Unit 4 Genetics
... • That external DNA combines with the cell’s DNA • As the cell copies its own DNA, it also copies the external DNA, since the 2 were combined during transformation ...
... • That external DNA combines with the cell’s DNA • As the cell copies its own DNA, it also copies the external DNA, since the 2 were combined during transformation ...
DNA etcTest Rev 07
... The sugar in DNA is deoyribose. The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides. A nucleotide is made of (3) a phosphate, a sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The four N-bases in DNA are thymine, adenine, guanine, & cytosine. A hydrogen bond is found between the N-bases in DNA. Thymine always bonds with aden ...
... The sugar in DNA is deoyribose. The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides. A nucleotide is made of (3) a phosphate, a sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The four N-bases in DNA are thymine, adenine, guanine, & cytosine. A hydrogen bond is found between the N-bases in DNA. Thymine always bonds with aden ...
SG 17,18,19
... What are endogenous and exogenous forces, what effect on DNA. Discuss how the structure of DNA was determined. Describe basic structure, types of DNA. Discuss supercoiling and it’s role in DNA replication. Define chromosome. Describe chomosomes in prokaryotes versus eukaryotes. Compare Prokaryotic g ...
... What are endogenous and exogenous forces, what effect on DNA. Discuss how the structure of DNA was determined. Describe basic structure, types of DNA. Discuss supercoiling and it’s role in DNA replication. Define chromosome. Describe chomosomes in prokaryotes versus eukaryotes. Compare Prokaryotic g ...
The Central Dogma of Genetics
... instructions (coded in DNA) from the nucleus into the cytoplasm. mRNA molecules are often called transcripts. • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – a structural component of ribosomes (the complexes that are involved in assembling proteins based upon information in mRNA templates) • Transfer RNA (tRNA) – acts as ...
... instructions (coded in DNA) from the nucleus into the cytoplasm. mRNA molecules are often called transcripts. • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – a structural component of ribosomes (the complexes that are involved in assembling proteins based upon information in mRNA templates) • Transfer RNA (tRNA) – acts as ...
Unit 4 exam - Geneti..
... B. It determines the characteristics that will be inherited. C. It is exactly the same in all organisms. D. It directly controls the synthesis of starch within a cell. 6. The presence of DNA is important for the cellular metabolic activities because DNA A. is the major component of the cytoplasm B. ...
... B. It determines the characteristics that will be inherited. C. It is exactly the same in all organisms. D. It directly controls the synthesis of starch within a cell. 6. The presence of DNA is important for the cellular metabolic activities because DNA A. is the major component of the cytoplasm B. ...
File - MRS. WILSON Science
... 8.3 Reinforcement KEY CONCEPT DNA replication copies the genetic information of a cell. ...
... 8.3 Reinforcement KEY CONCEPT DNA replication copies the genetic information of a cell. ...
8-3 Notes with Power point
... 1.The DNA is unwound and unzipped by the enzyme _______________________. The strands are held apart by single-stranded binding proteins (also known as ssbps) 2. Each original DNA strand is used as a ____________________________(or model) to make a new DNA strand with base pairing 3. The enzyme _____ ...
... 1.The DNA is unwound and unzipped by the enzyme _______________________. The strands are held apart by single-stranded binding proteins (also known as ssbps) 2. Each original DNA strand is used as a ____________________________(or model) to make a new DNA strand with base pairing 3. The enzyme _____ ...
Chapter 1
... A point mutation changes a single base pair. Point mutations can be caused by the chemical conversion of one base into another or by mistakes that occur during replication. A transition replaces a G-C base pair with an A-T base pair or vice versa. A transversion replaces a purine with a pyrimidine, ...
... A point mutation changes a single base pair. Point mutations can be caused by the chemical conversion of one base into another or by mistakes that occur during replication. A transition replaces a G-C base pair with an A-T base pair or vice versa. A transversion replaces a purine with a pyrimidine, ...
Title: GeneWiz browser: An Interactive Tool for Visualizing
... • Such availability of the analytics tools is limited and often requires users with both analytical and programming knowledge, hence the analysis of multiple genomes is not always easy in a broad range of the biological research. ...
... • Such availability of the analytics tools is limited and often requires users with both analytical and programming knowledge, hence the analysis of multiple genomes is not always easy in a broad range of the biological research. ...
Name: Period: ______
... So far, we’ve learned that DNA is the genetic material that organisms inherit from their parents, but have you thought about what exactly is encoded for by this DNA? How do our cells use DNA as a set of instructions for life? How is the information in our DNA and genes used by our bodies? And what h ...
... So far, we’ve learned that DNA is the genetic material that organisms inherit from their parents, but have you thought about what exactly is encoded for by this DNA? How do our cells use DNA as a set of instructions for life? How is the information in our DNA and genes used by our bodies? And what h ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... 1. evidence for spontaneous mutation was produced. 2. evidence for adaptive mutation was produced. 3. evidence that DNA is the genetic material was produced. 4. all of the above. ...
... 1. evidence for spontaneous mutation was produced. 2. evidence for adaptive mutation was produced. 3. evidence that DNA is the genetic material was produced. 4. all of the above. ...
Protein Synthesis - Doral Academy High School
... the mRNA into a polypeptide chain • Ribosomes read mRNA 1 codon at a time and construct the proteins • tRNA carrying the amino acid specified by the codon binds and a peptide bond is formed between the two amino acids. • This process continues until a stop codon is reached. • The ribosome then falls ...
... the mRNA into a polypeptide chain • Ribosomes read mRNA 1 codon at a time and construct the proteins • tRNA carrying the amino acid specified by the codon binds and a peptide bond is formed between the two amino acids. • This process continues until a stop codon is reached. • The ribosome then falls ...
The Living World
... The inner cell mass consists of embryonic stem cells These are pluripotent Capable of forming the entire organism As development proceeds, cells lose their pluripotency They become committed to one type of tissue They are then called adult stem cells ...
... The inner cell mass consists of embryonic stem cells These are pluripotent Capable of forming the entire organism As development proceeds, cells lose their pluripotency They become committed to one type of tissue They are then called adult stem cells ...
Slide ()
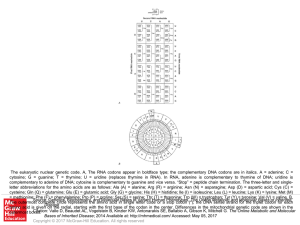
... The eukaryotic nuclear genetic code. A, The RNA codons appear in boldface type; the complementary DNA codons are in italics. A = adenine; C = cytosine; G = guanine; T = thymine; U = uridine (replaces thymine in RNA). In RNA, adenine is complementary to thymine of DNA; uridine is complementary to ade ...
... The eukaryotic nuclear genetic code. A, The RNA codons appear in boldface type; the complementary DNA codons are in italics. A = adenine; C = cytosine; G = guanine; T = thymine; U = uridine (replaces thymine in RNA). In RNA, adenine is complementary to thymine of DNA; uridine is complementary to ade ...
DNA, RNA and Protein
... •In opposite orientations •Held together by hydrogen bonds •Twisted into a helix ...
... •In opposite orientations •Held together by hydrogen bonds •Twisted into a helix ...
Ch. 10 Vocabs
... -Transformation: the transfer of genetic material in the form of DNA fragments from one cell to another or from one organism to another. -Bacteriophage a virus that infects bacteria. Section 2: -Nucleotide: in a nucleic-acid chain, a subunit that consists of a sugar, phosphate and nitrogenous base. ...
... -Transformation: the transfer of genetic material in the form of DNA fragments from one cell to another or from one organism to another. -Bacteriophage a virus that infects bacteria. Section 2: -Nucleotide: in a nucleic-acid chain, a subunit that consists of a sugar, phosphate and nitrogenous base. ...
Topic 12 (Ch9/7) – Microbial Genetics Genetics Chromosome
... – Short interference RNA (siRNA) • RNA molecule complementary to a portion of mRNA, tRNA, or a gene that binds and renders the target inactive ...
... – Short interference RNA (siRNA) • RNA molecule complementary to a portion of mRNA, tRNA, or a gene that binds and renders the target inactive ...
Study Island
... Development of the cell theory was made possible by advances in _______. A. physics B. chemistry C. microscopy D. anatomy 2. All living organisms use energy. They also grow and reproduce. What is another characteristic of all living organisms? A. All living organisms must consume food in order to ac ...
... Development of the cell theory was made possible by advances in _______. A. physics B. chemistry C. microscopy D. anatomy 2. All living organisms use energy. They also grow and reproduce. What is another characteristic of all living organisms? A. All living organisms must consume food in order to ac ...