Chapter 35: Uses of the Dative Case Chapter 35 covers the
... literal English equivalent will sound something like this: “There is a book to me,” which means “I have a book.” Be careful! While the “to be” verb is always third-person, its tense and number can and often do change, for example, Quondam omnibus iura haec erant, literally, “Once these rights were t ...
... literal English equivalent will sound something like this: “There is a book to me,” which means “I have a book.” Be careful! While the “to be” verb is always third-person, its tense and number can and often do change, for example, Quondam omnibus iura haec erant, literally, “Once these rights were t ...
Beneficiary (indirect object)
... To discover whether a sentence contains a beneficiary, follow these steps. 1) Look for a verb that has a meaning of giving, telling or showing. 2) Look for a direct object (something being given, told, or shown). 3) Look for a recipient, a person who is receiving something, being given, told, or sho ...
... To discover whether a sentence contains a beneficiary, follow these steps. 1) Look for a verb that has a meaning of giving, telling or showing. 2) Look for a direct object (something being given, told, or shown). 3) Look for a recipient, a person who is receiving something, being given, told, or sho ...
Indirect Objects: Exercise 4
... In the sentence above, you would ask of the verb Who gave? The answer is the subject scientists. The next question is Scientists gave what? The answer is the direct object, lecture. To find the indirect object, you ask, Scientists gave lecture to whom? The answer is the indirect object, students. On ...
... In the sentence above, you would ask of the verb Who gave? The answer is the subject scientists. The next question is Scientists gave what? The answer is the direct object, lecture. To find the indirect object, you ask, Scientists gave lecture to whom? The answer is the indirect object, students. On ...
Introduction to Linguistics Sound System and Word Formation
... The farmer is the active one, the person doing the chasing, and so is the subject. The bull is t because he is on the receiving end, i.e. he is being chased. Now the bull is the subject, while the farmer has become the object. To make this clear, the Engl have been moved. The Latin words, however, h ...
... The farmer is the active one, the person doing the chasing, and so is the subject. The bull is t because he is on the receiving end, i.e. he is being chased. Now the bull is the subject, while the farmer has become the object. To make this clear, the Engl have been moved. The Latin words, however, h ...
Catullus 51 - WhippleHill
... d. Quintus Caecilius Metellus 3. What use of the infinitive can be seen in line 2? a. historical b. indirect statement c. complementary d. objective ...
... d. Quintus Caecilius Metellus 3. What use of the infinitive can be seen in line 2? a. historical b. indirect statement c. complementary d. objective ...
Lecture 04 - ELTE / SEAS
... I donated the money to charity He said something to you He reported the crime to the police I sent the parcel to London ...
... I donated the money to charity He said something to you He reported the crime to the police I sent the parcel to London ...
Dative Worksheet
... Hey! At least 2 cases have no special translation, so write “none” for these. ...
... Hey! At least 2 cases have no special translation, so write “none” for these. ...
Diagramming Indirect Objects
... placed on a horizontal line directly below the verb, with a diagonal line that joins it to the verb. When you think about it, an indirect object is diagrammed much like a prepositional phrase, only the diagonal line has no preposition on it (we might assume, however, that to or for is implied). Obse ...
... placed on a horizontal line directly below the verb, with a diagonal line that joins it to the verb. When you think about it, an indirect object is diagrammed much like a prepositional phrase, only the diagonal line has no preposition on it (we might assume, however, that to or for is implied). Obse ...
in defense of an old idea: the *-o stem origin of the
... might be exemplified by such Lithuanian sentences as (Daukšos Postilë 120): Jam (dat. sg. masc.) atëmë vis¹ šarv¹ ir ginkl¹ jo ‘(who) took away all his armor and weapon from him’ (literally ‘to him’); (LKÞ IV 80) Ir atëmei tiemdviem (dat. dual) t¹ meitëlá ‘you took away from both of them (literally ...
... might be exemplified by such Lithuanian sentences as (Daukšos Postilë 120): Jam (dat. sg. masc.) atëmë vis¹ šarv¹ ir ginkl¹ jo ‘(who) took away all his armor and weapon from him’ (literally ‘to him’); (LKÞ IV 80) Ir atëmei tiemdviem (dat. dual) t¹ meitëlá ‘you took away from both of them (literally ...
Functions of Nouns - Explanation Sheet
... C A word of caution is extended to those who wish to focus on the informational focus of a sentence. This is a semantic question rather than a grammatical one. What the sentence is about is called the topic and does not offer much help in determining the function of nouns. The topic can be nearly an ...
... C A word of caution is extended to those who wish to focus on the informational focus of a sentence. This is a semantic question rather than a grammatical one. What the sentence is about is called the topic and does not offer much help in determining the function of nouns. The topic can be nearly an ...
The instrumental: dative and its double 1. Introduction. We take our
... 3. With obliques: genitive/datives reversed. An analysis. Beginning with Kayne (1984), ditransitive verbs of the type illustrated in (3) are assumed to take a predication as their complement; the content of this predication is a possession relation between the direct object (the possessum) and the o ...
... 3. With obliques: genitive/datives reversed. An analysis. Beginning with Kayne (1984), ditransitive verbs of the type illustrated in (3) are assumed to take a predication as their complement; the content of this predication is a possession relation between the direct object (the possessum) and the o ...
passive with dative
... Passive Voice with Dative Elements Dative elements in an active-voice sentence cannot be raised to subject (nominative) status in passive voice. In German, specifically, objects of dative verbs and beneficiaries (indirect objects) must remain in the dative case in passive voice. This is in direct co ...
... Passive Voice with Dative Elements Dative elements in an active-voice sentence cannot be raised to subject (nominative) status in passive voice. In German, specifically, objects of dative verbs and beneficiaries (indirect objects) must remain in the dative case in passive voice. This is in direct co ...
1. Genitive singular
... objects will appear in the dative case. For first declension nouns, these endings = –ae or –is depending on whether the noun is singular or plural. For second declension, the singular = –o and plural = –is. *Notice that the dative plural for both declensions = –is. puerī laetīs puellīs multōs flōrēs ...
... objects will appear in the dative case. For first declension nouns, these endings = –ae or –is depending on whether the noun is singular or plural. For second declension, the singular = –o and plural = –is. *Notice that the dative plural for both declensions = –is. puerī laetīs puellīs multōs flōrēs ...
GERMAN CASES German has 4 grammatical cases: nominative
... This is different from Romance languages such as French, Italian, and Spanish. English, because it is a Germanic language, has a few remnants of cases. I’ll point these out to you as we go along. Nouns and pronouns have cases, not verbs. What case you use depends on what the noun’s or pronoun’s func ...
... This is different from Romance languages such as French, Italian, and Spanish. English, because it is a Germanic language, has a few remnants of cases. I’ll point these out to you as we go along. Nouns and pronouns have cases, not verbs. What case you use depends on what the noun’s or pronoun’s func ...
Study Guide: National Latin Exam
... Be on high alert for these verbs. (Verbs of GIVING, TELLING, SAYING, SHOWING) They will probably be followed by an object (accusative) and an indirect object (dative). E.g.: ...
... Be on high alert for these verbs. (Verbs of GIVING, TELLING, SAYING, SHOWING) They will probably be followed by an object (accusative) and an indirect object (dative). E.g.: ...
Study Guide: National Latin Exam
... Be on high alert for these verbs. (Verbs of GIVING, TELLING, SAYING, SHOWING) They will probably be followed by an object (accusative) and an indirect object (dative). E.g.: ...
... Be on high alert for these verbs. (Verbs of GIVING, TELLING, SAYING, SHOWING) They will probably be followed by an object (accusative) and an indirect object (dative). E.g.: ...
Whom or what - Pratt Perfection!
... The dative case is used to express the idea of ‘to’ or ‘for’ someone or something. The indirect object is the person or thing to whom something is offered, given, etc. Der Junge gibt dem Mann ein Geschenk. ‘The boy gives a present to the man.’ or ‘The boy gives the man a present.’ The English equiva ...
... The dative case is used to express the idea of ‘to’ or ‘for’ someone or something. The indirect object is the person or thing to whom something is offered, given, etc. Der Junge gibt dem Mann ein Geschenk. ‘The boy gives a present to the man.’ or ‘The boy gives the man a present.’ The English equiva ...
Case Songs
... Genitive is ae,i, is ae,i, is ae,i, is Genitive is ae,i, is it’s possession Genitive plural is ...
... Genitive is ae,i, is ae,i, is ae,i, is Genitive is ae,i, is it’s possession Genitive plural is ...
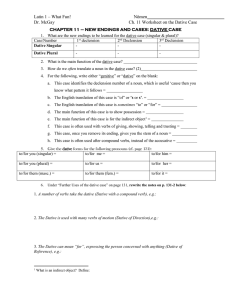
chapter 35
... this Dative appears to function as object of the preposition used as prefix: e.g. Aliis praestant, they surpass the others (prep: prae) Praeerat exercitui, he was in charge of the army (prep: prae) If the simple verb is transitive, then the compound may take an accusative as object of the root ve ...
... this Dative appears to function as object of the preposition used as prefix: e.g. Aliis praestant, they surpass the others (prep: prae) Praeerat exercitui, he was in charge of the army (prep: prae) If the simple verb is transitive, then the compound may take an accusative as object of the root ve ...
Dative of Purpose and Reference
... The dative of reference is used when the dative depends not on any one particular word (such as is the case with Dative following special adjectives like amīcus, fidēlis, idoneus, and similis or verbs like crēdō and noceō) but on the general meaning of the sentence. o It is often called the “Dativ ...
... The dative of reference is used when the dative depends not on any one particular word (such as is the case with Dative following special adjectives like amīcus, fidēlis, idoneus, and similis or verbs like crēdō and noceō) but on the general meaning of the sentence. o It is often called the “Dativ ...
The Special Datives
... advantage or disadvantage is expressed in the Dative Case, and is called a Dative of Reference. This function may answer a question such as, “For whom was the action done?” or “For whose benefit?” Note carefully this distinction: I am giving money to you. ...
... advantage or disadvantage is expressed in the Dative Case, and is called a Dative of Reference. This function may answer a question such as, “For whom was the action done?” or “For whose benefit?” Note carefully this distinction: I am giving money to you. ...
Review of the Einführung
... he doesn't play it, it is possible for the same person to play and watch soccer, but that would leave too little time for German homework...]). *** Nicht nur... sondern auch = not only... but also (this is a fixed phrase, and here aber is not used) Separable prefix verbs do not part with their prefi ...
... he doesn't play it, it is possible for the same person to play and watch soccer, but that would leave too little time for German homework...]). *** Nicht nur... sondern auch = not only... but also (this is a fixed phrase, and here aber is not used) Separable prefix verbs do not part with their prefi ...
Translating Inflected Languages S. Harris Inflected languages are
... function and the action function. For naming, we use the Latin word for name, nomen, and call words that name nouns. The portion of the sentence that names is called the noun phrase, or NP. For action or being we use the Latin for word, verbum, and call words that describe activity verbs. The portio ...
... function and the action function. For naming, we use the Latin word for name, nomen, and call words that name nouns. The portion of the sentence that names is called the noun phrase, or NP. For action or being we use the Latin for word, verbum, and call words that describe activity verbs. The portio ...