Exporter la page en pdf
... Cryptic unstable transcripts (CUTs) are synthesized from intra- and intergenic regions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and are rapidly degraded by RNA surveillance pathways, but their function(s) remain(s) elusive. Here, we show that an antisense TY1 CUT, starting within the Ty1 retrotransposon and enco ...
... Cryptic unstable transcripts (CUTs) are synthesized from intra- and intergenic regions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and are rapidly degraded by RNA surveillance pathways, but their function(s) remain(s) elusive. Here, we show that an antisense TY1 CUT, starting within the Ty1 retrotransposon and enco ...
Epigenetics: We often discuss genes as if their presence in our cells
... can have a different phenotypic effect if inherited from the mother or the father. The take home message of all this (to me) is that we are accumulating data faster than we can process it, and we realize now that we don't understand many of the very complex processes occurring in our cells. Recent s ...
... can have a different phenotypic effect if inherited from the mother or the father. The take home message of all this (to me) is that we are accumulating data faster than we can process it, and we realize now that we don't understand many of the very complex processes occurring in our cells. Recent s ...
a5_1_1-1_done
... 9. Explain differential gene expression… different cell types in a multicellular organism are due to what? This is because cells within the same genome express a different gene. 10. Chromatin structure: this is meant to help regulate gene expression location of the genes promoter sites where the DNA ...
... 9. Explain differential gene expression… different cell types in a multicellular organism are due to what? This is because cells within the same genome express a different gene. 10. Chromatin structure: this is meant to help regulate gene expression location of the genes promoter sites where the DNA ...
BCH-201:Nucleotides and Nucleic acids
... glycolysis). Other mRNAs are specific for only certain types of cells. These encode proteins needed for the function of that particular cell (e.g., the mRNA for hemoglobin in the precursors of red blood cells). Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) There are 4 kinds. In eukaryotes, these are ...
... glycolysis). Other mRNAs are specific for only certain types of cells. These encode proteins needed for the function of that particular cell (e.g., the mRNA for hemoglobin in the precursors of red blood cells). Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) There are 4 kinds. In eukaryotes, these are ...
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes Webquest
... the human genome. While it is estimated that the human genome comprises fewer than 25,000 genes, the total number of proteins in the human proteome is estimated at over 1 million. This means that single genes encode multiple proteins. ...
... the human genome. While it is estimated that the human genome comprises fewer than 25,000 genes, the total number of proteins in the human proteome is estimated at over 1 million. This means that single genes encode multiple proteins. ...
Study Guide A - WordPress.com
... Fill in the blank with the word or phrase that best completes the sentence. 7. The enzyme that helps a cell to make a strand of RNA is called ________________________. 8. The following sentences summarize the three key steps of transcription. Circle the word or phrase that best completes the sentenc ...
... Fill in the blank with the word or phrase that best completes the sentence. 7. The enzyme that helps a cell to make a strand of RNA is called ________________________. 8. The following sentences summarize the three key steps of transcription. Circle the word or phrase that best completes the sentenc ...
Chapter 8
... identities of these sequences were learned by comparing the sequences of genes to their spliced mRNA products. The GU dinucleotide at the 5' splice site of the intron and the AG dinucleotide at the 3' splice site are highly conserved. Also highly conserved within the intron is a branch point sequenc ...
... identities of these sequences were learned by comparing the sequences of genes to their spliced mRNA products. The GU dinucleotide at the 5' splice site of the intron and the AG dinucleotide at the 3' splice site are highly conserved. Also highly conserved within the intron is a branch point sequenc ...
AQA A2 level Biology
... 6 Explain why introns must be removed from the mRNA before leaving the nucleus. Once the mRNA has left the nucleus, it may be translated very quickly. If the introns were left in, a non-functional polypeptide would be made during translation. 7 Suggest why organisms regulate their gene expression. O ...
... 6 Explain why introns must be removed from the mRNA before leaving the nucleus. Once the mRNA has left the nucleus, it may be translated very quickly. If the introns were left in, a non-functional polypeptide would be made during translation. 7 Suggest why organisms regulate their gene expression. O ...
Binary Switches in Gene Expression: The Histone Code
... lies outside of the DNA itself. . This system relies on packaging DNA into a DNA-histone complex called chromatin, which is the physiological substrate of all cellular processes involving the DNA. The dynamic change of the three-dimensional architecture of chromatin makes certain genes more readily ...
... lies outside of the DNA itself. . This system relies on packaging DNA into a DNA-histone complex called chromatin, which is the physiological substrate of all cellular processes involving the DNA. The dynamic change of the three-dimensional architecture of chromatin makes certain genes more readily ...
Differential Gene Expression
... 2. Enhancers are the major determinants of differential transcription in cell types and through developmental stages. 3. There can be multiple signals (e.g. multiple enhancer sites) for a given gene, and each enhancer can be bound by more than one transcription factor (not at the same time). 4. Tran ...
... 2. Enhancers are the major determinants of differential transcription in cell types and through developmental stages. 3. There can be multiple signals (e.g. multiple enhancer sites) for a given gene, and each enhancer can be bound by more than one transcription factor (not at the same time). 4. Tran ...
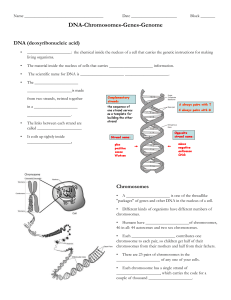
DNA-Chromosomes-Genes-Genome student notesheet
... • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...
... • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...
1. What is the advantage of meiosis in terms of survival
... 24. SKIN COLOR AND EYE COLOR ARE TRAITS THAT ARE AFFECTED BY WHAT KIND OF INHERITANCE? ...
... 24. SKIN COLOR AND EYE COLOR ARE TRAITS THAT ARE AFFECTED BY WHAT KIND OF INHERITANCE? ...
Dr. Becker`s Review – Exam 4 Notes provided by Kadie Keen
... pre-mRNA processed in spliceosome within the nucleus to form mature mRNA Requires 3 things 1. Remove introns (splice) 2. Apply 5’ cap (guanine cap – represented by a backwards “G”) 3. Apply 3’ tail (polyA – tail …AAAAAAAAA) Mature mRNA goes to translation (ribosomes are attaching at the same time) ...
... pre-mRNA processed in spliceosome within the nucleus to form mature mRNA Requires 3 things 1. Remove introns (splice) 2. Apply 5’ cap (guanine cap – represented by a backwards “G”) 3. Apply 3’ tail (polyA – tail …AAAAAAAAA) Mature mRNA goes to translation (ribosomes are attaching at the same time) ...
Dioxyribose Nucleic Acid
... Amino Acids – All amino acids have their own “three” digit code using nitrogen bases. – Amino acids make proteins in your body. • There are only 20 amino acids. ...
... Amino Acids – All amino acids have their own “three” digit code using nitrogen bases. – Amino acids make proteins in your body. • There are only 20 amino acids. ...
Chapter 2
... In this dissertation we frequently refer to the HGVS Nomenclature and when doing so we have a clear subset of its rules in mind. Usually, we will restrict ourselves to so-called genomic descriptions, i.e., descriptions based upon a genomic sequence, e.g. a chromosome, without any additional annotati ...
... In this dissertation we frequently refer to the HGVS Nomenclature and when doing so we have a clear subset of its rules in mind. Usually, we will restrict ourselves to so-called genomic descriptions, i.e., descriptions based upon a genomic sequence, e.g. a chromosome, without any additional annotati ...
Nucleus/Nucleolus
... A barrier between the nucleus and the cytoplasm The place where ribosome subunits assemble Uncoiled DNA that is used in protein synthesis The cell’s control center ...
... A barrier between the nucleus and the cytoplasm The place where ribosome subunits assemble Uncoiled DNA that is used in protein synthesis The cell’s control center ...
Lecture 12
... Consensus RNA motifs for the sites attracting four serine/arginine reach proteins acting as exonic splicing enhancers (ESE) ...
... Consensus RNA motifs for the sites attracting four serine/arginine reach proteins acting as exonic splicing enhancers (ESE) ...
Practice Science Olympiad Exam: Designer Genes
... 18. What is the “backbone” of DNA made from and what type of bonds does the element share with the adjacent sugars? 19. What is the protein called that connect two chromatids to form a chromosome? 20. What protein does DNA strands wrap around when coiling, and how many times does it wrap around the ...
... 18. What is the “backbone” of DNA made from and what type of bonds does the element share with the adjacent sugars? 19. What is the protein called that connect two chromatids to form a chromosome? 20. What protein does DNA strands wrap around when coiling, and how many times does it wrap around the ...
Exam IV 1710_1711 F'01.doc
... A gene or series of genes/operons,encoding catabolic pathway enzymes, which can be turned off and on as needed are likely to have their expression regulated in a/an __________ fashion (e.g. lac operon in E. coli): a. ...
... A gene or series of genes/operons,encoding catabolic pathway enzymes, which can be turned off and on as needed are likely to have their expression regulated in a/an __________ fashion (e.g. lac operon in E. coli): a. ...
code sequence practice
... Transcription – making mRNA from DNA 2. If this is your original DNA strand, what is the mRNA sequence that is synthesized? DNA Strand: C A G T G C A T T mRNA strand: 3. Now go backwards, if you are given the following mRNA strand, write the DNA strand that goes with it. mRNA strand: U C G A C C G A ...
... Transcription – making mRNA from DNA 2. If this is your original DNA strand, what is the mRNA sequence that is synthesized? DNA Strand: C A G T G C A T T mRNA strand: 3. Now go backwards, if you are given the following mRNA strand, write the DNA strand that goes with it. mRNA strand: U C G A C C G A ...
Primary transcript

A primary transcript is the single-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) product synthesized by transcription of DNA, and processed to yield various mature RNA products such as mRNAs, tRNAs, and rRNAs. The primary transcripts designated to be mRNAs are modified in preparation for translation. For example, a precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) is a type of primary transcript that becomes a messenger RNA (mRNA) after processing.There are several steps contributing to the production of primary transcripts. All these steps involve a series of interactions to initiate and complete the transcription of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Certain factors play key roles in the activation and inhibition of transcription, where they regulate primary transcript production. Transcription produces primary transcripts that are further modified by several processes. These processes include the 5' cap, 3'-polyadenylation, and alternative splicing. In particular, alternative splicing directly contributes to the diversity of mRNA found in cells. The modifications of primary transcripts have been further studied in research seeking greater knowledge of the role and significance of these transcripts. Experimental studies based on molecular changes to primary transcripts the processes before and after transcription have led to greater understanding of diseases involving primary transcripts.