Quiz: DNA, RNA and Protein
... 11. What kind of bond holds the DNA bases together? 12. A three nucleotide sequence of DNA is called a _______________. 13. How many different amino acids are there? 14. State three differences between DNA and RNA. 15. The base uracil pairs with what DNA nucleotide 16. If the DNA coding strand is GT ...
... 11. What kind of bond holds the DNA bases together? 12. A three nucleotide sequence of DNA is called a _______________. 13. How many different amino acids are there? 14. State three differences between DNA and RNA. 15. The base uracil pairs with what DNA nucleotide 16. If the DNA coding strand is GT ...
DNA
... • DNA is found in the mitochondria. • mDNA is only found in the egg. Sperm has no mitochondria so mDNA is passed to offspring from the mother. • One sequence of DNA is a genome or gene. • Unwind all our DNA, it will stretch from the moon and back 6000X. ...
... • DNA is found in the mitochondria. • mDNA is only found in the egg. Sperm has no mitochondria so mDNA is passed to offspring from the mother. • One sequence of DNA is a genome or gene. • Unwind all our DNA, it will stretch from the moon and back 6000X. ...
File
... experiments that Griffith did. •He is trying to figure out which molecule was transforming the harmless bacteria into killers. •He uses enzymes to break ...
... experiments that Griffith did. •He is trying to figure out which molecule was transforming the harmless bacteria into killers. •He uses enzymes to break ...
Whole Genome Scale DNA Methylation Differences in
... Conclusion: These results suggest that changes in DNA methylation represented by T1D-MVPs must arise very early in the etiological process that leads to overt T1D. These changes involve genes likely associated with the immune response. In addition we have developed a method to identify MVPs in small ...
... Conclusion: These results suggest that changes in DNA methylation represented by T1D-MVPs must arise very early in the etiological process that leads to overt T1D. These changes involve genes likely associated with the immune response. In addition we have developed a method to identify MVPs in small ...
DNA
... Histones are the major class of DNA-binding proteins involved in maintaining the compacted structure of chromatin. There are 5 different histone proteins identified as H1, H2A, H2B, H3 and H4. Histones are basic proteins because they contain a large quantity of basic amino acids – arginine and lysin ...
... Histones are the major class of DNA-binding proteins involved in maintaining the compacted structure of chromatin. There are 5 different histone proteins identified as H1, H2A, H2B, H3 and H4. Histones are basic proteins because they contain a large quantity of basic amino acids – arginine and lysin ...
Regulation of Gene Activity
... and how fast mRNA leaves the nucleus Translational control: when translation begins and how long it continues Posttranslational control: after protein synthesis, polypeptide may have to undergo additional changes before it is functional. ...
... and how fast mRNA leaves the nucleus Translational control: when translation begins and how long it continues Posttranslational control: after protein synthesis, polypeptide may have to undergo additional changes before it is functional. ...
Chapter 12
... Name: ____________________________________ Date: _____ Subterm 2 Final Review Guide (Ch. 11, 12, 15, 16, & 17-1) STUDY HINTS (so, where do I start.... ???) ...
... Name: ____________________________________ Date: _____ Subterm 2 Final Review Guide (Ch. 11, 12, 15, 16, & 17-1) STUDY HINTS (so, where do I start.... ???) ...
Mutations and DNA Technology Notes
... Selective Breeding cont. • Inbreeding- continued breeding of ind. with similar characteristics. – Ex- different dog breeds – Can be dangerous due to increased chance for genetic defects. ...
... Selective Breeding cont. • Inbreeding- continued breeding of ind. with similar characteristics. – Ex- different dog breeds – Can be dangerous due to increased chance for genetic defects. ...
Rita Levi Montalcini was born on April 22nd, 1909
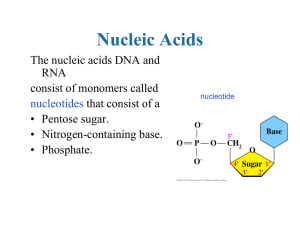
... middle of the last century, has a sort of double helix shape. It is made of different nucleid acids. Acids are made up from nucleotide molecules that have three parts: a sugar molecule, a phosphate group and a base containing nitrogen. These bases are called ...
... middle of the last century, has a sort of double helix shape. It is made of different nucleid acids. Acids are made up from nucleotide molecules that have three parts: a sugar molecule, a phosphate group and a base containing nitrogen. These bases are called ...
SEG exam 2 1
... The full chemical name of DNA is ______________________________________. A chart that displays all the chromosome pairs in size order is called a __________________. _________________ are alterations in the nucleotide sequence of the DNA molecule that can occur randomly and modify the genome. When a ...
... The full chemical name of DNA is ______________________________________. A chart that displays all the chromosome pairs in size order is called a __________________. _________________ are alterations in the nucleotide sequence of the DNA molecule that can occur randomly and modify the genome. When a ...
1 - web.biosci.utexas.edu
... a. encodes one major protein (the transposase) b. contains 13-bp inverted repeat at the termini (TIR) c. forms a two-element system d. first cloned from the waxy locus e. moves via cut-and-paste (gain-and-loss) mechanism 6. Many transposons in plants are inactive, but can be activated. Which mechani ...
... a. encodes one major protein (the transposase) b. contains 13-bp inverted repeat at the termini (TIR) c. forms a two-element system d. first cloned from the waxy locus e. moves via cut-and-paste (gain-and-loss) mechanism 6. Many transposons in plants are inactive, but can be activated. Which mechani ...
Name
... B) serves as a master control gene that functions during embryonic development by controlling the developmental fate of groups of cells. C) represses gene transcription and promotes mRNA translation. D) produces a product that controls the transcription of other genes. E) is found only in adult soma ...
... B) serves as a master control gene that functions during embryonic development by controlling the developmental fate of groups of cells. C) represses gene transcription and promotes mRNA translation. D) produces a product that controls the transcription of other genes. E) is found only in adult soma ...
BSN/Briefing 24 - British Society for Neuroendocrinology
... (see figure). Cellular phenotypes transmitted in this mode include parental imprinting and X chromosome inactivation. The modern usage of epigenetics however also incorporates structural changes in chromatin that mark, signal and propagate transcription states that are often transient and dynamic. T ...
... (see figure). Cellular phenotypes transmitted in this mode include parental imprinting and X chromosome inactivation. The modern usage of epigenetics however also incorporates structural changes in chromatin that mark, signal and propagate transcription states that are often transient and dynamic. T ...
Bulletin 1 - DNA: The Cookbook of Life - ctahr
... The DNA inside a cell is packaged very tightly into chromosomes. Within a human cell, 23 pairs of chromosomes fit in a structure that is one-tenth the width of a human hair, but if you unwound the chromosomes, the DNA would be six feet long. All living things contain DNA recipes and use them to make ...
... The DNA inside a cell is packaged very tightly into chromosomes. Within a human cell, 23 pairs of chromosomes fit in a structure that is one-tenth the width of a human hair, but if you unwound the chromosomes, the DNA would be six feet long. All living things contain DNA recipes and use them to make ...
Name
... DNA AND RNA Questions(pg 132-133) 10.What is the relationship between gene and DNA? A gene is a section of DNA that contains information to code for a specific protein. It is an active part of DNA 11.What is protein synthesis ? How are proteins made? During protein synthesis , the cell uses the info ...
... DNA AND RNA Questions(pg 132-133) 10.What is the relationship between gene and DNA? A gene is a section of DNA that contains information to code for a specific protein. It is an active part of DNA 11.What is protein synthesis ? How are proteins made? During protein synthesis , the cell uses the info ...
Dna: Hereditary molecules of life
... in all living things A gene is a region of DNA that codes for the building of a particular polypeptide Eukaryotic DNA is wound around histone proteins and organized into linear chromosomes. The chromosomes are found inside the nucleus of each cell ...
... in all living things A gene is a region of DNA that codes for the building of a particular polypeptide Eukaryotic DNA is wound around histone proteins and organized into linear chromosomes. The chromosomes are found inside the nucleus of each cell ...
Lab Quiz 4 Key
... 6. In the bacterial transformation lab, what were the dependent variables? (0.5 pt) [growth of colonies and whether the bacteria glow or not] ...
... 6. In the bacterial transformation lab, what were the dependent variables? (0.5 pt) [growth of colonies and whether the bacteria glow or not] ...
Human Genomic DNA Quality Controls for aCGH and Microarray
... DNA from research laboratories can be of uneven quality. Our DNA comes from immortalized cell lines, where the sequences are validated and the DNA is unchanging. ...
... DNA from research laboratories can be of uneven quality. Our DNA comes from immortalized cell lines, where the sequences are validated and the DNA is unchanging. ...
DNA – The Building Blocks of Life
... responsible for some of the traits you can inherit from your parents. An example is the brown-eyed gene. This is a specific protein that’s made using the instructions from DNA. If this protein doesn’t get made (because you don’t have the brown eyed gene), you have no or little pigment and you hav ...
... responsible for some of the traits you can inherit from your parents. An example is the brown-eyed gene. This is a specific protein that’s made using the instructions from DNA. If this protein doesn’t get made (because you don’t have the brown eyed gene), you have no or little pigment and you hav ...
Your name
... 21. What kind of ends are possible with the use of restriction enzymes? Sticky ends and blunt ends 22. What is the end result of the central dogma? proteins 23. What are the most basic units of genetic information? ...
... 21. What kind of ends are possible with the use of restriction enzymes? Sticky ends and blunt ends 22. What is the end result of the central dogma? proteins 23. What are the most basic units of genetic information? ...
Chapter 19 - Biology Junction
... 1. Define the following terms: a. Chromatin b. Nucleosome 2. Outline the levels of DNA packing in the eukaryotic nucleus below next to the diagram provided. ...
... 1. Define the following terms: a. Chromatin b. Nucleosome 2. Outline the levels of DNA packing in the eukaryotic nucleus below next to the diagram provided. ...
They are the offspring of these two people They are the
... Ulna and radius are always side by side. ...
... Ulna and radius are always side by side. ...
Nucleosome

A nucleosome is a basic unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes, consisting of a segment of DNA wound in sequence around eight histone protein cores. This structure is often compared to thread wrapped around a spool.Nucleosomes form the fundamental repeating units of eukaryotic chromatin, which is used to pack the large eukaryotic genomes into the nucleus while still ensuring appropriate access to it (in mammalian cells approximately 2 m of linear DNA have to be packed into a nucleus of roughly 10 µm diameter). Nucleosomes are folded through a series of successively higher order structures to eventually form a chromosome; this both compacts DNA and creates an added layer of regulatory control, which ensures correct gene expression. Nucleosomes are thought to carry epigenetically inherited information in the form of covalent modifications of their core histones.Nucleosomes were observed as particles in the electron microscope by Don and Ada Olins and their existence and structure (as histone octamers surrounded by approximately 200 base pairs of DNA) were proposed by Roger Kornberg. The role of the nucleosome as a general gene repressor was demonstrated by Lorch et al. in vitro and by Han and Grunstein in vivo.The nucleosome core particle consists of approximately 147 base pairs of DNA wrapped in 1.67 left-handed superhelical turns around a histone octamer consisting of 2 copies each of the core histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Core particles are connected by stretches of ""linker DNA"", which can be up to about 80 bp long. Technically, a nucleosome is defined as the core particle plus one of these linker regions; however the word is often synonymous with the core particle. Genome-wide nucleosome positioning maps are now available for many model organisms including mouse liver and brain.Linker histones such as H1 and its isoforms are involved in chromatin compaction and sit at the base of the nucleosome near the DNA entry and exit binding to the linker region of the DNA. Non-condensed nucleosomes without the linker histone resemble ""beads on a string of DNA"" under an electron microscope.In contrast to most eukaryotic cells, mature sperm cells largely use protamines to package their genomic DNA, most likely to achieve an even higher packaging ratio. Histone equivalents and a simplified chromatin structure have also been found in Archea, suggesting that eukaryotes are not the only organisms that use nucleosomes.