning
... Subunit Vaccines • a vaccine produced from specific protein subunits of a virus and thus having less risk of adverse reactions than whole virus vaccines. • Used to treat herpes and hepatitis – engineers splice genes from the coat of the virus into a fragment of cowpox (vaccinia) virus genome – the ...
... Subunit Vaccines • a vaccine produced from specific protein subunits of a virus and thus having less risk of adverse reactions than whole virus vaccines. • Used to treat herpes and hepatitis – engineers splice genes from the coat of the virus into a fragment of cowpox (vaccinia) virus genome – the ...
I. Immunity
... blood cells and antibodies 1. White blood cells: two types-T cells and B cells 2. Antibody—protein that disables antigens 3. B cells—makes antibodies 4. T cells—helps make antibodies, kills infected cells 5. Memory B cells—used if attacked again by same antigen -Draw Fig 39.12 p 1037 ...
... blood cells and antibodies 1. White blood cells: two types-T cells and B cells 2. Antibody—protein that disables antigens 3. B cells—makes antibodies 4. T cells—helps make antibodies, kills infected cells 5. Memory B cells—used if attacked again by same antigen -Draw Fig 39.12 p 1037 ...
Gene Expression - Phillips Scientific Methods
... • Active oncogenes + loss of tumor-suppressor genes • The longer we live, the more likely that cancer might develop ...
... • Active oncogenes + loss of tumor-suppressor genes • The longer we live, the more likely that cancer might develop ...
Natural Defence - MedicalBooks.com
... The skin and mucous membranes form the body's first line of defense against disease. Most microscopic pathogens, or microbes, cannot pass through unbroken skin, although they can easily enter through cuts and other wounds. Mucous membranes protect internal organs that are connected with the outside ...
... The skin and mucous membranes form the body's first line of defense against disease. Most microscopic pathogens, or microbes, cannot pass through unbroken skin, although they can easily enter through cuts and other wounds. Mucous membranes protect internal organs that are connected with the outside ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 4. Which one of the following cell type is least effective against extra cellular bacterial pathogen? a) B cells b) cytotoxic Tcells c) TNFγ d) macrophages 5. Immuno suppression is not induced by a) anti histamines b) removal of lymphoid tissue c)use of anti lymphocyte antibodies d) cytotoxic drugs ...
... 4. Which one of the following cell type is least effective against extra cellular bacterial pathogen? a) B cells b) cytotoxic Tcells c) TNFγ d) macrophages 5. Immuno suppression is not induced by a) anti histamines b) removal of lymphoid tissue c)use of anti lymphocyte antibodies d) cytotoxic drugs ...
No Slide Title
... You remove the part of the nucleic acid that does not code for the above functions and add foreign DNA. The virus can then be put into the blood stream and it will enter the cell it is designed to attack and transfer its code ...
... You remove the part of the nucleic acid that does not code for the above functions and add foreign DNA. The virus can then be put into the blood stream and it will enter the cell it is designed to attack and transfer its code ...
Chapter 13 Genetic Engineering - Mrs. Moyer
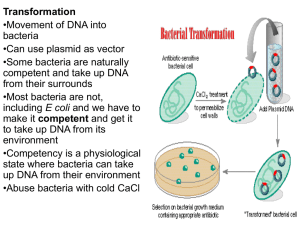
... can synthesize a DNA strand and connect it to a circular DNA molecule known as a plasmid… which can be found naturally in bacteria. This bacteria can then be injected into a plant, and will insert its DNA into the plant. ► If transformation is successful, the recombinant DNA is integrated into one o ...
... can synthesize a DNA strand and connect it to a circular DNA molecule known as a plasmid… which can be found naturally in bacteria. This bacteria can then be injected into a plant, and will insert its DNA into the plant. ► If transformation is successful, the recombinant DNA is integrated into one o ...
Introduction
... or 800µl of plasma, as well as on genomic DNA from an unaffected and a positive control. On an unaffected DNA sample, restriction digest of the PCR product with BsrG1 will not cut the DNA, giving rise to a single 132bp fragment, whereas if the mutation is present a BsrG1 restriction site is created, ...
... or 800µl of plasma, as well as on genomic DNA from an unaffected and a positive control. On an unaffected DNA sample, restriction digest of the PCR product with BsrG1 will not cut the DNA, giving rise to a single 132bp fragment, whereas if the mutation is present a BsrG1 restriction site is created, ...
HEREDITY: INHERITANCE and TRENDS Unit Cover Page Topic
... All cells contain genetic information in the form of DNA molecules. Genes are regions in the DNA that contain instructions that code for the formation of proteins. (LS1.A) ...
... All cells contain genetic information in the form of DNA molecules. Genes are regions in the DNA that contain instructions that code for the formation of proteins. (LS1.A) ...
Intermediate Inheritance or Incomplete Dominance
... • Guanine will bond to Cytosine • Genes are considered to be segments of these molecules with the sequence of bases coding for the amino acids in protein ...
... • Guanine will bond to Cytosine • Genes are considered to be segments of these molecules with the sequence of bases coding for the amino acids in protein ...
Cloning and selection
... When do the cutting and sticking of plasmid and foreign DNA there are several possible outcomes 1. Successful sticking of the plasmid and foreign DNA 2. Recircularization of plasmid without the foreign DNA 3. Circulization of plasmid with other plasmids or several inserts to make huge circular mol ...
... When do the cutting and sticking of plasmid and foreign DNA there are several possible outcomes 1. Successful sticking of the plasmid and foreign DNA 2. Recircularization of plasmid without the foreign DNA 3. Circulization of plasmid with other plasmids or several inserts to make huge circular mol ...
PowerPoint Genetic Technology Notes
... The patient’s cells are then ___________ with the genetically engineered virus. In theory the virus will insert the ___________ gene into the target cell and correct the defect. Gene therapy can be ___________. Genetic Testing Genetic testing can be used to determine if two prospective parents are c ...
... The patient’s cells are then ___________ with the genetically engineered virus. In theory the virus will insert the ___________ gene into the target cell and correct the defect. Gene therapy can be ___________. Genetic Testing Genetic testing can be used to determine if two prospective parents are c ...
6.2 Recombinant DNA Technology
... Fragments of human DNA and plasmid mixed together and join Plasmids enter the bacterial cells, copy themselves, carry recombinant DNA into bacteria Bacteria express gene, synthesize the human protein, can be used for treatments, vaccines, or other purposes ...
... Fragments of human DNA and plasmid mixed together and join Plasmids enter the bacterial cells, copy themselves, carry recombinant DNA into bacteria Bacteria express gene, synthesize the human protein, can be used for treatments, vaccines, or other purposes ...
DNA vaccination

DNA vaccination is a technique for protecting an animal against disease by injecting it with genetically engineered DNA so cells directly produce an antigen, resulting in a protective immunological response. Several DNA vaccines have been released for veterinary use, and there has been promising research using the vaccines for viral, bacterial and parasitic diseases, as well as to several tumour types. Although only one DNA vaccine has been approved for human use, DNA vaccines may have a number of potential advantages over conventional vaccines, including the ability to induce a wider range of immune response types.