From Gene to Protein Protein Synthesis
... pries DNA apart and hooks RNA nucleotides together from the DNA code Promoter region on DNA: where RNA polymerase attaches and where initiation of RNA begins Terminator region: sequence that signals the end of transcription Transcription unit: stretch of DNA transcribed into an RNA molecule ...
... pries DNA apart and hooks RNA nucleotides together from the DNA code Promoter region on DNA: where RNA polymerase attaches and where initiation of RNA begins Terminator region: sequence that signals the end of transcription Transcription unit: stretch of DNA transcribed into an RNA molecule ...
Document
... - Shotgun cloning: one first clones a large number of DNA fragments, knowing that one or more contains the DNA of interest. - Gene library: a collection of clones containing all the DNA fragments from one source Creating a genomic DNA library ...
... - Shotgun cloning: one first clones a large number of DNA fragments, knowing that one or more contains the DNA of interest. - Gene library: a collection of clones containing all the DNA fragments from one source Creating a genomic DNA library ...
Concept Check Questions with answers
... family and the globin gene families. How do these gene families benefit the organism? ...
... family and the globin gene families. How do these gene families benefit the organism? ...
Researchers ACT on DNA Storage
... Unlike many forms of information storage, DNA is extremely long-lasting and does not require constant electrical power. Plus, it's tiny—a small cup of DNA can store one hundred million hours of high-quality video. But until now, this storage method has faced too many obstacles: DNA synthesis is expe ...
... Unlike many forms of information storage, DNA is extremely long-lasting and does not require constant electrical power. Plus, it's tiny—a small cup of DNA can store one hundred million hours of high-quality video. But until now, this storage method has faced too many obstacles: DNA synthesis is expe ...
Mutations
... Most mutations are random and occur in regions of DNA that do NOT code for proteins --- Called SILENT MUTATIONS ...
... Most mutations are random and occur in regions of DNA that do NOT code for proteins --- Called SILENT MUTATIONS ...
Genetic Engineering and The Human Genome
... Human Chromosomes • 23 pairs of Chromosomes for a total of 46. – 1-22: autosomal – 23: sex chromosomes ...
... Human Chromosomes • 23 pairs of Chromosomes for a total of 46. – 1-22: autosomal – 23: sex chromosomes ...
genetic engineering and recombinant dna technology
... I. GENETIC ENGINEERING-the transfer of genes from one chromosome to another. A. This has become a much studied area in the field of genetics. It is also very controversial. B. Genetic engineering can be conducted in a variety of ways. II. RESTRICTION ENZYMES-special enzymes that can be used to isola ...
... I. GENETIC ENGINEERING-the transfer of genes from one chromosome to another. A. This has become a much studied area in the field of genetics. It is also very controversial. B. Genetic engineering can be conducted in a variety of ways. II. RESTRICTION ENZYMES-special enzymes that can be used to isola ...
DNA Glossary - FutureLearn
... A homozygote has identical alleles for a specified gene A heterozygote has different alleles for a specified gene on each chromosome The human genome consists of the total DNA structure, consisting of over 3 billion base pairs Twenty-two of the 23 pairs of chromosomes look the same and carry the sam ...
... A homozygote has identical alleles for a specified gene A heterozygote has different alleles for a specified gene on each chromosome The human genome consists of the total DNA structure, consisting of over 3 billion base pairs Twenty-two of the 23 pairs of chromosomes look the same and carry the sam ...
Biology Chapter 12 Review 5-6
... 7. What units make up the backbone of DNA? 8. Explain how the information Watson and Crick acquired from Rosalind Franklin and Chargaff was used to determine the structure of DNA. 9. Explain complementary base pairing and the bases involved. 10. What hold base pairs together and how many? 11. Explai ...
... 7. What units make up the backbone of DNA? 8. Explain how the information Watson and Crick acquired from Rosalind Franklin and Chargaff was used to determine the structure of DNA. 9. Explain complementary base pairing and the bases involved. 10. What hold base pairs together and how many? 11. Explai ...
Red Line - iPlant Pods
... • How does a gene relate to the central dogma of molecular biology: DNA <> RNA > Protein? • How does a gene encode a protein? • How is the mathematical evidence used to predict genes? • How does biological evidence (from RNA and proteins) confirm gene predictions? ...
... • How does a gene relate to the central dogma of molecular biology: DNA <> RNA > Protein? • How does a gene encode a protein? • How is the mathematical evidence used to predict genes? • How does biological evidence (from RNA and proteins) confirm gene predictions? ...
INSERT A-3c
... Explanation/Answer: If all of the DNA is present and the breakage for the translocation did not occur within a gene, then the phenotype of the individual can be normal. However, when that individual’s sex cells undergo meiosis, some of the resulting gametes will not contain the normal amount of DNA. ...
... Explanation/Answer: If all of the DNA is present and the breakage for the translocation did not occur within a gene, then the phenotype of the individual can be normal. However, when that individual’s sex cells undergo meiosis, some of the resulting gametes will not contain the normal amount of DNA. ...
AP Biology - TeacherWeb
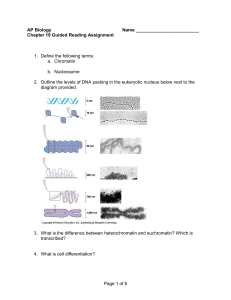
... 5. IF cells carry all of the genetic differences, why then are cells so unique – what is responsible for this? 6. In the diagram below – highlight all of the potential locations for gene expression regulation in eukaryotic cells. How does this compare with prokaryotic cells? ...
... 5. IF cells carry all of the genetic differences, why then are cells so unique – what is responsible for this? 6. In the diagram below – highlight all of the potential locations for gene expression regulation in eukaryotic cells. How does this compare with prokaryotic cells? ...
: Determining DNA sequences
... lengths of chain are produced. • Lengths are separated based on weight and analysed to give • The complementary sequence of the template strand. [ note the sequences in part 1 and part4] ...
... lengths of chain are produced. • Lengths are separated based on weight and analysed to give • The complementary sequence of the template strand. [ note the sequences in part 1 and part4] ...
2nd Semester Review The second semester test covers Meiosis
... you prepare. You should also look over all the review documents that you have in your workbook for these units. ...
... you prepare. You should also look over all the review documents that you have in your workbook for these units. ...
Organization of Eukaryotic DNA Dr: Hussein abdelaziz
... Gene is the fundamental unit of hereditary It's a segment of DNA on a specific position (Locus) on chromosome Each gene is a part of DNA sequences that contains genetic information coding for synthesis of one polypeptide (protein) Genome is the total number of genes within one mature cell of ...
... Gene is the fundamental unit of hereditary It's a segment of DNA on a specific position (Locus) on chromosome Each gene is a part of DNA sequences that contains genetic information coding for synthesis of one polypeptide (protein) Genome is the total number of genes within one mature cell of ...
Genetic engineering
... genetic constitutions of organisms by their selection of plants and animals in the new activity of agriculture .The breeding of domesticated species of plants and animals involves artificial selection and natural hybridization between related species and the doubling of whole sets of chromosomes to ...
... genetic constitutions of organisms by their selection of plants and animals in the new activity of agriculture .The breeding of domesticated species of plants and animals involves artificial selection and natural hybridization between related species and the doubling of whole sets of chromosomes to ...
01 - HomeworkNOW.com
... Directed Reading 14.3 Section: Genome Interactions Read each question, and write your answer in the space provided. ...
... Directed Reading 14.3 Section: Genome Interactions Read each question, and write your answer in the space provided. ...
DNA and Genetic Engineering Midterm Review Chapter 12 Review
... 13. The condition in which cells have many sets of chromosomes; it may instantly produce new plant species that are larger and stronger. 16. Gel electrophoresis enables scientists to separate and analyze DNA fragments, to compare genomes of different individuals and organisms, and to identify a spec ...
... 13. The condition in which cells have many sets of chromosomes; it may instantly produce new plant species that are larger and stronger. 16. Gel electrophoresis enables scientists to separate and analyze DNA fragments, to compare genomes of different individuals and organisms, and to identify a spec ...
ppt
... -Only mutations in germ-line tissues (gametes) are passed on to offspring -Germ-line mutations have larger impact on evolution That said, few mutations are helpful. Most mutations either have no effect on the organism or are harmful. ...
... -Only mutations in germ-line tissues (gametes) are passed on to offspring -Germ-line mutations have larger impact on evolution That said, few mutations are helpful. Most mutations either have no effect on the organism or are harmful. ...
here - VCU
... A nucleotide consists of a base (one of four chemicals: adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine) plus a molecule of sugar and one of phosphoric acid. Dinucleotide: A sequence of 2 base pairs. Oligonucleotides are short sequences of nucleotides (RNA or DNA), typically with twenty or fewer bases. Auto ...
... A nucleotide consists of a base (one of four chemicals: adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine) plus a molecule of sugar and one of phosphoric acid. Dinucleotide: A sequence of 2 base pairs. Oligonucleotides are short sequences of nucleotides (RNA or DNA), typically with twenty or fewer bases. Auto ...
Chpt. 5 Review Questions
... When a person has one recessive allele but does not have the trait? ...
... When a person has one recessive allele but does not have the trait? ...