Kinetic proofreading of gene activation by chromatin remodeling
... histone tail modifiers, chromatin remodelers, and transcription factors allows to discriminate right from wrong genes to be activated. While in our example we have distinguished between an acetylated versus a deacetylated state, other covalent modifications and their combinations [the “histone code, ...
... histone tail modifiers, chromatin remodelers, and transcription factors allows to discriminate right from wrong genes to be activated. While in our example we have distinguished between an acetylated versus a deacetylated state, other covalent modifications and their combinations [the “histone code, ...
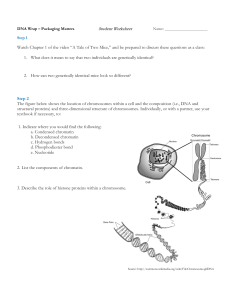
Student Worksheet
... distribution among genetically identical offspring whose mothers received a diet supplemented with 250 mg/kg diet of genistein. The shifts in coat color and body weight were mediated by increased methylation … of the Agouti gene. Hypermethylation in the genistein-supplemented population results in d ...
... distribution among genetically identical offspring whose mothers received a diet supplemented with 250 mg/kg diet of genistein. The shifts in coat color and body weight were mediated by increased methylation … of the Agouti gene. Hypermethylation in the genistein-supplemented population results in d ...
76d26f86fc8fd4690d9502156978f6866d36b66a
... Has allowed molecular genetics to become part of ______________________ investigations. Applications. ...
... Has allowed molecular genetics to become part of ______________________ investigations. Applications. ...
DNA PPT - McKinney ISD Staff Sites
... instructions for making proteins (a few make RNA). • Humans have 20,000-25,000 genes. • Only about 2% of our DNA is genes – The noncoding regions function to provide chromosomal structural integrity and to regulate where, when, and in what quantity proteins are made. ...
... instructions for making proteins (a few make RNA). • Humans have 20,000-25,000 genes. • Only about 2% of our DNA is genes – The noncoding regions function to provide chromosomal structural integrity and to regulate where, when, and in what quantity proteins are made. ...
Bell Ringer
... Genes in cells are made of DNA, which is a complex molecule. The structure of a DNA molecule contains the information that a cell needs to carry out all of its functions. In a way, DNA is like the cell’s encyclopedia. Suppose that you go to the library to do research for a science project. You find ...
... Genes in cells are made of DNA, which is a complex molecule. The structure of a DNA molecule contains the information that a cell needs to carry out all of its functions. In a way, DNA is like the cell’s encyclopedia. Suppose that you go to the library to do research for a science project. You find ...
交通大學特色研究計畫邀請 - 國立交通大學生物資訊研究所
... DNA molecule into distinct topological domains. Our approach is based on the successful construction of a series of plasmid DNA templates that contain many tandem copies of one or two DNA-binding sites in two different locations. With these approaches and atomic force microscopy, we discovered that ...
... DNA molecule into distinct topological domains. Our approach is based on the successful construction of a series of plasmid DNA templates that contain many tandem copies of one or two DNA-binding sites in two different locations. With these approaches and atomic force microscopy, we discovered that ...
Exam Review 2B -- Rodermel
... 12. RNA polymerases carry out transcription at a much slower rate than that at which DNA polymerases carry out replication. Why is speed more important in replication than in transcription? ...
... 12. RNA polymerases carry out transcription at a much slower rate than that at which DNA polymerases carry out replication. Why is speed more important in replication than in transcription? ...
Changes in DNA can produce Variation
... Not smoking can prevent emphysema and many types of cancer ...
... Not smoking can prevent emphysema and many types of cancer ...
BIO SOL Review 16
... carrying coded information from the nucleus? a. mRNA b. The ribosomes c. ATP d. The cell membrane 11. (2005-13) Tissue samples taken from the heart and stomach of a grasshopper would be expected to have the same — a. metabolic rates b. cell shape c. DNA d. cell size 12. (2003-9) Which of the followi ...
... carrying coded information from the nucleus? a. mRNA b. The ribosomes c. ATP d. The cell membrane 11. (2005-13) Tissue samples taken from the heart and stomach of a grasshopper would be expected to have the same — a. metabolic rates b. cell shape c. DNA d. cell size 12. (2003-9) Which of the followi ...
Electrophoresis literally means “the condition of
... A segment of DNA has two restriction sites–I and II. When incubated with restriction enzymes I and II, three fragments will be formed–a, b, and c. Which of the following gels produced by electrophoresis would represent the separation and identity of these fragments? ...
... A segment of DNA has two restriction sites–I and II. When incubated with restriction enzymes I and II, three fragments will be formed–a, b, and c. Which of the following gels produced by electrophoresis would represent the separation and identity of these fragments? ...
Nuclear genome 1
... • DNA organized in chromosomes & replicated as in other systems • Euchromatin & Heterochromatin (transcriptionally inactive) present • DNA packaged by histones into nucleosomes, then further coiled into 30 nm fibers • DNA also attached to the nuclear matrix: – SAR (scaffold attachment regions)- A-T ...
... • DNA organized in chromosomes & replicated as in other systems • Euchromatin & Heterochromatin (transcriptionally inactive) present • DNA packaged by histones into nucleosomes, then further coiled into 30 nm fibers • DNA also attached to the nuclear matrix: – SAR (scaffold attachment regions)- A-T ...
Sc9 - a 3.1(teacher notes)
... These variations in forms are called alleles. The ultimate combination of the chromosome pair is what makes the variation possible - combining the different variations of different characteristics to create a unique variation. ...
... These variations in forms are called alleles. The ultimate combination of the chromosome pair is what makes the variation possible - combining the different variations of different characteristics to create a unique variation. ...
2013 DNA, Repl, Trans and Transl Review
... 1. What are the subunits called that make up DNA? 2. What three things make up a nucleotide? 3. Describe the structure of DNA. 4. An organism's characteristics and directions for proteins synthesis are coded for by molecules of __________. 5. What are the monomers of proteins? How many of these mono ...
... 1. What are the subunits called that make up DNA? 2. What three things make up a nucleotide? 3. Describe the structure of DNA. 4. An organism's characteristics and directions for proteins synthesis are coded for by molecules of __________. 5. What are the monomers of proteins? How many of these mono ...
DNA, RNA, PROTEINS STARTS WITH
... 2. The group of 3 nitrogen bases in the mRNA message that is read together is called a _C_ __ __ __ __. 3. In dividing cells, the DNA is scrunched into _C_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ so it can be moved. 4. The mRNA message tells the ribosomes which _A_ __ __ __ __ _A_ __ __ __ to put in next when ...
... 2. The group of 3 nitrogen bases in the mRNA message that is read together is called a _C_ __ __ __ __. 3. In dividing cells, the DNA is scrunched into _C_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ so it can be moved. 4. The mRNA message tells the ribosomes which _A_ __ __ __ __ _A_ __ __ __ to put in next when ...
verbal quiz genetics 2017
... 10. Each step of the ladder are made up of / two matching bases (one base pair) 11. In DNA the bases always pair / A-T , C-G 12. What part of the DNA contains the genetic code / Our genetic code is in the sequence of bases in our DNA 13. During DNA replication the DNA unzips between the / Nitrogen b ...
... 10. Each step of the ladder are made up of / two matching bases (one base pair) 11. In DNA the bases always pair / A-T , C-G 12. What part of the DNA contains the genetic code / Our genetic code is in the sequence of bases in our DNA 13. During DNA replication the DNA unzips between the / Nitrogen b ...
Exporter la page en pdf
... The SANT domain is a nucleosome recognition module found in transcriptional regulatory proteins, including chromatin-modifying enzymes. It shows high functional degeneracy between species, varying in sequence and copy number. Here, we investigate functions in vivo associated with two SANT motifs, SA ...
... The SANT domain is a nucleosome recognition module found in transcriptional regulatory proteins, including chromatin-modifying enzymes. It shows high functional degeneracy between species, varying in sequence and copy number. Here, we investigate functions in vivo associated with two SANT motifs, SA ...
HNF4a Network - University of Wisconsin–Madison
... Ifld2 (Nipk, Trb3 ) Induced in fatty liver dystrophy 2 Bglu1 QTL Blood glucose level 1 Hnf4 a Hepatic nuclear factor 4 alpha C/EBP b CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta ...
... Ifld2 (Nipk, Trb3 ) Induced in fatty liver dystrophy 2 Bglu1 QTL Blood glucose level 1 Hnf4 a Hepatic nuclear factor 4 alpha C/EBP b CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta ...
2559 P Ramsfield
... harknessii) is a serious threat to exotic Pinus radiata forests in New Zealand. As the pathogen is not present in New Zealand and because of the long period of time between infection and spore production, a DNA based marker has been developed that is able to detect the presence of pathogen DNA withi ...
... harknessii) is a serious threat to exotic Pinus radiata forests in New Zealand. As the pathogen is not present in New Zealand and because of the long period of time between infection and spore production, a DNA based marker has been developed that is able to detect the presence of pathogen DNA withi ...
Nucleosome

A nucleosome is a basic unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes, consisting of a segment of DNA wound in sequence around eight histone protein cores. This structure is often compared to thread wrapped around a spool.Nucleosomes form the fundamental repeating units of eukaryotic chromatin, which is used to pack the large eukaryotic genomes into the nucleus while still ensuring appropriate access to it (in mammalian cells approximately 2 m of linear DNA have to be packed into a nucleus of roughly 10 µm diameter). Nucleosomes are folded through a series of successively higher order structures to eventually form a chromosome; this both compacts DNA and creates an added layer of regulatory control, which ensures correct gene expression. Nucleosomes are thought to carry epigenetically inherited information in the form of covalent modifications of their core histones.Nucleosomes were observed as particles in the electron microscope by Don and Ada Olins and their existence and structure (as histone octamers surrounded by approximately 200 base pairs of DNA) were proposed by Roger Kornberg. The role of the nucleosome as a general gene repressor was demonstrated by Lorch et al. in vitro and by Han and Grunstein in vivo.The nucleosome core particle consists of approximately 147 base pairs of DNA wrapped in 1.67 left-handed superhelical turns around a histone octamer consisting of 2 copies each of the core histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Core particles are connected by stretches of ""linker DNA"", which can be up to about 80 bp long. Technically, a nucleosome is defined as the core particle plus one of these linker regions; however the word is often synonymous with the core particle. Genome-wide nucleosome positioning maps are now available for many model organisms including mouse liver and brain.Linker histones such as H1 and its isoforms are involved in chromatin compaction and sit at the base of the nucleosome near the DNA entry and exit binding to the linker region of the DNA. Non-condensed nucleosomes without the linker histone resemble ""beads on a string of DNA"" under an electron microscope.In contrast to most eukaryotic cells, mature sperm cells largely use protamines to package their genomic DNA, most likely to achieve an even higher packaging ratio. Histone equivalents and a simplified chromatin structure have also been found in Archea, suggesting that eukaryotes are not the only organisms that use nucleosomes.