suggested essay-type questions for next exam
... bromide, a planar molecule, “intercalates” itself between the stacked DNA base pairs, thereby unwinding the supercoils. However, the linking number of the DNA is not changed! Explain the physical basis for the ability of ethidium bromide to “unwind” these supercoils. (You will have to look at the de ...
... bromide, a planar molecule, “intercalates” itself between the stacked DNA base pairs, thereby unwinding the supercoils. However, the linking number of the DNA is not changed! Explain the physical basis for the ability of ethidium bromide to “unwind” these supercoils. (You will have to look at the de ...
2nd Semester Review The second semester test covers Meiosis
... Physiology: Digestive System, Circulatory System and Respiratory System, and Ecology. This list will help you prepare. You should also look over all the review documents that you have in your workbook for these units. ...
... Physiology: Digestive System, Circulatory System and Respiratory System, and Ecology. This list will help you prepare. You should also look over all the review documents that you have in your workbook for these units. ...
Webquest
... Please tour the following website based on the DNA content you have been learning recently. They will show you visually some of what is going on and help you to understand exactly what it happening. You will have to answer some questions based on what you see. 1. First go to the page: http://learn.g ...
... Please tour the following website based on the DNA content you have been learning recently. They will show you visually some of what is going on and help you to understand exactly what it happening. You will have to answer some questions based on what you see. 1. First go to the page: http://learn.g ...
DNA - KSUMSC
... Nucleus is very small to have a large of DNA so DNA will organized into chromatin ...
... Nucleus is very small to have a large of DNA so DNA will organized into chromatin ...
A Tour of the Cell - Ursuline High School
... membrane separated by a 20-40 nm space. Inner membrane supported by a protein matrix (braces) which gives the shape to the nucleus. ...
... membrane separated by a 20-40 nm space. Inner membrane supported by a protein matrix (braces) which gives the shape to the nucleus. ...
GDR ADN 2014 Chromatin folding in estrogen regulated
... Variations in the three-dimensional organization of chromosomes guide genome function from gene expression to DNA repair and recombination. DNA-bound transcription factors recruit many chromatin remodeling and modifying complexes to activate transcription. How the local chromatin environment prepare ...
... Variations in the three-dimensional organization of chromosomes guide genome function from gene expression to DNA repair and recombination. DNA-bound transcription factors recruit many chromatin remodeling and modifying complexes to activate transcription. How the local chromatin environment prepare ...
4.1 Le Noyau
... • A joins with T • G joins with C • But the order and number of these bases can vary greatly within the DNA molecule ...
... • A joins with T • G joins with C • But the order and number of these bases can vary greatly within the DNA molecule ...
1. The products of mitosis are .
... 2. Genetically diverse offspring result from __________. A. binary fission B. mitosis C. sexual reproduction D. cytokinesis E. cloning 3. How many chromosomes do humans have in their body cells? A. 48 B. 46 C. 50 4. Which answer is in order from SMALLEST to BIGGEST? A. gene, chromosome, cell B. chro ...
... 2. Genetically diverse offspring result from __________. A. binary fission B. mitosis C. sexual reproduction D. cytokinesis E. cloning 3. How many chromosomes do humans have in their body cells? A. 48 B. 46 C. 50 4. Which answer is in order from SMALLEST to BIGGEST? A. gene, chromosome, cell B. chro ...
It all started in the 700s when Chinese used fingerprints to launch
... of significant documents. Afterward, a new field entitled Forensic Science was formed by merging Mathematics, Chemistry, Physics and Biology, toward the designing of novel techniques that will assist in cracking crimes. Sherlock Homes said: ‘’it has long been an axiom of mine that the little things ...
... of significant documents. Afterward, a new field entitled Forensic Science was formed by merging Mathematics, Chemistry, Physics and Biology, toward the designing of novel techniques that will assist in cracking crimes. Sherlock Homes said: ‘’it has long been an axiom of mine that the little things ...
Genetics
... What is the genetic material? In eukaryotes & prokaryotes it is DNA, in viruses it can be either DNA or RNA. What do DNA & RNA stand for? DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid / RNA: ribonucleic ...
... What is the genetic material? In eukaryotes & prokaryotes it is DNA, in viruses it can be either DNA or RNA. What do DNA & RNA stand for? DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid / RNA: ribonucleic ...
Biology: Cells and Organisms Notes
... More nuclear pores if highly active and connect outer and inner membranes of nuclear envelope (continuous). Pores are selective – RNA passes through. Long strands of DNA are covered in globular proteins – histones. DNA double wraps around histone to form a nucleosome. Histones are +ve, DNA –ve. A co ...
... More nuclear pores if highly active and connect outer and inner membranes of nuclear envelope (continuous). Pores are selective – RNA passes through. Long strands of DNA are covered in globular proteins – histones. DNA double wraps around histone to form a nucleosome. Histones are +ve, DNA –ve. A co ...
MolecularBiology1APLab6
... • Contain random DNA fragments that are collected or exchanged w/ other bacteria • Contain nonsense information • Sometimes contain useful information like antibiotic resistance ...
... • Contain random DNA fragments that are collected or exchanged w/ other bacteria • Contain nonsense information • Sometimes contain useful information like antibiotic resistance ...
DNA Cloning - MrMsciences
... from a single ancestor • produces many copies of a piece of DNA • uses a little fraction as gene of interest • cultivates a large amount for studying functions ...
... from a single ancestor • produces many copies of a piece of DNA • uses a little fraction as gene of interest • cultivates a large amount for studying functions ...
Ch. 13 Genetic Engineering, Chapter Summary Date
... 2. scientists manipulate the DNA molecule in hopes to increase this. 3. a tool used to ensure that the characteristics that make each breed unique will preserved by crossing individuals with similar characteristics. 4. these bacteria have been engineered to produce human proteins like insulin, human ...
... 2. scientists manipulate the DNA molecule in hopes to increase this. 3. a tool used to ensure that the characteristics that make each breed unique will preserved by crossing individuals with similar characteristics. 4. these bacteria have been engineered to produce human proteins like insulin, human ...
Genetics Science Learning Center
... Center Objective: Students will browse the Genetics Science Learning Center Website to learn about basic genetics, including the structure of DNA, transcription and translation, and the relationship between genes, proteins and traits. Site Location: http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/ .............Click ...
... Center Objective: Students will browse the Genetics Science Learning Center Website to learn about basic genetics, including the structure of DNA, transcription and translation, and the relationship between genes, proteins and traits. Site Location: http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/ .............Click ...
Jeopardy - Grayslake Central High School
... Potpourri for 400 What is transformation, and why is it an important step in gene cloning? It is the absorption of foreign plasmid DNA into bacterial cells. Once the plasmid is absorbed, the bacteria can express the new genes, and they copy the whole plasmid whenever they carry out binary fission. ...
... Potpourri for 400 What is transformation, and why is it an important step in gene cloning? It is the absorption of foreign plasmid DNA into bacterial cells. Once the plasmid is absorbed, the bacteria can express the new genes, and they copy the whole plasmid whenever they carry out binary fission. ...
Study Guide for LS
... ultraviolet rays. A mutation in DNA could result in no change, death or a genetic disorder. Your phenotype (physical appearance) can be affected by heredity and the environment. ...
... ultraviolet rays. A mutation in DNA could result in no change, death or a genetic disorder. Your phenotype (physical appearance) can be affected by heredity and the environment. ...
Genetic Changes = Mutations
... c. THE DOG BIT THE CAR (each word is representing an amino acid. The whole sentence represents a protein d. Sickle cell anemia is an example of a disease caused by this very tiny DNA error 8. Frameshift mutation: a. a single base is added or deleted in the DNA sequence b. resulting in every amino ac ...
... c. THE DOG BIT THE CAR (each word is representing an amino acid. The whole sentence represents a protein d. Sickle cell anemia is an example of a disease caused by this very tiny DNA error 8. Frameshift mutation: a. a single base is added or deleted in the DNA sequence b. resulting in every amino ac ...
Go to - Net Start Class
... This explore is best when the students can use computers but can be done globally if necessary. ...
... This explore is best when the students can use computers but can be done globally if necessary. ...
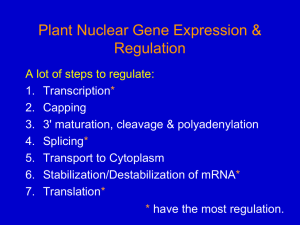
Nuclear gene expression 1
... Nucleosome core = octamer of histones (2 each of H2A, H2B, H3, H4) + 2 wraps (145 bp) of DNA ...
... Nucleosome core = octamer of histones (2 each of H2A, H2B, H3, H4) + 2 wraps (145 bp) of DNA ...
BIO_Protein_Synthesis_Outline - Cole Camp R-1
... ▸Describe the DNA molecule as being Spiral in Shape with the BASES on the inside and the Sugar- Phosphate Groups on the outside. ...
... ▸Describe the DNA molecule as being Spiral in Shape with the BASES on the inside and the Sugar- Phosphate Groups on the outside. ...
DNA!
... tech to create a karyotype (a map of chromosomes) to determine if trisomy 21 (3 chromosomes at 21 instead of 2) occurs. 2. PKU – tested using a blood sample to look for the presence or absence of certain proteins. This indicated whether a person’s genes are functioning normally. PKU is when a person ...
... tech to create a karyotype (a map of chromosomes) to determine if trisomy 21 (3 chromosomes at 21 instead of 2) occurs. 2. PKU – tested using a blood sample to look for the presence or absence of certain proteins. This indicated whether a person’s genes are functioning normally. PKU is when a person ...
Nucleosome

A nucleosome is a basic unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes, consisting of a segment of DNA wound in sequence around eight histone protein cores. This structure is often compared to thread wrapped around a spool.Nucleosomes form the fundamental repeating units of eukaryotic chromatin, which is used to pack the large eukaryotic genomes into the nucleus while still ensuring appropriate access to it (in mammalian cells approximately 2 m of linear DNA have to be packed into a nucleus of roughly 10 µm diameter). Nucleosomes are folded through a series of successively higher order structures to eventually form a chromosome; this both compacts DNA and creates an added layer of regulatory control, which ensures correct gene expression. Nucleosomes are thought to carry epigenetically inherited information in the form of covalent modifications of their core histones.Nucleosomes were observed as particles in the electron microscope by Don and Ada Olins and their existence and structure (as histone octamers surrounded by approximately 200 base pairs of DNA) were proposed by Roger Kornberg. The role of the nucleosome as a general gene repressor was demonstrated by Lorch et al. in vitro and by Han and Grunstein in vivo.The nucleosome core particle consists of approximately 147 base pairs of DNA wrapped in 1.67 left-handed superhelical turns around a histone octamer consisting of 2 copies each of the core histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Core particles are connected by stretches of ""linker DNA"", which can be up to about 80 bp long. Technically, a nucleosome is defined as the core particle plus one of these linker regions; however the word is often synonymous with the core particle. Genome-wide nucleosome positioning maps are now available for many model organisms including mouse liver and brain.Linker histones such as H1 and its isoforms are involved in chromatin compaction and sit at the base of the nucleosome near the DNA entry and exit binding to the linker region of the DNA. Non-condensed nucleosomes without the linker histone resemble ""beads on a string of DNA"" under an electron microscope.In contrast to most eukaryotic cells, mature sperm cells largely use protamines to package their genomic DNA, most likely to achieve an even higher packaging ratio. Histone equivalents and a simplified chromatin structure have also been found in Archea, suggesting that eukaryotes are not the only organisms that use nucleosomes.