Expressing Genetic Information
... 1. Study the scanning electron micrograph of human chromosomes during mitosis. Locate the chromatids and centromere. Now, study the fine detail of the chromatin. How would you describe it? 2. What is stored in the chromatin, the genetic material of DNA? 3. Genes are discrete units of DNA that act in ...
... 1. Study the scanning electron micrograph of human chromosomes during mitosis. Locate the chromatids and centromere. Now, study the fine detail of the chromatin. How would you describe it? 2. What is stored in the chromatin, the genetic material of DNA? 3. Genes are discrete units of DNA that act in ...
Enterococcus faecalis VRE, Genomic DNA
... Purified Genomic DNA is designed for use as an amplification and/or detection control for nucleic acid testing of E. faecalis. It can also be used to determine a limit of detection (LOD), in diagnostic ...
... Purified Genomic DNA is designed for use as an amplification and/or detection control for nucleic acid testing of E. faecalis. It can also be used to determine a limit of detection (LOD), in diagnostic ...
DNA Replication - The Biology Corner
... 2. DNA polymerase adds the complementary nucleotides and binds the sugars and phosphates. DNA polymerase travels from the 3' to the 5' end. The DNA is called the template strand. 3. DNA polymerase adds complementary nucleotides on the other side of the ladder. Traveling in the opposite direction. 4. ...
... 2. DNA polymerase adds the complementary nucleotides and binds the sugars and phosphates. DNA polymerase travels from the 3' to the 5' end. The DNA is called the template strand. 3. DNA polymerase adds complementary nucleotides on the other side of the ladder. Traveling in the opposite direction. 4. ...
Name
... A BIO Ch 11 Test – DNA, RNA & Protein Synthesis Review Sheet QUESTIONS 1. Molecules of DNA and RNA are made of chains of this monomer 2. List the three parts of a nucleotide 3. DNA is named for which part of the molecule it contains (hint: RNA contains a different one of these) 4. What two scientist ...
... A BIO Ch 11 Test – DNA, RNA & Protein Synthesis Review Sheet QUESTIONS 1. Molecules of DNA and RNA are made of chains of this monomer 2. List the three parts of a nucleotide 3. DNA is named for which part of the molecule it contains (hint: RNA contains a different one of these) 4. What two scientist ...
DNA to Proteins….a REVIEW
... 1. Under what circumstance does DNA need to make an exact copy of itself? ...
... 1. Under what circumstance does DNA need to make an exact copy of itself? ...
Gypsy Vanner Horse Society DNA Analysis Form
... The purpose of the DNA sampling is to verify parentage and to identify the DNA type for the individual horse. The information received from the test will be held by the Gypsy Vanner Horse Society and the University of Kentucky. The University may use the samples in its research. The GVHS does author ...
... The purpose of the DNA sampling is to verify parentage and to identify the DNA type for the individual horse. The information received from the test will be held by the Gypsy Vanner Horse Society and the University of Kentucky. The University may use the samples in its research. The GVHS does author ...
DNA Webquest - Jackson School District
... 3. Franklin worked with Raymond Gosling and was able to get photos of DNA fibers. What did she conclude from these photos (two things)? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Go to ...
... 3. Franklin worked with Raymond Gosling and was able to get photos of DNA fibers. What did she conclude from these photos (two things)? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Go to ...
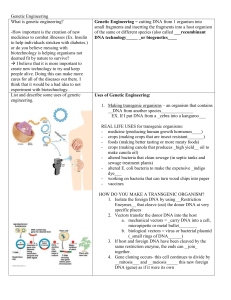
Genetic Engineering Guied Notes
... deemed fit by nature to survive? I believe that it is more important to create new technology to try and keep people alive. Doing this can make more cures for all of the diseases out there. I think that it would be a bad idea to not experiment with biotechnology. List and describe some uses of gen ...
... deemed fit by nature to survive? I believe that it is more important to create new technology to try and keep people alive. Doing this can make more cures for all of the diseases out there. I think that it would be a bad idea to not experiment with biotechnology. List and describe some uses of gen ...
M-DNA: synthesis, chemical structure and physical properties
... measurements and pH titration. The presence of metal ions in DNA structure would reduce the total charge of the helix and consequently compact the helix. In other aspects, the structure of so called M-DNA doesn’t deviate much form that of B-DNA and can be reversibly converted back to B-DNA by adding ...
... measurements and pH titration. The presence of metal ions in DNA structure would reduce the total charge of the helix and consequently compact the helix. In other aspects, the structure of so called M-DNA doesn’t deviate much form that of B-DNA and can be reversibly converted back to B-DNA by adding ...
4. The diagram below shows a segment of DNA with a total length of
... The diagram below shows a segment of DNA with a total length of 4,900 base pairs. The arrows indicate reaction sites for two restriction enzymes (enzyme X and enzyme Y). ...
... The diagram below shows a segment of DNA with a total length of 4,900 base pairs. The arrows indicate reaction sites for two restriction enzymes (enzyme X and enzyme Y). ...
Genetics 1
... and is an instruction (code) to the cell to make a particular substance, which helps regulate a trait of an organism, e.g. the gene for tongue-rolling in humans. There are two possible genes you can have. One gives you the ability to roll your tongue. The other does not give you this ability. These ...
... and is an instruction (code) to the cell to make a particular substance, which helps regulate a trait of an organism, e.g. the gene for tongue-rolling in humans. There are two possible genes you can have. One gives you the ability to roll your tongue. The other does not give you this ability. These ...
DNA Extraction Laboratory
... 2. Add 3 drops of detergent, a pinch of salt, and 10 mL of water to the bag and squish the contents with your hands for one minute more. 3. Add a pinch of meat tenderizer, and squeeze one minute. 4. Pour the strawberry mush through a funnel lined with a thin layer of cotton into a beaker. Pour the s ...
... 2. Add 3 drops of detergent, a pinch of salt, and 10 mL of water to the bag and squish the contents with your hands for one minute more. 3. Add a pinch of meat tenderizer, and squeeze one minute. 4. Pour the strawberry mush through a funnel lined with a thin layer of cotton into a beaker. Pour the s ...
DNA Packaging and Ch..
... • If the DNA in a typical human cell were stretched out, what length would it be? What is the diameter of the nucleus in which human DNA must be packaged? • What degree of DNA packaging corresponds with “diffuse DNA” associated with G1? What kind of DNA packaging is associated with Mphase (“condense ...
... • If the DNA in a typical human cell were stretched out, what length would it be? What is the diameter of the nucleus in which human DNA must be packaged? • What degree of DNA packaging corresponds with “diffuse DNA” associated with G1? What kind of DNA packaging is associated with Mphase (“condense ...
State what is meant by the topological problem and explain how
... 10. List the DNA polymerases involved in DNA replication in Escherichia coli and in eukaryotes, and summarize the function of each enzyme. 11. Explain why the ends of a chromosomal DNA molecule could become shortened after repeated rounds of DNA replication, and show how telomerase prevents this fro ...
... 10. List the DNA polymerases involved in DNA replication in Escherichia coli and in eukaryotes, and summarize the function of each enzyme. 11. Explain why the ends of a chromosomal DNA molecule could become shortened after repeated rounds of DNA replication, and show how telomerase prevents this fro ...
DNA- Experiments and People
... Grow E. coli bacteria with radioactive 15N (its heavier than 14N) so bacteria incorporate heavy N into their DNA Then grow in media with only 14N Centrifuge DNA at different times to separate by size. (The more 15N it has the heavier it is) Pattern shows which model is correct ...
... Grow E. coli bacteria with radioactive 15N (its heavier than 14N) so bacteria incorporate heavy N into their DNA Then grow in media with only 14N Centrifuge DNA at different times to separate by size. (The more 15N it has the heavier it is) Pattern shows which model is correct ...
DNA People - Biology Junction
... Grow E. coli bacteria with radioactive 15N (its heavier than 14N) so bacteria incorporate heavy N into their DNA Then grow in media with only 14N Centrifuge DNA at different times to separate by size. (The more 15N it has the heavier it is) Pattern shows which model is correct ...
... Grow E. coli bacteria with radioactive 15N (its heavier than 14N) so bacteria incorporate heavy N into their DNA Then grow in media with only 14N Centrifuge DNA at different times to separate by size. (The more 15N it has the heavier it is) Pattern shows which model is correct ...
Deciphering the Structure of the Hereditary Material
... People have wondered since ancient times how the characteristics of parents are passed on to children. The puzzle was finally solved in detail in the 1950s in probably the greatest scientific advance of the twentieth century. This breakthrough gave birth to genetic engineering, molecular genetics an ...
... People have wondered since ancient times how the characteristics of parents are passed on to children. The puzzle was finally solved in detail in the 1950s in probably the greatest scientific advance of the twentieth century. This breakthrough gave birth to genetic engineering, molecular genetics an ...
Gene Regulation
... Regions of DNA where factors that regulate transcription can also bind Always present in cell, but most likely have to be activated before they will bind to DNA Gene Regulation ...
... Regions of DNA where factors that regulate transcription can also bind Always present in cell, but most likely have to be activated before they will bind to DNA Gene Regulation ...
Pre/Post Test
... A. one molecule with two original strands and one molecule with two new strands B. two molecules, each with one original and one new strand C. two molecules, each with two new strands ...
... A. one molecule with two original strands and one molecule with two new strands B. two molecules, each with one original and one new strand C. two molecules, each with two new strands ...
Eukaryotic transcriptional control
... hACF; RSF; etc) all contain a helicase/ATPase component to disrupt interactions between base-paired nucleic acids or between nucleic acids and proteins. ...
... hACF; RSF; etc) all contain a helicase/ATPase component to disrupt interactions between base-paired nucleic acids or between nucleic acids and proteins. ...
DNA: Structure and Function
... • DNA is composed of 2 chains of nucleotides that form a double helix shape • The two strands are antiparallel. • The backbone of the DNA molecule is composed of alternating phosphate groups and sugars • The complimentary bases form hydrogen bonds between the strands • A is complimentary to T • G is ...
... • DNA is composed of 2 chains of nucleotides that form a double helix shape • The two strands are antiparallel. • The backbone of the DNA molecule is composed of alternating phosphate groups and sugars • The complimentary bases form hydrogen bonds between the strands • A is complimentary to T • G is ...
Greatest Discoveries with Bill Nye: Genetics
... 1. What plants did Mendel work with? 2. What happened when Mendel crossed a round seed with a wrinkled? 3. What happened when Mendel crossed the round offspring seeds? 4. About how many of the second generation seeds were wrinkled? 5. How many of Mendel’s genetic factors are contributed by each pare ...
... 1. What plants did Mendel work with? 2. What happened when Mendel crossed a round seed with a wrinkled? 3. What happened when Mendel crossed the round offspring seeds? 4. About how many of the second generation seeds were wrinkled? 5. How many of Mendel’s genetic factors are contributed by each pare ...
Nucleosome

A nucleosome is a basic unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes, consisting of a segment of DNA wound in sequence around eight histone protein cores. This structure is often compared to thread wrapped around a spool.Nucleosomes form the fundamental repeating units of eukaryotic chromatin, which is used to pack the large eukaryotic genomes into the nucleus while still ensuring appropriate access to it (in mammalian cells approximately 2 m of linear DNA have to be packed into a nucleus of roughly 10 µm diameter). Nucleosomes are folded through a series of successively higher order structures to eventually form a chromosome; this both compacts DNA and creates an added layer of regulatory control, which ensures correct gene expression. Nucleosomes are thought to carry epigenetically inherited information in the form of covalent modifications of their core histones.Nucleosomes were observed as particles in the electron microscope by Don and Ada Olins and their existence and structure (as histone octamers surrounded by approximately 200 base pairs of DNA) were proposed by Roger Kornberg. The role of the nucleosome as a general gene repressor was demonstrated by Lorch et al. in vitro and by Han and Grunstein in vivo.The nucleosome core particle consists of approximately 147 base pairs of DNA wrapped in 1.67 left-handed superhelical turns around a histone octamer consisting of 2 copies each of the core histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Core particles are connected by stretches of ""linker DNA"", which can be up to about 80 bp long. Technically, a nucleosome is defined as the core particle plus one of these linker regions; however the word is often synonymous with the core particle. Genome-wide nucleosome positioning maps are now available for many model organisms including mouse liver and brain.Linker histones such as H1 and its isoforms are involved in chromatin compaction and sit at the base of the nucleosome near the DNA entry and exit binding to the linker region of the DNA. Non-condensed nucleosomes without the linker histone resemble ""beads on a string of DNA"" under an electron microscope.In contrast to most eukaryotic cells, mature sperm cells largely use protamines to package their genomic DNA, most likely to achieve an even higher packaging ratio. Histone equivalents and a simplified chromatin structure have also been found in Archea, suggesting that eukaryotes are not the only organisms that use nucleosomes.