How are we different? …at the RNA level.
... – A 92 bp deletion in a gene that codes for a hydroxylase, results in an un-hydroxylated secretion protein in our immune system. ...
... – A 92 bp deletion in a gene that codes for a hydroxylase, results in an un-hydroxylated secretion protein in our immune system. ...
Genetics 3500 winter Test ii_ansers
... Much of the genome is transcribed as NcRNA some of which overlap protein sequences Exons can be shared by unrelated proteins. Introns can contain open reading frames of oother genes. RNA editing so proteins do not reflect DNA sequence Chromatin modification, Methylation of DNA and Histone modificati ...
... Much of the genome is transcribed as NcRNA some of which overlap protein sequences Exons can be shared by unrelated proteins. Introns can contain open reading frames of oother genes. RNA editing so proteins do not reflect DNA sequence Chromatin modification, Methylation of DNA and Histone modificati ...
workshop module 6: dna, rna and proteins - Peer
... The discovery of DNA structure as a double helix and its function as the genetic material of the cell were major scientific achievements of the 20th century. Countless scientists have contributed to our understanding of the process by which DNA is replicated prior to cell division, and the functiona ...
... The discovery of DNA structure as a double helix and its function as the genetic material of the cell were major scientific achievements of the 20th century. Countless scientists have contributed to our understanding of the process by which DNA is replicated prior to cell division, and the functiona ...
Answered copy of exam 3
... IX. In cattle C_ animals are normal and cc develop cataracts. A DNA based polymorphism detected by PCR is just 4 map units from the cataracts gene. It’s alleles are designated A35 or A50 for the size of the amplified product. Suppose a bull has the genotype ...
... IX. In cattle C_ animals are normal and cc develop cataracts. A DNA based polymorphism detected by PCR is just 4 map units from the cataracts gene. It’s alleles are designated A35 or A50 for the size of the amplified product. Suppose a bull has the genotype ...
Unit 5 Free Response
... By using the techniques of genetic engineering, scientists are able to modify genetic material so that a particular gene of interest from one cell can be incorporated into a different cell. - Describe a procedure by which this can be done. - Explain the purpose of each step of your procedure. - Desc ...
... By using the techniques of genetic engineering, scientists are able to modify genetic material so that a particular gene of interest from one cell can be incorporated into a different cell. - Describe a procedure by which this can be done. - Explain the purpose of each step of your procedure. - Desc ...
HEREDITY: INHERITANCE and TRENDS Unit Cover Page Topic
... All cells contain genetic information in the form of DNA molecules. Genes are regions in the DNA that contain instructions that code for the formation of proteins. (LS1.A) ...
... All cells contain genetic information in the form of DNA molecules. Genes are regions in the DNA that contain instructions that code for the formation of proteins. (LS1.A) ...
4. Protein Synthesis and Biotechnology
... parental strands. Each strand acts as a template to form a complementary daughter strand of DNA. The new daughter strands are formed when complementary new nucleotides are added to the bases of the nucleotides on the parental strands. The nucleotide sequence of the parental strand dictates the order ...
... parental strands. Each strand acts as a template to form a complementary daughter strand of DNA. The new daughter strands are formed when complementary new nucleotides are added to the bases of the nucleotides on the parental strands. The nucleotide sequence of the parental strand dictates the order ...
BIO 220 Chapter 8 lecture outline Vocabulary Central dogma of
... 2. What is the central dogma of biology? Who proposed this theory? 3. What is the difference between the terms genotype and phenotype? Are bacteria typically diploid or haploid? What do diploid and haploid mean? 4. How many chromosomes does the typical bacterial cell have? In what form do these chro ...
... 2. What is the central dogma of biology? Who proposed this theory? 3. What is the difference between the terms genotype and phenotype? Are bacteria typically diploid or haploid? What do diploid and haploid mean? 4. How many chromosomes does the typical bacterial cell have? In what form do these chro ...
Gral Regents Review Part 2
... DNA regulates cell processes with its specific code to synthesize proteins. DNA to RNA to Protein Information flows from gene to protein. DNA (a gene) is copied to make RNA in the cell's nucleus. The RNA travels to the ribosome where it is translated into the specific amino acid sequence of a prote ...
... DNA regulates cell processes with its specific code to synthesize proteins. DNA to RNA to Protein Information flows from gene to protein. DNA (a gene) is copied to make RNA in the cell's nucleus. The RNA travels to the ribosome where it is translated into the specific amino acid sequence of a prote ...
AQA Biology Question number Answer Marks Guidance 1 a i (In all
... 4 Changes tertiary structure of protein (so non-functional) ...
... 4 Changes tertiary structure of protein (so non-functional) ...
Honors Biology Module 7 Cellular Reproduction
... A strand of mRNA can be thought of as a bunch of three-nucleotide sequence. Each threenucleotide base sequence is called a codon. A strand of tRNA contains a three-nucleotide base seque4nce called an anticodon. A certain anticodon on tRNA results in an certan amino acid boded to the tRNA. Since the ...
... A strand of mRNA can be thought of as a bunch of three-nucleotide sequence. Each threenucleotide base sequence is called a codon. A strand of tRNA contains a three-nucleotide base seque4nce called an anticodon. A certain anticodon on tRNA results in an certan amino acid boded to the tRNA. Since the ...
BIO101 Objectives Unit3 Blinderman Mercer County Community
... genetic material 2. Explain how radioactively labeled molecules such as 35S-proteins and 32P-DNA can be used as tracers 3. Review the basic steps of bacteriophage infection of bacteria 4. Examine composition of DNA including Chargaff’s observations concerning relative concentrations of purines and p ...
... genetic material 2. Explain how radioactively labeled molecules such as 35S-proteins and 32P-DNA can be used as tracers 3. Review the basic steps of bacteriophage infection of bacteria 4. Examine composition of DNA including Chargaff’s observations concerning relative concentrations of purines and p ...
Chapter Outline
... Steps in Translation of mRNA • Converts language of nucleotides into sequence of amino acids in a protein • Ribosome in cytosol or on rough ER – small subunit attaches to mRNA leader sequence – large subunit joins and pulls mRNA along as it “reads” it • start codon (AUG) begins protein synthesis ...
... Steps in Translation of mRNA • Converts language of nucleotides into sequence of amino acids in a protein • Ribosome in cytosol or on rough ER – small subunit attaches to mRNA leader sequence – large subunit joins and pulls mRNA along as it “reads” it • start codon (AUG) begins protein synthesis ...
1. The I gene determines the synthesis of a repressor molecule
... Another way of labeling mutants of the operator is to denote that they lead to a constitutive phenotype; lacO– (or a–) can also be written as lacOc. There are also mutations of the repressor that fail to bind inducer (allolactose) as opposed to fail to bind DNA. These two classes have quite differen ...
... Another way of labeling mutants of the operator is to denote that they lead to a constitutive phenotype; lacO– (or a–) can also be written as lacOc. There are also mutations of the repressor that fail to bind inducer (allolactose) as opposed to fail to bind DNA. These two classes have quite differen ...
DNA Study Guide CP2015
... ______2. Fruit flies with the curly-wing trait will develop straight wings if kept at a temperature of 16°C during development and curly wings if kept at 25°C. The best explanation for this change in the shape of wings is that the a. genes for curly wings and genes for straight wings are found on di ...
... ______2. Fruit flies with the curly-wing trait will develop straight wings if kept at a temperature of 16°C during development and curly wings if kept at 25°C. The best explanation for this change in the shape of wings is that the a. genes for curly wings and genes for straight wings are found on di ...
Analytical and Chromatography - Sigma
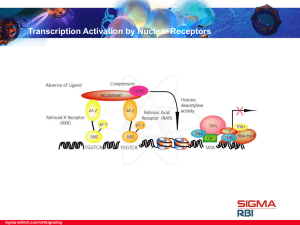
... • Retinoid X receptor (RXR) and Retinoic Acid receptor (RAR) are nuclear receptors that bind either all trans-retinoic (tRA) or 9-cis-retinoic acid (9cis-RA). In the absence of ligand, corepressors, such as Nuclear Receptor Corepressor (NCoR), Silencing Mediator of Retinoid and Thyroid Hormone Recep ...
... • Retinoid X receptor (RXR) and Retinoic Acid receptor (RAR) are nuclear receptors that bind either all trans-retinoic (tRA) or 9-cis-retinoic acid (9cis-RA). In the absence of ligand, corepressors, such as Nuclear Receptor Corepressor (NCoR), Silencing Mediator of Retinoid and Thyroid Hormone Recep ...
RNA & Protein Synthesis
... decoding mRNA to produce a sequence of amino acids in a chain (protein) mRNA = messenger RNA Amino Acids = building blocks ...
... decoding mRNA to produce a sequence of amino acids in a chain (protein) mRNA = messenger RNA Amino Acids = building blocks ...
DNA, RNA, & Meiosis Review
... – Metaphase I – homologous chromosomes line up in middle of cell and spindle fibers attach to them – Anaphase I – homologous chromosomes are pulled to opposite sides of cell by spindle fibers – Telophase I – nuclear membrane reforms around the separated homologous chromosomes, spindle breaks down, c ...
... – Metaphase I – homologous chromosomes line up in middle of cell and spindle fibers attach to them – Anaphase I – homologous chromosomes are pulled to opposite sides of cell by spindle fibers – Telophase I – nuclear membrane reforms around the separated homologous chromosomes, spindle breaks down, c ...
doc
... 4. Write the following sequence on the board, and ask students if it is DNA or RNA: TACGGCACGATT. Have students copy the DNA sequence onto a piece of paper. 5. Review the process of transcription. Have students write down the RNA sequence that would come from the DNA on the board. 6. Pass out the su ...
... 4. Write the following sequence on the board, and ask students if it is DNA or RNA: TACGGCACGATT. Have students copy the DNA sequence onto a piece of paper. 5. Review the process of transcription. Have students write down the RNA sequence that would come from the DNA on the board. 6. Pass out the su ...
Molecular Genetics Notes (Ch 8)
... Anticodon-a sequence of 3 bases that are complementary base pairs to a codon in the mRNA ...
... Anticodon-a sequence of 3 bases that are complementary base pairs to a codon in the mRNA ...
Designer Genes - Heredity
... Messenger RNA – carries blueprint Transfer RNA – brings amino acids Ribosomal RNA – reads code ...
... Messenger RNA – carries blueprint Transfer RNA – brings amino acids Ribosomal RNA – reads code ...
Primary transcript

A primary transcript is the single-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) product synthesized by transcription of DNA, and processed to yield various mature RNA products such as mRNAs, tRNAs, and rRNAs. The primary transcripts designated to be mRNAs are modified in preparation for translation. For example, a precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) is a type of primary transcript that becomes a messenger RNA (mRNA) after processing.There are several steps contributing to the production of primary transcripts. All these steps involve a series of interactions to initiate and complete the transcription of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Certain factors play key roles in the activation and inhibition of transcription, where they regulate primary transcript production. Transcription produces primary transcripts that are further modified by several processes. These processes include the 5' cap, 3'-polyadenylation, and alternative splicing. In particular, alternative splicing directly contributes to the diversity of mRNA found in cells. The modifications of primary transcripts have been further studied in research seeking greater knowledge of the role and significance of these transcripts. Experimental studies based on molecular changes to primary transcripts the processes before and after transcription have led to greater understanding of diseases involving primary transcripts.