The protein that assesses distances
... Trieste, and Kuni Iwasa, from the US National Institutes of Health (NIH), have answered this question by means of a theoretical study. Both Florescu and Iwasa were at the Max Planck Institute for Physics of Complex Systems in Dresden when they started their work for this research. “It is indeed a ...
... Trieste, and Kuni Iwasa, from the US National Institutes of Health (NIH), have answered this question by means of a theoretical study. Both Florescu and Iwasa were at the Max Planck Institute for Physics of Complex Systems in Dresden when they started their work for this research. “It is indeed a ...
2.5.4. DNA Revision Qs
... 3 Say if the following variations are inherited or acquired. (a) freckles _____________________________________ (b) the production of an enzyme _____________________________________ (c) the ability to play a musical instrument _____________________________________ (d) the ability to form a blood clo ...
... 3 Say if the following variations are inherited or acquired. (a) freckles _____________________________________ (b) the production of an enzyme _____________________________________ (c) the ability to play a musical instrument _____________________________________ (d) the ability to form a blood clo ...
Does your DNA define you Ans
... Now we have more understanding of the epigenome and how it is related to health and disease, this knowledge can be exploited to help develop drugs which change gene expression profiles. Unlike the genome which is largely static, the epigenome is more dynamic and we have more influence over it. Since ...
... Now we have more understanding of the epigenome and how it is related to health and disease, this knowledge can be exploited to help develop drugs which change gene expression profiles. Unlike the genome which is largely static, the epigenome is more dynamic and we have more influence over it. Since ...
Organization of Eukaryotic DNA Dr: Hussein abdelaziz
... 30nm fiber also called nucleofilament which look like solenoid (cylindrical coil) ...
... 30nm fiber also called nucleofilament which look like solenoid (cylindrical coil) ...
Webquests_files/Genes and DNA SWQ
... The four nucleotides Difference between dominant and recessive alleles ...
... The four nucleotides Difference between dominant and recessive alleles ...
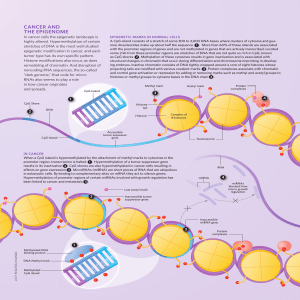
CaNCer aND THe ePIGeNOMe
... A CpG island consists of a stretch of some 300 to 3,000 DNA bases where clusters of cytosine and guanine dinucleotides make up about half the sequence 1 . More than 60% of these islands are associated with the promoter regions of genes and are not methylated in genes that are actively transcribed. ...
... A CpG island consists of a stretch of some 300 to 3,000 DNA bases where clusters of cytosine and guanine dinucleotides make up about half the sequence 1 . More than 60% of these islands are associated with the promoter regions of genes and are not methylated in genes that are actively transcribed. ...
Setting the stage for passing on epigenetic information to the next
... chromatin based epigenetic information is retained during the development of the sperm that eventually may be passed on to the next generation. In sperm, DNA is 10- to 20-fold more tightly packed than in nuclei of regular cells. The tight packaging of DNA is mediated by protamine proteins, which are ...
... chromatin based epigenetic information is retained during the development of the sperm that eventually may be passed on to the next generation. In sperm, DNA is 10- to 20-fold more tightly packed than in nuclei of regular cells. The tight packaging of DNA is mediated by protamine proteins, which are ...
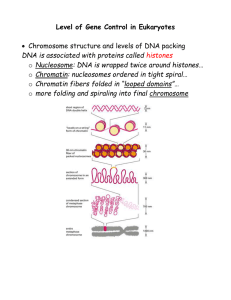
struktur dan fungsi kromosom
... Histones – small proteins with basic, positively charged amino acids lysine and arginine Bind to and neutralize negatively charged DNA Make up half of all chromatin protein by weight Five types: H1, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 Core histones make up nucleosome: H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 DNA and histone synthesis ...
... Histones – small proteins with basic, positively charged amino acids lysine and arginine Bind to and neutralize negatively charged DNA Make up half of all chromatin protein by weight Five types: H1, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 Core histones make up nucleosome: H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 DNA and histone synthesis ...
WS 12 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State University
... Why is dATP one of the four precursors of DNA, but dAMP is not? ...
... Why is dATP one of the four precursors of DNA, but dAMP is not? ...
Genetic Controls in Eukaryotes
... - Histone modification o Histone acetylation (acetyl groups -C0CH3) are attached to + (lysine) histone tails. o When acetylated = neutral and cannot bind to neighboring nucleosomes o No binding = loose structure = easier access to genes for transcription. o Remove these = deacetylation. = inactive g ...
... - Histone modification o Histone acetylation (acetyl groups -C0CH3) are attached to + (lysine) histone tails. o When acetylated = neutral and cannot bind to neighboring nucleosomes o No binding = loose structure = easier access to genes for transcription. o Remove these = deacetylation. = inactive g ...
A surprising application of polynomials in daily life
... Knot theory in mathematics has some exciting applications in biology – human DNA. ...
... Knot theory in mathematics has some exciting applications in biology – human DNA. ...
Scientists Say They`ve Found a Code Beyond Genetics in DNA
... was “a profound insight if true,” because it would explain many aspects of how the DNA is controlled. The nucleosome is made up of proteins known as histones, which are among the most highly conserved in evolution, meaning that they change very little from one species to another. A histone of peas a ...
... was “a profound insight if true,” because it would explain many aspects of how the DNA is controlled. The nucleosome is made up of proteins known as histones, which are among the most highly conserved in evolution, meaning that they change very little from one species to another. A histone of peas a ...
MSc / BSc positions in Systems Biology of Gene Regulation
... What defines the identity of a cell? How is the same genetic code used to build more than 200 different cell types with distinct physiological and morphological properties? These fundamental questions drive our enthusiasm for understanding how information processing is regulated at the level of chro ...
... What defines the identity of a cell? How is the same genetic code used to build more than 200 different cell types with distinct physiological and morphological properties? These fundamental questions drive our enthusiasm for understanding how information processing is regulated at the level of chro ...
Vocabulary 7
... • When one of the 4 base pairs is : –(substitution) “replaced” or –(insertion) “added” or –(deletion) “removed” ...
... • When one of the 4 base pairs is : –(substitution) “replaced” or –(insertion) “added” or –(deletion) “removed” ...
No Slide Title
... HAT complexes often contain several trancription regulatory proteins. • Example of the SAGA complex components: • Gcn5: catalytic subunit, histone acetyl transferase • Ada proteins – transcription adaptor proteins required for function of some activators in yeast. • Spt proteins (TBP-group) – regul ...
... HAT complexes often contain several trancription regulatory proteins. • Example of the SAGA complex components: • Gcn5: catalytic subunit, histone acetyl transferase • Ada proteins – transcription adaptor proteins required for function of some activators in yeast. • Spt proteins (TBP-group) – regul ...
DNA Personal Ads
... sequence is really dull, and I’m ready to move on to more exciting things. I’m looking for my true love, mRNA. (transcription) ...
... sequence is really dull, and I’m ready to move on to more exciting things. I’m looking for my true love, mRNA. (transcription) ...
Nucleosome

A nucleosome is a basic unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes, consisting of a segment of DNA wound in sequence around eight histone protein cores. This structure is often compared to thread wrapped around a spool.Nucleosomes form the fundamental repeating units of eukaryotic chromatin, which is used to pack the large eukaryotic genomes into the nucleus while still ensuring appropriate access to it (in mammalian cells approximately 2 m of linear DNA have to be packed into a nucleus of roughly 10 µm diameter). Nucleosomes are folded through a series of successively higher order structures to eventually form a chromosome; this both compacts DNA and creates an added layer of regulatory control, which ensures correct gene expression. Nucleosomes are thought to carry epigenetically inherited information in the form of covalent modifications of their core histones.Nucleosomes were observed as particles in the electron microscope by Don and Ada Olins and their existence and structure (as histone octamers surrounded by approximately 200 base pairs of DNA) were proposed by Roger Kornberg. The role of the nucleosome as a general gene repressor was demonstrated by Lorch et al. in vitro and by Han and Grunstein in vivo.The nucleosome core particle consists of approximately 147 base pairs of DNA wrapped in 1.67 left-handed superhelical turns around a histone octamer consisting of 2 copies each of the core histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Core particles are connected by stretches of ""linker DNA"", which can be up to about 80 bp long. Technically, a nucleosome is defined as the core particle plus one of these linker regions; however the word is often synonymous with the core particle. Genome-wide nucleosome positioning maps are now available for many model organisms including mouse liver and brain.Linker histones such as H1 and its isoforms are involved in chromatin compaction and sit at the base of the nucleosome near the DNA entry and exit binding to the linker region of the DNA. Non-condensed nucleosomes without the linker histone resemble ""beads on a string of DNA"" under an electron microscope.In contrast to most eukaryotic cells, mature sperm cells largely use protamines to package their genomic DNA, most likely to achieve an even higher packaging ratio. Histone equivalents and a simplified chromatin structure have also been found in Archea, suggesting that eukaryotes are not the only organisms that use nucleosomes.