Genes and Evolution - Mad River Local Schools
... evolution? a. Changing of organisms over time b. The descent of an organism from a common ancestor c. Phenotypes of an organism and how they fit with the environment d. Both a and b ...
... evolution? a. Changing of organisms over time b. The descent of an organism from a common ancestor c. Phenotypes of an organism and how they fit with the environment d. Both a and b ...
Biotechnology
... – Forensic science (crime scene “fingerprints”) – Determining paternity – Looking at disease risk ...
... – Forensic science (crime scene “fingerprints”) – Determining paternity – Looking at disease risk ...
Biology Chapter 12 Review 5-6
... b. Organism(s) and/or viruses used c. Overview of experimental design/procedures d. One sentence conclusion 2. What type of macromolecule is DNA? 3. DNA is composed of what monomer? 4. What are the three units to the above monomer? 5. Identify the 4 different types of nitrogenous bases? 6. Nitrogeno ...
... b. Organism(s) and/or viruses used c. Overview of experimental design/procedures d. One sentence conclusion 2. What type of macromolecule is DNA? 3. DNA is composed of what monomer? 4. What are the three units to the above monomer? 5. Identify the 4 different types of nitrogenous bases? 6. Nitrogeno ...
Lecture
... 1.045 billion bases sequenced 1800 microbial species estimated to exist in sample, ...
... 1.045 billion bases sequenced 1800 microbial species estimated to exist in sample, ...
DNA NOTES
... forming an amino acid chain (protein). (pg. 184) 21. Define Codon: (pg. 184) 22. Define Anticodon: (pg. 185) 23. Use figure 8.4 (pg. 185) to answer the following questions. a. What is the codon sequence labeled in the diagram? ______________ b. On what molecule will you find the codon? _____________ ...
... forming an amino acid chain (protein). (pg. 184) 21. Define Codon: (pg. 184) 22. Define Anticodon: (pg. 185) 23. Use figure 8.4 (pg. 185) to answer the following questions. a. What is the codon sequence labeled in the diagram? ______________ b. On what molecule will you find the codon? _____________ ...
Combinatorial Control of Gene Activation and Coordinately
... • In eukaryotes, the precise control of transcription depends on the binding of activators to DNA control elements. • There are only about twelve nucleotide sequences that make up control elements and they appear over and over again. • Each enhancer-a group of control elements- contains about ten nu ...
... • In eukaryotes, the precise control of transcription depends on the binding of activators to DNA control elements. • There are only about twelve nucleotide sequences that make up control elements and they appear over and over again. • Each enhancer-a group of control elements- contains about ten nu ...
Assignment 1
... This is the only ORF that shows no in-frame stop codon in the sequence given. And these are three amino acids following the first Met amino acid for this ORF. Q10. If the third base (U) of the resulting mRNA is mutated to G, then what would be the effect of the mutation on the polypeptide being synt ...
... This is the only ORF that shows no in-frame stop codon in the sequence given. And these are three amino acids following the first Met amino acid for this ORF. Q10. If the third base (U) of the resulting mRNA is mutated to G, then what would be the effect of the mutation on the polypeptide being synt ...
Changes in DNA can produce variation
... DNA sequence can change • There is a large number of DNA bases in any organism that need to be copied • Errors can occur when DNA is copied or affected by environment – UV radiation – X-rays – Toxins ...
... DNA sequence can change • There is a large number of DNA bases in any organism that need to be copied • Errors can occur when DNA is copied or affected by environment – UV radiation – X-rays – Toxins ...
Lec:1 Dr.Mohammed Alhamdany Molecular and genetic factors in
... polyadenylation signal, acts as a signal for termination of the RNA transcript. The activity of RNA polymerase II is regulated by transcription factors (promoters and enhancers) The histone proteins associated with chromatin can also be methylated, phosphorylated or acetylated at specific amino acid ...
... polyadenylation signal, acts as a signal for termination of the RNA transcript. The activity of RNA polymerase II is regulated by transcription factors (promoters and enhancers) The histone proteins associated with chromatin can also be methylated, phosphorylated or acetylated at specific amino acid ...
The Good, the bad and the ugly of Genetic Engineering
... Put plasmid back into bacteria (a process called transformation) Bacteria will transcribe and translate our insulin gene even though the insulin protein doesn’t do anything for a bacterial cell. Then we can take out the insulin protein and use it to treat diabetics. ...
... Put plasmid back into bacteria (a process called transformation) Bacteria will transcribe and translate our insulin gene even though the insulin protein doesn’t do anything for a bacterial cell. Then we can take out the insulin protein and use it to treat diabetics. ...
Xeroderma Pigmentosum(XP)
... 的) pyrimidines(嘧啶) on a DNA strand have a tendency to interact with one another to form a covalent(共价的) dimer complex.(example as TT--胸腺嘧啶二具体) ...
... 的) pyrimidines(嘧啶) on a DNA strand have a tendency to interact with one another to form a covalent(共价的) dimer complex.(example as TT--胸腺嘧啶二具体) ...
Unit 1 - Glen Rose FFA
... DNA of nucleus is stored by wrapping it around five proteins to form a nucleosome. ...
... DNA of nucleus is stored by wrapping it around five proteins to form a nucleosome. ...
Nessun titolo diapositiva
... Heterochromatin is nucleated at a specific sequence and the inactive structure propagates along the chromatin fiber. Genes within regions of heterochromatin are inactivated. Because the length of the inactive region varies from cell to cell, inactivation of genes in this vicinity causes position ...
... Heterochromatin is nucleated at a specific sequence and the inactive structure propagates along the chromatin fiber. Genes within regions of heterochromatin are inactivated. Because the length of the inactive region varies from cell to cell, inactivation of genes in this vicinity causes position ...
Nucleic acid review sheet
... What is the material in each cell that contains a set of instructions that controls all genetic traits? ...
... What is the material in each cell that contains a set of instructions that controls all genetic traits? ...
Describe the operon hypothesis and discuss
... Describe the operon hypothesis and discuss how it explains the control of messenger RNA production and the regulation of protein synthesis in bacterial cells. STANDARDS: BACKGROUND: ...
... Describe the operon hypothesis and discuss how it explains the control of messenger RNA production and the regulation of protein synthesis in bacterial cells. STANDARDS: BACKGROUND: ...
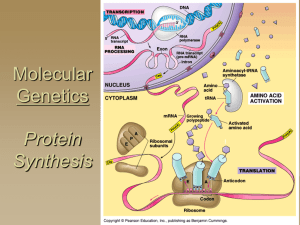
Molecular Genetics
... A gene is a DNA segment that encodes a particular polypeptide Gene expression is the process in which proteins are assembled from the information contained in DNA ...
... A gene is a DNA segment that encodes a particular polypeptide Gene expression is the process in which proteins are assembled from the information contained in DNA ...
8.6 Gene Expression and Regulation
... start matching base pairs Chemical such as growth factors and hormones may determine how tightly the DNA is coiled ...
... start matching base pairs Chemical such as growth factors and hormones may determine how tightly the DNA is coiled ...
Human Genetics
... A mutation in PAH could cause the protein to misfold and not produce functional PAH enzyme. This is ok because we have two copies of chromosome 12, and therefore two copies of PAH, so one will work. However, if both copies of the gene are mutated, a person will have PKU. ...
... A mutation in PAH could cause the protein to misfold and not produce functional PAH enzyme. This is ok because we have two copies of chromosome 12, and therefore two copies of PAH, so one will work. However, if both copies of the gene are mutated, a person will have PKU. ...
“Algorithms for genomes” 2b Central Dogma Transcription start and
... DNA winds around histone proteins (nucleosomes). ...
... DNA winds around histone proteins (nucleosomes). ...
Unit VII Objectives Biotechnology
... 2. What is meant by the universality of the genetic code? 3. Define polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Describe what is needed for PCR to happen, its process of DNA amplification, and list several uses. 4. Describe the process of gel electrophoresis and how it is used. 5. Define and describe DNA seque ...
... 2. What is meant by the universality of the genetic code? 3. Define polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Describe what is needed for PCR to happen, its process of DNA amplification, and list several uses. 4. Describe the process of gel electrophoresis and how it is used. 5. Define and describe DNA seque ...
Evolution and Genetics
... Antibiotic-resistant strains of microorganisms that cause diseases, such as tuberculosis, are increasing in number due to natural selection ...
... Antibiotic-resistant strains of microorganisms that cause diseases, such as tuberculosis, are increasing in number due to natural selection ...
Chapter 8 Microbial Genetics
... • Nucleotides • Deoxyribose, phosphate, nitrogen base • Adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine • Double helix • 2 chains of nucleotides • Alternating units of sugar and phosphate • Nitrogen base is attached to the sugar molecule ...
... • Nucleotides • Deoxyribose, phosphate, nitrogen base • Adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine • Double helix • 2 chains of nucleotides • Alternating units of sugar and phosphate • Nitrogen base is attached to the sugar molecule ...