Chapter 4. The Epigenetics of Non
... RITS (RNAi-Induced Transcriptional Silencing) complex is similar to RISC in containing Argonaute, but (unlike RISC) RITS localizes exclusively to the nucleus and contains at least one chromatin-binding module called a chromodomain [9]. Bound to a siRNA it mediates sequence specific heterochromatin f ...
... RITS (RNAi-Induced Transcriptional Silencing) complex is similar to RISC in containing Argonaute, but (unlike RISC) RITS localizes exclusively to the nucleus and contains at least one chromatin-binding module called a chromodomain [9]. Bound to a siRNA it mediates sequence specific heterochromatin f ...
Amino Acids - Biology Learning Center
... he abstractly described the gene, the ribosome, and the messenger. ...
... he abstractly described the gene, the ribosome, and the messenger. ...
Central Dogma PowerPoint
... genome, located in the nucleus of the cell, to the ribosomes, which are located outside of the nucleus either in the cytosol or on the endoplasmic reticulum ...
... genome, located in the nucleus of the cell, to the ribosomes, which are located outside of the nucleus either in the cytosol or on the endoplasmic reticulum ...
Promega Notes: T4 RNA Ligase: A Molecular Tool for RNA and DNA
... amino acid. This improvement greatly simplified the original anticodon loop replacement procedure, and they demonstrated that, while lacking post-transcriptional base modifications, the efficiency of amber suppression of the run-off suppressor tRNA was equivalent to a suppressor tRNA constructed by ...
... amino acid. This improvement greatly simplified the original anticodon loop replacement procedure, and they demonstrated that, while lacking post-transcriptional base modifications, the efficiency of amber suppression of the run-off suppressor tRNA was equivalent to a suppressor tRNA constructed by ...
No Slide Title
... 1) DNA provides the “workers” with the instructions for making proteins; 2) The workers (RNA molecules!) follow the instructions from DNA and build the proteins; 3) Other workers (other RNA molecules) bring parts (AMINO ACIDS) over to the assembly line ...
... 1) DNA provides the “workers” with the instructions for making proteins; 2) The workers (RNA molecules!) follow the instructions from DNA and build the proteins; 3) Other workers (other RNA molecules) bring parts (AMINO ACIDS) over to the assembly line ...
P{11/27/11 PPPP RNA and Protein Synthesis Notes Review DNA 1
... directions for the needed protein. RNA nucleotides come in and bind with the DNA nitrogen Bases So, transcription is 42. __________________ the mRNA code from a strand of DNA Occurs in the nucleus so the message can be sent from 43. DNA to the ______________________ 44. DNA never leaves ____________ ...
... directions for the needed protein. RNA nucleotides come in and bind with the DNA nitrogen Bases So, transcription is 42. __________________ the mRNA code from a strand of DNA Occurs in the nucleus so the message can be sent from 43. DNA to the ______________________ 44. DNA never leaves ____________ ...
View Poster - Technology Networks
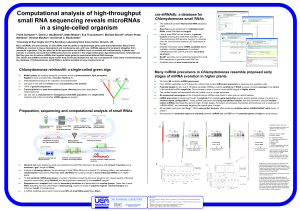
... We found 68 candidate miRNA precursors Four miRNA candidates out of 8 tested by northern blot showed differential expression in gametes and vegetative cells Potential targets for four out of 18 tested candidate miRNAs could be verified by 5’ RACE analysis, showing cleavage in the centre of the predi ...
... We found 68 candidate miRNA precursors Four miRNA candidates out of 8 tested by northern blot showed differential expression in gametes and vegetative cells Potential targets for four out of 18 tested candidate miRNAs could be verified by 5’ RACE analysis, showing cleavage in the centre of the predi ...
12–3 RNA and Protein Synthesis
... nucleotide sequence of DNA into a complementary sequence in RNA. This process is called transcription. Transcription requires another enzyme, RNA polymerase. ...
... nucleotide sequence of DNA into a complementary sequence in RNA. This process is called transcription. Transcription requires another enzyme, RNA polymerase. ...
Gene Section DIRC3 (disrupted in renal carcinoma 3) in Oncology and Haematology
... DIRC3-HSPBAP1 is formed by replacing the first coding exon of HSPBAP1 by the first two exons of DIRC3. The fusion transcript most likely encodes a truncated HSPBAP1 protein starting from a internal initiation side embedded in a strong Kozak consensus sequence. ...
... DIRC3-HSPBAP1 is formed by replacing the first coding exon of HSPBAP1 by the first two exons of DIRC3. The fusion transcript most likely encodes a truncated HSPBAP1 protein starting from a internal initiation side embedded in a strong Kozak consensus sequence. ...
LEARNING GOALS - PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Main Idea
... tRNA molecules bind specific amino acids and allow information in the mRNA to be translated to a linear peptide sequence. rRNA molecules are functional building blocks of ribosomes. The role of RNAi includes regulation of gene expression at the level of mRNA transcription ...
... tRNA molecules bind specific amino acids and allow information in the mRNA to be translated to a linear peptide sequence. rRNA molecules are functional building blocks of ribosomes. The role of RNAi includes regulation of gene expression at the level of mRNA transcription ...
key
... 1. A critical feature of cloning plasmids is the presence of a selectable marker such as antibiotic (or ampicillin or …) resistance. 2. Northern blotting is a technique in which RNA is fractionated on a gel, and transferred to a membrane. The RNA attached to the membrane is incubated with a labeled ...
... 1. A critical feature of cloning plasmids is the presence of a selectable marker such as antibiotic (or ampicillin or …) resistance. 2. Northern blotting is a technique in which RNA is fractionated on a gel, and transferred to a membrane. The RNA attached to the membrane is incubated with a labeled ...
How Proteins are Made - MDC Faculty Web Pages
... (example is sugar lactose, called an inducer). • Three genes involved, y (permease enzyme to help lactose enter the cell), z (β-galactosidase enzyme to cut lactose into galactose and glucose), and the a gene. ...
... (example is sugar lactose, called an inducer). • Three genes involved, y (permease enzyme to help lactose enter the cell), z (β-galactosidase enzyme to cut lactose into galactose and glucose), and the a gene. ...
CHAPTER 10: DNA,RNA & Protein Synthesis
... carries the code for building a protein from the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. It acts as a messenger. ...
... carries the code for building a protein from the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. It acts as a messenger. ...
Biology and computers - Cal State LA
... is/are the same in all 3 organisms). Start your paragraph as a hypothesis as to which parts are most important, and write your discussion as a defense of your hypothesis. Find out the chromosomal location of the gene that causes sickle cell anemia. Give the name of the gene. State the nucleotide cha ...
... is/are the same in all 3 organisms). Start your paragraph as a hypothesis as to which parts are most important, and write your discussion as a defense of your hypothesis. Find out the chromosomal location of the gene that causes sickle cell anemia. Give the name of the gene. State the nucleotide cha ...
Lecture#5 - Introduction to gene regulation and operons in
... Central Dogma - Genetic Information and Genes Information flows: DNA -------> RNA ------> Protein Gene expression involves: 1) Transcription - Information is transferred from the DNA sequence into an RNA sequence - messenger RNA. 2) Translation - Information is transferred from the mRNA to protein s ...
... Central Dogma - Genetic Information and Genes Information flows: DNA -------> RNA ------> Protein Gene expression involves: 1) Transcription - Information is transferred from the DNA sequence into an RNA sequence - messenger RNA. 2) Translation - Information is transferred from the mRNA to protein s ...
Chapter 10: How Proteins are Made
... • After transcription, mRNA travels into cytoplasm and anchors to the ribosome, forming a ribosome-mRNA complex – Recall: mRNA contains a universal “start” codon (AUG) signaling where a gene begins and, hence, where translation will begin • AUG oriented in P site of ribosome • Meanwhile, tRNA molecu ...
... • After transcription, mRNA travels into cytoplasm and anchors to the ribosome, forming a ribosome-mRNA complex – Recall: mRNA contains a universal “start” codon (AUG) signaling where a gene begins and, hence, where translation will begin • AUG oriented in P site of ribosome • Meanwhile, tRNA molecu ...
DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis
... • 3 of the main enzymes are: – Helicase: untwists the DNA – DNA polymerase: adds new nucleotides and connects them to build up a new strand (follows base-pairing rules!) – Ligase: Joins DNA fragments together ...
... • 3 of the main enzymes are: – Helicase: untwists the DNA – DNA polymerase: adds new nucleotides and connects them to build up a new strand (follows base-pairing rules!) – Ligase: Joins DNA fragments together ...
Chapter 25: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... The Genetic Code DNA specifies the synthesis of proteins because it contains a triplet code: every three bases stand for one amino acid. Each three-letter unit of an mRNA molecule is called a codon. Most amino acids have more than one codon; there are 20 amino acids with a ...
... The Genetic Code DNA specifies the synthesis of proteins because it contains a triplet code: every three bases stand for one amino acid. Each three-letter unit of an mRNA molecule is called a codon. Most amino acids have more than one codon; there are 20 amino acids with a ...
Chapter 16 Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
... 2. RNA polymerase III transcribes the tRNAs and other small RNAs 3. RNA polymerase II transcribes all protein-encoding genes 4. Cis-acting regulatory regions recognized by pol II consist of a promoter and one or more enhancers B. Trans-acting proteins control transcription from class II promoters 1. ...
... 2. RNA polymerase III transcribes the tRNAs and other small RNAs 3. RNA polymerase II transcribes all protein-encoding genes 4. Cis-acting regulatory regions recognized by pol II consist of a promoter and one or more enhancers B. Trans-acting proteins control transcription from class II promoters 1. ...
Overview: The Flow of Genetic Information • The information content
... • The discovery of ribozymes rendered obsolete the belief that all biological catalysts were proteins • Three properties of RNA enable it to function as an enzyme – It can form a three-dimensional structure because of its ability to base-pair with itself – Some bases in RNA contain functional groups ...
... • The discovery of ribozymes rendered obsolete the belief that all biological catalysts were proteins • Three properties of RNA enable it to function as an enzyme – It can form a three-dimensional structure because of its ability to base-pair with itself – Some bases in RNA contain functional groups ...