DNA - VanityWolveriine
... encoded in the sequence of the bases and is transcribed as the strands unwind and replicate.” ...
... encoded in the sequence of the bases and is transcribed as the strands unwind and replicate.” ...
genetics science learning center – internet lesson
... Hint: look at the navigation bar at the top, you’ll need to click on “What is a Gene” to continue. 6. What is a gene? ...
... Hint: look at the navigation bar at the top, you’ll need to click on “What is a Gene” to continue. 6. What is a gene? ...
Chapter 12 DNA Analysis Checkpoint Answers In the nucleus of the
... packed into the nucleus. 4. The Human Genome Project is a unified effort to identify and determine the sequence of all genes found on the human chromosome. 5. The nucleus 6. Adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine 7. The phosphate groups give DNA its acidic properties. 8. Blood, semen, saliva, hair foll ...
... packed into the nucleus. 4. The Human Genome Project is a unified effort to identify and determine the sequence of all genes found on the human chromosome. 5. The nucleus 6. Adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine 7. The phosphate groups give DNA its acidic properties. 8. Blood, semen, saliva, hair foll ...
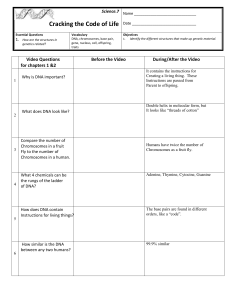
Science.7 Cracking the Code of Life Name Date Essential Questions
... It helps us understand ourselves, as well as diseases and disorders in living things. ...
... It helps us understand ourselves, as well as diseases and disorders in living things. ...
Honors Biology
... 4. Compare and contrast RNA with DNA (consider both the structure of each and the purpose of each in the cell). 5. Describe the process of protein synthesis (both transcription and translation). 6. Explain the steps of mRNA processing and how it can result in different proteins. 7. Describe the rela ...
... 4. Compare and contrast RNA with DNA (consider both the structure of each and the purpose of each in the cell). 5. Describe the process of protein synthesis (both transcription and translation). 6. Explain the steps of mRNA processing and how it can result in different proteins. 7. Describe the rela ...
UNIT 7 – MOLECULAR GENETICS Mon, 1/23 – Mon, 2/13 Unit
... Distinguish among mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA in terms of location and function. Describe the structure of a ribosome and explain how this structure relates to its function. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes. Define codon and list the three stop and one start codons. Sequence the st ...
... Distinguish among mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA in terms of location and function. Describe the structure of a ribosome and explain how this structure relates to its function. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes. Define codon and list the three stop and one start codons. Sequence the st ...
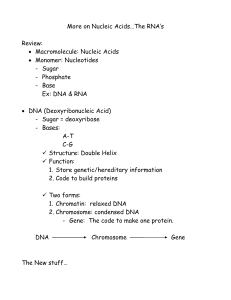
Notes: More on Nucleic Acids
... 1. Store genetic/hereditary information 2. Code to build proteins Two forms: 1. Chromatin: relaxed DNA 2. Chromosome: condensed DNA - Gene: The code to make one protein. DNA ...
... 1. Store genetic/hereditary information 2. Code to build proteins Two forms: 1. Chromatin: relaxed DNA 2. Chromosome: condensed DNA - Gene: The code to make one protein. DNA ...
Science and Society: Unit 2 Review Packet Directions: Use your
... mRNA ________________________________________________________ amino acids ________________________________________________________ ...
... mRNA ________________________________________________________ amino acids ________________________________________________________ ...
Bio 313 worksheet 2 - Iowa State University
... technique called electrophoresis. With this technique, DNA molecules are placed in a gel, an electrical current is applied to the gel, and the DNA molecules migrate toward the positive pole of the current. What aspect of its structure causes a DNA molecule to migrate toward the positive pole? ...
... technique called electrophoresis. With this technique, DNA molecules are placed in a gel, an electrical current is applied to the gel, and the DNA molecules migrate toward the positive pole of the current. What aspect of its structure causes a DNA molecule to migrate toward the positive pole? ...
Acetyl-Histone H4 (Lys5) Polyclonal Antibody
... consists of four core histone proteins (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4), which undergo multiple types of post-translational modifications, including acetylation, phosphorylation, methylation, and ubiquitination (1,2). Histone acetylation occurs mainly on the amino-terminal tail domains of histones H2A (Lys5), ...
... consists of four core histone proteins (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4), which undergo multiple types of post-translational modifications, including acetylation, phosphorylation, methylation, and ubiquitination (1,2). Histone acetylation occurs mainly on the amino-terminal tail domains of histones H2A (Lys5), ...
DNA to Protein - Duplin County Schools
... http://www.classzone.com/cz/books/bio_07/resources/htmls/interactive_review/bio_intrev.html ...
... http://www.classzone.com/cz/books/bio_07/resources/htmls/interactive_review/bio_intrev.html ...
Document
... DNA Forensics and Civil Liberties Workshop Summary •Perspective on DNA Testing & Forensics - Rothstein •Daubert Standard •Listen to the Experts -- Daubert, Frye, and California ...
... DNA Forensics and Civil Liberties Workshop Summary •Perspective on DNA Testing & Forensics - Rothstein •Daubert Standard •Listen to the Experts -- Daubert, Frye, and California ...
Chapter 10
... The following is a list of the main themes covered in this chapter and some study objectives. As you study, focus on these areas. Understand how the information you study fits into these themes and how these themes relate to each other. Be sure you master each objective before moving on. 1. Various ...
... The following is a list of the main themes covered in this chapter and some study objectives. As you study, focus on these areas. Understand how the information you study fits into these themes and how these themes relate to each other. Be sure you master each objective before moving on. 1. Various ...
notes
... • First method is by “cloning”, i.e. introduce the gene into a bacterial cell then grow up large amounts and extract DNA (in vivo) • Second method is by “polymerase chain reaction” (PCR) using DNA polymerase to amplify the gene in a test-tube (in vitro) • Both methods have their uses but PCR is pref ...
... • First method is by “cloning”, i.e. introduce the gene into a bacterial cell then grow up large amounts and extract DNA (in vivo) • Second method is by “polymerase chain reaction” (PCR) using DNA polymerase to amplify the gene in a test-tube (in vitro) • Both methods have their uses but PCR is pref ...
Use the diagram to match the letter (A-C) to the correct term(1
... 1. _______ 5-Carbon sugar (deoxyribose) 2. ________ Nitrogen base (adenine) 3. ________ Phosphate group Use the diagram to match the letter (W-Z) to the correct term(4-7). 4. ______ Complementary base pair. 5. ______ Hydrogen bond. 6. ______ Individual nitrogen base. 7. ______ Sugar-phosphate backbo ...
... 1. _______ 5-Carbon sugar (deoxyribose) 2. ________ Nitrogen base (adenine) 3. ________ Phosphate group Use the diagram to match the letter (W-Z) to the correct term(4-7). 4. ______ Complementary base pair. 5. ______ Hydrogen bond. 6. ______ Individual nitrogen base. 7. ______ Sugar-phosphate backbo ...
DNA and Heritable Traits - JA Williams High School
... Describe the type of cell division that occurs in the body cells of multicellular organisms ...
... Describe the type of cell division that occurs in the body cells of multicellular organisms ...
Class 11
... between histones and DNA with ~1/2 forming between amino acids and phosphates on the DNA Hydrophobic bonds and salt bridges also hold the core together and the DNA The long amino terminal tails of each histone extend out from the central portion of the nucleosome ...
... between histones and DNA with ~1/2 forming between amino acids and phosphates on the DNA Hydrophobic bonds and salt bridges also hold the core together and the DNA The long amino terminal tails of each histone extend out from the central portion of the nucleosome ...
Nucleosome

A nucleosome is a basic unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes, consisting of a segment of DNA wound in sequence around eight histone protein cores. This structure is often compared to thread wrapped around a spool.Nucleosomes form the fundamental repeating units of eukaryotic chromatin, which is used to pack the large eukaryotic genomes into the nucleus while still ensuring appropriate access to it (in mammalian cells approximately 2 m of linear DNA have to be packed into a nucleus of roughly 10 µm diameter). Nucleosomes are folded through a series of successively higher order structures to eventually form a chromosome; this both compacts DNA and creates an added layer of regulatory control, which ensures correct gene expression. Nucleosomes are thought to carry epigenetically inherited information in the form of covalent modifications of their core histones.Nucleosomes were observed as particles in the electron microscope by Don and Ada Olins and their existence and structure (as histone octamers surrounded by approximately 200 base pairs of DNA) were proposed by Roger Kornberg. The role of the nucleosome as a general gene repressor was demonstrated by Lorch et al. in vitro and by Han and Grunstein in vivo.The nucleosome core particle consists of approximately 147 base pairs of DNA wrapped in 1.67 left-handed superhelical turns around a histone octamer consisting of 2 copies each of the core histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Core particles are connected by stretches of ""linker DNA"", which can be up to about 80 bp long. Technically, a nucleosome is defined as the core particle plus one of these linker regions; however the word is often synonymous with the core particle. Genome-wide nucleosome positioning maps are now available for many model organisms including mouse liver and brain.Linker histones such as H1 and its isoforms are involved in chromatin compaction and sit at the base of the nucleosome near the DNA entry and exit binding to the linker region of the DNA. Non-condensed nucleosomes without the linker histone resemble ""beads on a string of DNA"" under an electron microscope.In contrast to most eukaryotic cells, mature sperm cells largely use protamines to package their genomic DNA, most likely to achieve an even higher packaging ratio. Histone equivalents and a simplified chromatin structure have also been found in Archea, suggesting that eukaryotes are not the only organisms that use nucleosomes.