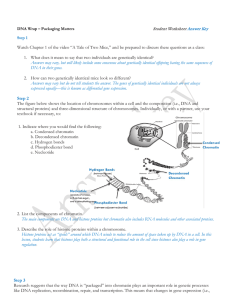
DNA!
... trisomy 21 (3 chromosomes at 21 instead of 2) occurs. 2. PKU – tested using a blood sample to look for the presence or absence of certain proteins. This indicated whether a person’s genes are functioning normally. PKU is when a person cannot digest a certain protein in food and the build up can be t ...
... trisomy 21 (3 chromosomes at 21 instead of 2) occurs. 2. PKU – tested using a blood sample to look for the presence or absence of certain proteins. This indicated whether a person’s genes are functioning normally. PKU is when a person cannot digest a certain protein in food and the build up can be t ...
Selfish DNA and the wonderful world of RNA
... Does natural selection “ choose” the most fit individuals or the most fit genes? ...
... Does natural selection “ choose” the most fit individuals or the most fit genes? ...
DNA Day research - DNA model construction
... ~DNA polymerase adds appropriate nucleotides to new strand of DNA ~leading strand elongates as DNA unwinds, lagging strand elongates away from replication * JOINING ~DNA polymerase replaces RNA primer with nucleotides. ~DNA ligase links 2 sections ...
... ~DNA polymerase adds appropriate nucleotides to new strand of DNA ~leading strand elongates as DNA unwinds, lagging strand elongates away from replication * JOINING ~DNA polymerase replaces RNA primer with nucleotides. ~DNA ligase links 2 sections ...
Gene Therapy
... a mixture of DNA fragments is placed at one end of a gel and an electric current is run through the gel DNA molecules which are negatively charged move toward the positive end of the gel; the smaller the fragment of DNA the faster and farther it moves ...
... a mixture of DNA fragments is placed at one end of a gel and an electric current is run through the gel DNA molecules which are negatively charged move toward the positive end of the gel; the smaller the fragment of DNA the faster and farther it moves ...
Recombinant DNA Technology
... of the egg. These mRNAs are inactive due to masking by proteins. Fertilization of the egg initiates unmasking and translation of these mRNAs. • Availability of specific tRNAs – In the embryonic development of a hornworm, an mRNA is present from day 1 but a specific tRNA needed for its translation is ...
... of the egg. These mRNAs are inactive due to masking by proteins. Fertilization of the egg initiates unmasking and translation of these mRNAs. • Availability of specific tRNAs – In the embryonic development of a hornworm, an mRNA is present from day 1 but a specific tRNA needed for its translation is ...
Macroevolution
... genes are passed from generation to generation (vertical gene transfer). – Hitchhiking genes from other species lead to phylogenetic complexity referred to as lateral gene transfer. ...
... genes are passed from generation to generation (vertical gene transfer). – Hitchhiking genes from other species lead to phylogenetic complexity referred to as lateral gene transfer. ...
Gene Regulation Summary Slide Questions with
... phosphorylates the CREB in the nucleus, which binds to CBP.....this causes histone acetylation and remodeling, opening up the DNA for gene expression. Thanks, epi. 17. How many genes do transcription factors regulate? What do they bind to DNA through and where? One TF may regulate many genes. They b ...
... phosphorylates the CREB in the nucleus, which binds to CBP.....this causes histone acetylation and remodeling, opening up the DNA for gene expression. Thanks, epi. 17. How many genes do transcription factors regulate? What do they bind to DNA through and where? One TF may regulate many genes. They b ...
Name: Genetics Study Guide
... What does codominance mean in genetics? How is it different from Incomplete dominance? Know the difference between a hybrid and a purebred. In what decade was the DNA structure discovered? Who discovered the structure of DNA? What is the scientific name of the DNA structure? Which is the correct ord ...
... What does codominance mean in genetics? How is it different from Incomplete dominance? Know the difference between a hybrid and a purebred. In what decade was the DNA structure discovered? Who discovered the structure of DNA? What is the scientific name of the DNA structure? Which is the correct ord ...
Genetic engineering
... genetic constitutions of organisms by their selection of plants and animals in the new activity of agriculture .The breeding of domesticated species of plants and animals involves artificial selection and natural hybridization between related species and the doubling of whole sets of chromosomes to ...
... genetic constitutions of organisms by their selection of plants and animals in the new activity of agriculture .The breeding of domesticated species of plants and animals involves artificial selection and natural hybridization between related species and the doubling of whole sets of chromosomes to ...
投影片 1
... mediates binding to negatively charged sialic acid residues on the cell surface. 3. Amounts of liposome, DNA, and the exposure time are different with cell types, and may be critical for transfection . 4. Liposome aggregates DNA. The method is good for co-transfection, or for insertion of multiple c ...
... mediates binding to negatively charged sialic acid residues on the cell surface. 3. Amounts of liposome, DNA, and the exposure time are different with cell types, and may be critical for transfection . 4. Liposome aggregates DNA. The method is good for co-transfection, or for insertion of multiple c ...
Answer Key
... transcribed into mRNA and then translated (conversion of mRNA sequence into amino acids) into a protein. An individual’s environment, even in the womb, can influence these factors and permanently alter the expression of genes in the adult. Alterations in epigenetic mechanisms lead to development of ...
... transcribed into mRNA and then translated (conversion of mRNA sequence into amino acids) into a protein. An individual’s environment, even in the womb, can influence these factors and permanently alter the expression of genes in the adult. Alterations in epigenetic mechanisms lead to development of ...
4.4 Genetic engineering and biotechnology - McLain
... B. Its nucleus is replaced by the nucleus of the differentiated cell. C. Its nucleus is fused with the nucleus of the differentiated cell. D. Its nucleus is exchanged with the nucleus of the sperm. ...
... B. Its nucleus is replaced by the nucleus of the differentiated cell. C. Its nucleus is fused with the nucleus of the differentiated cell. D. Its nucleus is exchanged with the nucleus of the sperm. ...
CSI” Plant Style: From Laboratory to your Lunch Tray
... How Do We Determine Which Seeds Carry The Trait We Are Interested In? ...
... How Do We Determine Which Seeds Carry The Trait We Are Interested In? ...
DNA & Heredity
... of the genes Gene- the chemical factors that determine traits Alleles-the different forms of a gene Cloning-making an exact genetic copy of something Pedigree- is your family line Mutation- change in the DNA Inheritance- passing on of something from parent to ...
... of the genes Gene- the chemical factors that determine traits Alleles-the different forms of a gene Cloning-making an exact genetic copy of something Pedigree- is your family line Mutation- change in the DNA Inheritance- passing on of something from parent to ...
Protein Synthesis - Simon Technology
... predict the physical characteristics of an organism based on its genetic make up. understand the general pathway by which ribosomes make proteins. explain the causes of gene and chromosomal mutations in multicellular organisms. understand how changes in DNA sequences can cause changes in the protein ...
... predict the physical characteristics of an organism based on its genetic make up. understand the general pathway by which ribosomes make proteins. explain the causes of gene and chromosomal mutations in multicellular organisms. understand how changes in DNA sequences can cause changes in the protein ...
Protein Synthesis
... predict the physical characteristics of an organism based on its genetic make up. understand the general pathway by which ribosomes make proteins. explain the causes of gene and chromosomal mutations in multicellular organisms. understand how changes in DNA sequences can cause changes in the protein ...
... predict the physical characteristics of an organism based on its genetic make up. understand the general pathway by which ribosomes make proteins. explain the causes of gene and chromosomal mutations in multicellular organisms. understand how changes in DNA sequences can cause changes in the protein ...
Supplementary Fig S7: A Schematic Figure of the Key Driver Analysis
... Supplementary Fig S7: A Schematic Figure of the Key Driver Analysis (KDA). In order to test if gene G (shown in red) is a KD or not, the subnetwork of G is first extracted by retrieving its 1st to 3rdlayer neighbor genes in the network. Subsequently, the enrichment of genes in a given BP gene set (s ...
... Supplementary Fig S7: A Schematic Figure of the Key Driver Analysis (KDA). In order to test if gene G (shown in red) is a KD or not, the subnetwork of G is first extracted by retrieving its 1st to 3rdlayer neighbor genes in the network. Subsequently, the enrichment of genes in a given BP gene set (s ...
4.1 Genetics
... Bellringer 2/23 • DNA is able to control cellular activities most directly by regulating the process of (1) meiotic division (2) protein synthesis (3) active transport (4) selective breeding ...
... Bellringer 2/23 • DNA is able to control cellular activities most directly by regulating the process of (1) meiotic division (2) protein synthesis (3) active transport (4) selective breeding ...
Example of BLASTN output
... The title of this primary literature journal article suggests that the authors did experiments to show that the house fly sequence is equivalent to the Drosophila sequence. We can click on the link (9376318) to see the Abstract from the journal article. The abstract is a concise summary of the infor ...
... The title of this primary literature journal article suggests that the authors did experiments to show that the house fly sequence is equivalent to the Drosophila sequence. We can click on the link (9376318) to see the Abstract from the journal article. The abstract is a concise summary of the infor ...
What Is Gene cloning and How Is It Used? 1. Explain what is meant
... Indicate the purpose of the vector and name the two types of vectors used. ...
... Indicate the purpose of the vector and name the two types of vectors used. ...
What Is Gene cloning and How Is It Used? 1. Explain what is meant
... Indicate the purpose of the vector and name the two types of vectors used. ...
... Indicate the purpose of the vector and name the two types of vectors used. ...