ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
... 2. The nitrogenous bases in purines have a two-ringed structure while those in pyrimidines have a single-ring structure. 3. DNA must be replicated so that a complete set of genetic instructions is passed to daughter cells when a cell divides. 4. Such a molecule would bulge where purines paired with ...
... 2. The nitrogenous bases in purines have a two-ringed structure while those in pyrimidines have a single-ring structure. 3. DNA must be replicated so that a complete set of genetic instructions is passed to daughter cells when a cell divides. 4. Such a molecule would bulge where purines paired with ...
Biotechnology Key Terms and Concepts
... A. Definition-use of organisms to perform practical tasks for humans B. Much of biotechnology deals with analyzing and manipulating genomes of organisms at the molecular level (DNA technology) C. Genome-complete set of an organism’s genetic material D. Human genome project– a project aimed at sequen ...
... A. Definition-use of organisms to perform practical tasks for humans B. Much of biotechnology deals with analyzing and manipulating genomes of organisms at the molecular level (DNA technology) C. Genome-complete set of an organism’s genetic material D. Human genome project– a project aimed at sequen ...
Sc9 - a 3.1(student notes)
... Activity: How DNA is organized! Create a project that explains to the class how DNA is organized. Ex: Kids book, A comparison, a 3-D diorama ...
... Activity: How DNA is organized! Create a project that explains to the class how DNA is organized. Ex: Kids book, A comparison, a 3-D diorama ...
cancer epigenetics - Experimental oncology
... Studies of epigenetic alterations started a new era of cancer research. In a few years key discoveries have changed the vision of the determinants of cancer. Genetic and epigenetic alterations accumulated within cells and the interactions of such altered cells with the surrounding stroma components ...
... Studies of epigenetic alterations started a new era of cancer research. In a few years key discoveries have changed the vision of the determinants of cancer. Genetic and epigenetic alterations accumulated within cells and the interactions of such altered cells with the surrounding stroma components ...
Protein Synthesis
... The amino acids called for in the DNA recipe are linked together in a long chain called a polypeptide The polypeptide is folded into a specific shape The shape determines what protein it is The protein will become a part of the cell or part of an organelle ...
... The amino acids called for in the DNA recipe are linked together in a long chain called a polypeptide The polypeptide is folded into a specific shape The shape determines what protein it is The protein will become a part of the cell or part of an organelle ...
Site-specific recombination mechanisms exploit DNA
... bacteriophage (Mu) changes its host range through expression of different tail fibers by changing the orientation of a specific DNA segment, the G segment, in its genome1. The phage-encoded Gin recombinase protein specifically recombined the G segment located between short inverted DNA sequences, bu ...
... bacteriophage (Mu) changes its host range through expression of different tail fibers by changing the orientation of a specific DNA segment, the G segment, in its genome1. The phage-encoded Gin recombinase protein specifically recombined the G segment located between short inverted DNA sequences, bu ...
Lecture 14
... i. Similar to degree to structure of proteins ii. Second degree: wrapped around protein assembly, called histones iii. Nucleosome, not base pair specific iv. Then packed into coils continuous contracting of molecule v. Most of the time, contracted DNA is still accessible to proteins that engage in ...
... i. Similar to degree to structure of proteins ii. Second degree: wrapped around protein assembly, called histones iii. Nucleosome, not base pair specific iv. Then packed into coils continuous contracting of molecule v. Most of the time, contracted DNA is still accessible to proteins that engage in ...
STUDY GUIDE for MICROBIAL GENETICS 1. Define the following
... What is the Rolling Circle Model of bacterial DNA replication? In other words, describe the bidirectionality of bacterial DNA replication. Describe transcription and translation. a. What is the function of RNA Polymerase? b. In prokaryotic cells, where does transcription occur? In eukaryotic cells, ...
... What is the Rolling Circle Model of bacterial DNA replication? In other words, describe the bidirectionality of bacterial DNA replication. Describe transcription and translation. a. What is the function of RNA Polymerase? b. In prokaryotic cells, where does transcription occur? In eukaryotic cells, ...
Unit 2 Review
... 8. State where rRNA, mRNA and tRNA is made and where proteins are made. 9. Sketch a short DNA molecule of 4 base pairs. Label the sugar-phosphate backbone, label the bases you have chosen along with their partners, label H-bonds. 10. Define semiconservative replication, complementary, genome. How ac ...
... 8. State where rRNA, mRNA and tRNA is made and where proteins are made. 9. Sketch a short DNA molecule of 4 base pairs. Label the sugar-phosphate backbone, label the bases you have chosen along with their partners, label H-bonds. 10. Define semiconservative replication, complementary, genome. How ac ...
What`s the Big Deal About DNA?
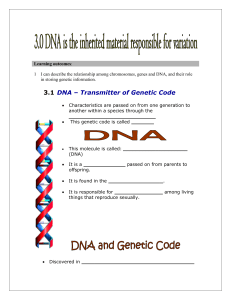
... 1. Describe what DNA looks like, or draw a picture in the space provided. What is a double helix? What do the letters A, T, C, and G stand for? ...
... 1. Describe what DNA looks like, or draw a picture in the space provided. What is a double helix? What do the letters A, T, C, and G stand for? ...
Viruses
... of copies of viruse’s DNA • new virus particles are made • the infected cell then lyses, or busts • 100’s of virus particles are released ...
... of copies of viruse’s DNA • new virus particles are made • the infected cell then lyses, or busts • 100’s of virus particles are released ...
Unit 1 - Glen Rose FFA
... DNA of nucleus is stored by wrapping it around five proteins to form a nucleosome. ...
... DNA of nucleus is stored by wrapping it around five proteins to form a nucleosome. ...
Beads on a string Bowater Biochem Soc Trans 2012
... for the interaction of ISW1 on a unit of two nucleosome particles and showed how ISW1 could set the spacing between adjacent nucleosomes. The data from the Richmond laboratory provide support for ATP-dependent remodelling factors as the important driver of nucleosome positioning. The location of nuc ...
... for the interaction of ISW1 on a unit of two nucleosome particles and showed how ISW1 could set the spacing between adjacent nucleosomes. The data from the Richmond laboratory provide support for ATP-dependent remodelling factors as the important driver of nucleosome positioning. The location of nuc ...
Chromatin Structure Is a Focus for Regulation 30.2
... – Results in alteration of the position of a particular sequence on the nucleosomal suface ...
... – Results in alteration of the position of a particular sequence on the nucleosomal suface ...
Microbiology Unit 3 Study Guide
... 5. Which enzyme makes RNA by reading a strand of DNA? 6. Which enzymes cut DNA in specific locations? 7. What occurs during transcription? 8. What are the steps to obtaining DNA fragments for gel electrophoresis? 9. Which enzyme reads DNA to make a new copy of DNA? 10. How has Escherichia coli been ...
... 5. Which enzyme makes RNA by reading a strand of DNA? 6. Which enzymes cut DNA in specific locations? 7. What occurs during transcription? 8. What are the steps to obtaining DNA fragments for gel electrophoresis? 9. Which enzyme reads DNA to make a new copy of DNA? 10. How has Escherichia coli been ...
AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 16 OUTLINE
... A. The search for the genetic material led to DNA: science as a process Proteins were thought to be the genetic material because: ...
... A. The search for the genetic material led to DNA: science as a process Proteins were thought to be the genetic material because: ...
Introduction to Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources
... Introduction to Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources ...
... Introduction to Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources ...
CALF THYMUS DNA, ACTIVATED - Sigma
... of α- P-TTP (3000 Ci/mmol); and 20 units of DNA Polymerase (Sigma Catalog No. D 9380). 39% of the ...
... of α- P-TTP (3000 Ci/mmol); and 20 units of DNA Polymerase (Sigma Catalog No. D 9380). 39% of the ...
DNA Structure powerpoint
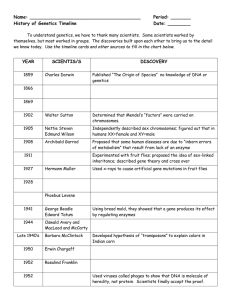
... A. Frederick Griffith – Discovers that a factor in diseased bacteria can transform harmless bacteria into deadly bacteria ...
... A. Frederick Griffith – Discovers that a factor in diseased bacteria can transform harmless bacteria into deadly bacteria ...
國立嘉義大學九十七學年度
... genomic DNA (4 x 106 nucleotide pairs) with HaeIII (4-base recognition site)? or with EcoR I (6base recognition site)? (6%) (3) Which of the following statements are correct? For the incorrect statements, correct them specifically (hint: the correction should not be simply from “can” to “cannot”, or ...
... genomic DNA (4 x 106 nucleotide pairs) with HaeIII (4-base recognition site)? or with EcoR I (6base recognition site)? (6%) (3) Which of the following statements are correct? For the incorrect statements, correct them specifically (hint: the correction should not be simply from “can” to “cannot”, or ...
Nucleosome

A nucleosome is a basic unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes, consisting of a segment of DNA wound in sequence around eight histone protein cores. This structure is often compared to thread wrapped around a spool.Nucleosomes form the fundamental repeating units of eukaryotic chromatin, which is used to pack the large eukaryotic genomes into the nucleus while still ensuring appropriate access to it (in mammalian cells approximately 2 m of linear DNA have to be packed into a nucleus of roughly 10 µm diameter). Nucleosomes are folded through a series of successively higher order structures to eventually form a chromosome; this both compacts DNA and creates an added layer of regulatory control, which ensures correct gene expression. Nucleosomes are thought to carry epigenetically inherited information in the form of covalent modifications of their core histones.Nucleosomes were observed as particles in the electron microscope by Don and Ada Olins and their existence and structure (as histone octamers surrounded by approximately 200 base pairs of DNA) were proposed by Roger Kornberg. The role of the nucleosome as a general gene repressor was demonstrated by Lorch et al. in vitro and by Han and Grunstein in vivo.The nucleosome core particle consists of approximately 147 base pairs of DNA wrapped in 1.67 left-handed superhelical turns around a histone octamer consisting of 2 copies each of the core histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Core particles are connected by stretches of ""linker DNA"", which can be up to about 80 bp long. Technically, a nucleosome is defined as the core particle plus one of these linker regions; however the word is often synonymous with the core particle. Genome-wide nucleosome positioning maps are now available for many model organisms including mouse liver and brain.Linker histones such as H1 and its isoforms are involved in chromatin compaction and sit at the base of the nucleosome near the DNA entry and exit binding to the linker region of the DNA. Non-condensed nucleosomes without the linker histone resemble ""beads on a string of DNA"" under an electron microscope.In contrast to most eukaryotic cells, mature sperm cells largely use protamines to package their genomic DNA, most likely to achieve an even higher packaging ratio. Histone equivalents and a simplified chromatin structure have also been found in Archea, suggesting that eukaryotes are not the only organisms that use nucleosomes.