Semester 2 – Final Exam Review2016
... 8. List the steps of RNA transcription (ending with the product): ...
... 8. List the steps of RNA transcription (ending with the product): ...
Goal 3
... Injury Repair Disadvantages of the overproduction, underproduction or production of proteins at the incorrect times: Cancer ...
... Injury Repair Disadvantages of the overproduction, underproduction or production of proteins at the incorrect times: Cancer ...
Glossary - The Birman Cat Club
... Nucleotide: building blocks of DNA and RNA, there are four for RNA and four for DNA Penetrance: the frequency with which a genotype manifests itself in a given phenotype Phenotype: the observable characteristics of a cell or organism Point mutation: usually a single nucleotide change Polymorphism: t ...
... Nucleotide: building blocks of DNA and RNA, there are four for RNA and four for DNA Penetrance: the frequency with which a genotype manifests itself in a given phenotype Phenotype: the observable characteristics of a cell or organism Point mutation: usually a single nucleotide change Polymorphism: t ...
File
... Mutations can arise in a number of ways. Errors during DNA replication or recombination can lead to nucleotide-pair substitutions, insertions, or deletions, as well as to mutations affecting longer stretches of DNA. If an incorrect nucleotide is added to a growing chain during replication, for examp ...
... Mutations can arise in a number of ways. Errors during DNA replication or recombination can lead to nucleotide-pair substitutions, insertions, or deletions, as well as to mutations affecting longer stretches of DNA. If an incorrect nucleotide is added to a growing chain during replication, for examp ...
An in vitro RNA synthesis reaction was set up and allowed to
... nonradioactive ribonucleotides (NTPs). After several minutes had passed, radioactive NTPs were added and RNA synthesis was allowed to continue. Then the RNA molecules were isolated from the reaction mixture and analyzed for the presence of radioactive nucleotides at the 5' and the 3' ends. Based on ...
... nonradioactive ribonucleotides (NTPs). After several minutes had passed, radioactive NTPs were added and RNA synthesis was allowed to continue. Then the RNA molecules were isolated from the reaction mixture and analyzed for the presence of radioactive nucleotides at the 5' and the 3' ends. Based on ...
Lecture Outline ()
... • Discovery of the double helix – by 1900:components of DNA were known – by 1953: xray diffraction determined geometry of DNA molecule – Nobel Prize awarded in 1962 to 3 men: Watson, Crick and Wilkins but not to Rosalind Franklin who died of cancer at 37 from the xray data that provided the answers. ...
... • Discovery of the double helix – by 1900:components of DNA were known – by 1953: xray diffraction determined geometry of DNA molecule – Nobel Prize awarded in 1962 to 3 men: Watson, Crick and Wilkins but not to Rosalind Franklin who died of cancer at 37 from the xray data that provided the answers. ...
What is a gene? - Ecology and Evolution Unit
... says. “It used to be we could give a one-off definition and now it’s much more complicated.” In classical genetics, a gene was an abstract concept — a unit of inheritance that ferried a characteristic from parent to child. As biochemistry came into its own, those characteristics were associated with ...
... says. “It used to be we could give a one-off definition and now it’s much more complicated.” In classical genetics, a gene was an abstract concept — a unit of inheritance that ferried a characteristic from parent to child. As biochemistry came into its own, those characteristics were associated with ...
Gene Technology
... manipulating genes for practical purposes Recombinant DNA – DNA made from 2 or ...
... manipulating genes for practical purposes Recombinant DNA – DNA made from 2 or ...
AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 16 OUTLINE
... OUTLINE THE MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE I. DNA AS THE GENETIC MATERIAL A. The search for the genetic material led to DNA: science as a process Proteins were thought to be the genetic material because: ...
... OUTLINE THE MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE I. DNA AS THE GENETIC MATERIAL A. The search for the genetic material led to DNA: science as a process Proteins were thought to be the genetic material because: ...
Biotechnology - Hicksville Public Schools / Homepage
... Bacteria, help us make yogurt & cheese. ...
... Bacteria, help us make yogurt & cheese. ...
Practicing Protein Synthesis
... mRNA directly below the DNA strand (remember to substitute U's for T's in RNA). Use a codon chart to determine what amino acids are assembled to make the insulin protein in both the cow and the human. Write your amino acid chain directly below the RNA sequence. Table 1: Human Sequence DNA ...
... mRNA directly below the DNA strand (remember to substitute U's for T's in RNA). Use a codon chart to determine what amino acids are assembled to make the insulin protein in both the cow and the human. Write your amino acid chain directly below the RNA sequence. Table 1: Human Sequence DNA ...
Why-do-cells
... Efficiency of moving materials into the cell – The larger the cell becomes the less efficient it is – The volume of the cell increases faster then its surface area – Cells that grow too large no longer have enough surface area to take in nutrients and ...
... Efficiency of moving materials into the cell – The larger the cell becomes the less efficient it is – The volume of the cell increases faster then its surface area – Cells that grow too large no longer have enough surface area to take in nutrients and ...
Genetically Modified Food
... Mechanism1 : Isolating/synthesizing the target gene The ‘shotgun’ approach, using type II restriction enzyme(restriction endonuclease ) - the enzyme cuts at recognition sites, to obtain a desired gene - sticky ends or blunt ends produced (there are figures later) Making a copy of the gene from ...
... Mechanism1 : Isolating/synthesizing the target gene The ‘shotgun’ approach, using type II restriction enzyme(restriction endonuclease ) - the enzyme cuts at recognition sites, to obtain a desired gene - sticky ends or blunt ends produced (there are figures later) Making a copy of the gene from ...
Keystone Review: Quiz 4
... d. The process used to form proteins by transcription and translation 3.) A mutation occurs at the midpoint of a gene, altering all amino acids encoded after the point of mutation. Which mutation could have produced this change? a. Deletion of a nucleotide b. Deletion of three nucleotides c. Inserti ...
... d. The process used to form proteins by transcription and translation 3.) A mutation occurs at the midpoint of a gene, altering all amino acids encoded after the point of mutation. Which mutation could have produced this change? a. Deletion of a nucleotide b. Deletion of three nucleotides c. Inserti ...
biology final review sheet answers
... wing and bird wing. 18. What are vestigial organs? What are some examples of vestigial organs? Vestigial organs are structures that are inherited from common ancestors but have lost much or all of its original function. Examples of vestigial organs in humans include wisdom teeth, appendix, tail bone ...
... wing and bird wing. 18. What are vestigial organs? What are some examples of vestigial organs? Vestigial organs are structures that are inherited from common ancestors but have lost much or all of its original function. Examples of vestigial organs in humans include wisdom teeth, appendix, tail bone ...
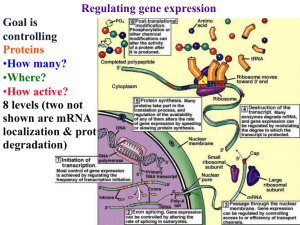
Gene expression and DNA microarrays
... • Level of RNA produced from a gene is controlled by: – Transcription – Stability/Degradation ...
... • Level of RNA produced from a gene is controlled by: – Transcription – Stability/Degradation ...
Chapter 12: Mechanisms and Regulation of Transcription I
... a. Certain genes specific to epidermal cells will be expressed in epidermal cells and not other cell types b. Certain genes specific to neurons will be expressed only in neurons c. Certain genes specific to sex will only be expressed at a given time in only a certain set of cells 4. One way to contr ...
... a. Certain genes specific to epidermal cells will be expressed in epidermal cells and not other cell types b. Certain genes specific to neurons will be expressed only in neurons c. Certain genes specific to sex will only be expressed at a given time in only a certain set of cells 4. One way to contr ...
6 Principles of Gene Regulation
... IHF: Heterodimer sharp bends: >140° May repress or stimulate transcription FIS: Homodimer Bends DNA by 90° ...
... IHF: Heterodimer sharp bends: >140° May repress or stimulate transcription FIS: Homodimer Bends DNA by 90° ...
Final Review: 2nd Semester Biology Answer Key
... The enzyme helicase unwinds the double helix, separating the two strands. The enzyme DNA polymerase constructs the new DNA by adding the complementary nucleotides. In the end, each of the 2 DNA molecules produced contains one original strand of nucleotides (that served as the template) and one new s ...
... The enzyme helicase unwinds the double helix, separating the two strands. The enzyme DNA polymerase constructs the new DNA by adding the complementary nucleotides. In the end, each of the 2 DNA molecules produced contains one original strand of nucleotides (that served as the template) and one new s ...
Primary transcript

A primary transcript is the single-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) product synthesized by transcription of DNA, and processed to yield various mature RNA products such as mRNAs, tRNAs, and rRNAs. The primary transcripts designated to be mRNAs are modified in preparation for translation. For example, a precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) is a type of primary transcript that becomes a messenger RNA (mRNA) after processing.There are several steps contributing to the production of primary transcripts. All these steps involve a series of interactions to initiate and complete the transcription of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Certain factors play key roles in the activation and inhibition of transcription, where they regulate primary transcript production. Transcription produces primary transcripts that are further modified by several processes. These processes include the 5' cap, 3'-polyadenylation, and alternative splicing. In particular, alternative splicing directly contributes to the diversity of mRNA found in cells. The modifications of primary transcripts have been further studied in research seeking greater knowledge of the role and significance of these transcripts. Experimental studies based on molecular changes to primary transcripts the processes before and after transcription have led to greater understanding of diseases involving primary transcripts.