DNA, RNA, Genes, Chromosomes
... moment and, as cells mature, many of their genes become permanently inactive. It is the pattern of active and inactive genes in a cell and its resulting protein composition that determines what kind of cell it is and what it can and cannot do. 9. What is DNA, and how is it related to genes? In chemi ...
... moment and, as cells mature, many of their genes become permanently inactive. It is the pattern of active and inactive genes in a cell and its resulting protein composition that determines what kind of cell it is and what it can and cannot do. 9. What is DNA, and how is it related to genes? In chemi ...
Does your DNA define you Qu
... Epigenetics provides the mechanism through which the environment can change the cell without causing mutations in genes to cause the induction of a particular disease. Since epigenetic alterations can alter which genes are expressed, changes can be associated with particular diseases such as cancer ...
... Epigenetics provides the mechanism through which the environment can change the cell without causing mutations in genes to cause the induction of a particular disease. Since epigenetic alterations can alter which genes are expressed, changes can be associated with particular diseases such as cancer ...
Chapter 12 “DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis” Reading/Study Guide
... 19. What are 3 differences between RNA and DNA? ...
... 19. What are 3 differences between RNA and DNA? ...
DNA technology
... Recombinant DNA & Plasmids Combining genes from different sources and/or species ...
... Recombinant DNA & Plasmids Combining genes from different sources and/or species ...
Genetics - California Science Teacher
... 16. Process in which naked DNA is taken up by bacterial or yeast cell 17. Process in which RNA is produced by using a DNA template. 18. Process that results in the production of cDNA from an RNA molecule. 19. Process in which DNA is produced by using a DNA template ...
... 16. Process in which naked DNA is taken up by bacterial or yeast cell 17. Process in which RNA is produced by using a DNA template. 18. Process that results in the production of cDNA from an RNA molecule. 19. Process in which DNA is produced by using a DNA template ...
Neutral DNA - Penn State University
... • About 5-6% of the human genome is under purifying selection since the rodent-primate divergence • About 1.2% codes for protein • The 4 to 5% of the human genome that is under selection but does not code for protein should have: – Regulatory sequences – Non-protein coding genes (UTRs and noncoding ...
... • About 5-6% of the human genome is under purifying selection since the rodent-primate divergence • About 1.2% codes for protein • The 4 to 5% of the human genome that is under selection but does not code for protein should have: – Regulatory sequences – Non-protein coding genes (UTRs and noncoding ...
Genetics Science Learning Center
... 12. If you stretched out all the DNA from a single cell, how long would it be?? _________________________ 13. How many chromosomes are in a human cell? _____ a mosquito? _____ a carp? _____ ...
... 12. If you stretched out all the DNA from a single cell, how long would it be?? _________________________ 13. How many chromosomes are in a human cell? _____ a mosquito? _____ a carp? _____ ...
Your genes
... Date _______________________________ Objectives 1. Identify the different structures that make up genetic ...
... Date _______________________________ Objectives 1. Identify the different structures that make up genetic ...
Jeopardy - Grayslake Central High School
... DNA Tech for 400 What is the major functional difference between adult stem cells and embryonic stem cells? ASCs are pluripotent. They can divide to produce a few different types of somatic cells. ESCs are totipotent. They can divide to produce any cell in the body (or a whole new embryo). ...
... DNA Tech for 400 What is the major functional difference between adult stem cells and embryonic stem cells? ASCs are pluripotent. They can divide to produce a few different types of somatic cells. ESCs are totipotent. They can divide to produce any cell in the body (or a whole new embryo). ...
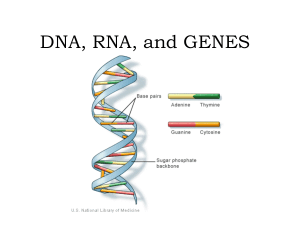
DNA, RNA, and GENES
... • the rungs of the ladder are made up of nitrogen bases. The bonding of these bases is • Adenine bonds with Thymine • Cytosine bonds with Guanine • A to T and C to G ...
... • the rungs of the ladder are made up of nitrogen bases. The bonding of these bases is • Adenine bonds with Thymine • Cytosine bonds with Guanine • A to T and C to G ...
Chapter 10
... Discuss how the structure of DNA allows genes to contain instructions for polypeptide synthesis. List some exceptions to this rule. 3. DNA synthesis is a very precise process by which both strands are reproduced. Thoroughly explain the process of DNA replication. Discuss continuous and disco ...
... Discuss how the structure of DNA allows genes to contain instructions for polypeptide synthesis. List some exceptions to this rule. 3. DNA synthesis is a very precise process by which both strands are reproduced. Thoroughly explain the process of DNA replication. Discuss continuous and disco ...
genome that an organism carries in its DNA. analysis of chromosomes.
... Focus on the bottom of the activity only! Crime Scene Analysis CASE 1 and CASE 2 ...
... Focus on the bottom of the activity only! Crime Scene Analysis CASE 1 and CASE 2 ...
Document
... • DNA is accurately replicated prior to each cell division. • DNA encodes proteins needed by the cell. • DNA is capable of mutation, providing raw material for evolutionary change. ...
... • DNA is accurately replicated prior to each cell division. • DNA encodes proteins needed by the cell. • DNA is capable of mutation, providing raw material for evolutionary change. ...
DNA to Protein - Duplin County Schools
... 1. After watching the animation, what is the correct sequence of the following statements? ___________ A. B. C. D. E. ...
... 1. After watching the animation, what is the correct sequence of the following statements? ___________ A. B. C. D. E. ...
Name:
... 3. Try to match the bases (the letters) together to replicate the DNA strands. What do you notice about how the letters pair together? 4. Move on to “Protein Synthesis”. After unzipping the DNA, the process of transcription begins. What is the goal of this process? 5. What is different about how the ...
... 3. Try to match the bases (the letters) together to replicate the DNA strands. What do you notice about how the letters pair together? 4. Move on to “Protein Synthesis”. After unzipping the DNA, the process of transcription begins. What is the goal of this process? 5. What is different about how the ...
Higher Human Biology unit 1 section 3 BIOINFORMATI
... and development into useful products? 6. Should the NHS prioritise spending money reducing the waiting lists of thousands of patients stuck on hospital surgery waiting lists for life threatening diseases, or invest the money in genomic research? ...
... and development into useful products? 6. Should the NHS prioritise spending money reducing the waiting lists of thousands of patients stuck on hospital surgery waiting lists for life threatening diseases, or invest the money in genomic research? ...
Genes and Mutations 1. Define: Genetics – Genetics may be defined
... 11. One per 100 million copies of the DNA present/ at least one. The m-concentration for a bacterial culture is usually around 10-9 cells/ml of medium (that’s 1 billion cells/ml). 12. Substitutions/ The substitution of one base for another within a gene may or may not change the amino acid sequence ...
... 11. One per 100 million copies of the DNA present/ at least one. The m-concentration for a bacterial culture is usually around 10-9 cells/ml of medium (that’s 1 billion cells/ml). 12. Substitutions/ The substitution of one base for another within a gene may or may not change the amino acid sequence ...
Things to Cover for Exam 1
... What amino acid corresponds to the mRNA codon AAC? Eukaryotic chromosomes contain an alternation of exons and introns. What is the difference between an intron and an exon? Which one has the information coding for a sequence of amino acids? Before the mRNA exits the nucleus it is edited. Are t ...
... What amino acid corresponds to the mRNA codon AAC? Eukaryotic chromosomes contain an alternation of exons and introns. What is the difference between an intron and an exon? Which one has the information coding for a sequence of amino acids? Before the mRNA exits the nucleus it is edited. Are t ...