Punnett Squares
... Name: _____KEY_______________________________ Date: ______________________ Period: ______ ...
... Name: _____KEY_______________________________ Date: ______________________ Period: ______ ...
Std.8 Genetics Study Guide
... _________________ alleles need only 1 allele to be expressed; ____________________ alleles must have two alleles to be expressed. ...
... _________________ alleles need only 1 allele to be expressed; ____________________ alleles must have two alleles to be expressed. ...
int_2015_Bio_9
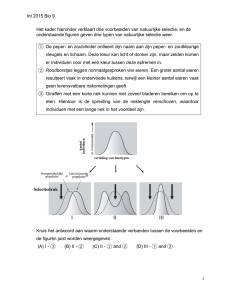
... Directional selection (I): a mode of natural selection in which a single phenotype is favored, causing the allele frequency to continuously shift in one direction. The genetic variance of the population shifts toward a new phenotype when exposed to environmental changes. In the case of such selectio ...
... Directional selection (I): a mode of natural selection in which a single phenotype is favored, causing the allele frequency to continuously shift in one direction. The genetic variance of the population shifts toward a new phenotype when exposed to environmental changes. In the case of such selectio ...
Document
... April 2010, Second edition, Hardcover, 216 pages, ISBN: 978‑1‑4051‑8857‑9, Wiley‑Blackwell, £79.50 / €91.50. Description: 1 What is genetic variation? DNA, RNA. Protein structure, chromosomes. How does sexual reproduction produce variation? Mitochondrial and chloroplast DNA. 2 How can genetic variat ...
... April 2010, Second edition, Hardcover, 216 pages, ISBN: 978‑1‑4051‑8857‑9, Wiley‑Blackwell, £79.50 / €91.50. Description: 1 What is genetic variation? DNA, RNA. Protein structure, chromosomes. How does sexual reproduction produce variation? Mitochondrial and chloroplast DNA. 2 How can genetic variat ...
Ch - TeacherWeb
... b. The gene pool of this population never experienced mutation or gene flow. c. A very small number of mink may have colonized this island, and this founder effect and subsequent genetic drift could have fixed many alleles. d. Natural selection has selected for and fixed the best adapted alleles at ...
... b. The gene pool of this population never experienced mutation or gene flow. c. A very small number of mink may have colonized this island, and this founder effect and subsequent genetic drift could have fixed many alleles. d. Natural selection has selected for and fixed the best adapted alleles at ...
1. In each generation, the tails of puppies were cut short for four
... B. Organisms that are the best adapted to their environment survive, produce more offspring, and pass their genes on to these offspring. C. People get to select who survives and reproduces. D. Organisms can change a trait by using it in a specific way during their lifetime, then they pass this on to ...
... B. Organisms that are the best adapted to their environment survive, produce more offspring, and pass their genes on to these offspring. C. People get to select who survives and reproduces. D. Organisms can change a trait by using it in a specific way during their lifetime, then they pass this on to ...
Chapter 22-25 Packet O` Fun
... A. The widespread use of DDT in the mid-1900s put pressure on insect populations to evolve resistance to DDT. As a result, large populations of insects today are resistant to DDT. Answer: This is a Lamarckian statement. DDT worked only against insects that had no DDTresistance genes. The genes for D ...
... A. The widespread use of DDT in the mid-1900s put pressure on insect populations to evolve resistance to DDT. As a result, large populations of insects today are resistant to DDT. Answer: This is a Lamarckian statement. DDT worked only against insects that had no DDTresistance genes. The genes for D ...
Study Guide for Evolution and Genetics Final Exam
... 36. What is the only mechanism for evolution that creates new traits? 37. If a parent gets a tan, do they pass their tan onto their baby? Why not? What is the difference between adapting to an environment and evolution? 38. What is genetic biodiversity? Why is genetic variation in a species importan ...
... 36. What is the only mechanism for evolution that creates new traits? 37. If a parent gets a tan, do they pass their tan onto their baby? Why not? What is the difference between adapting to an environment and evolution? 38. What is genetic biodiversity? Why is genetic variation in a species importan ...
Linkage Disequilibrium
... On average, how fast LD decays across the genome Useful to determine the number of markers needed for an association mapping experiment ...
... On average, how fast LD decays across the genome Useful to determine the number of markers needed for an association mapping experiment ...
If you have BRCA in the family (England and Wales)
... My maternal/paternal (select one) mother/father/grandmother/grandfather/uncle/aunt (select one) is a BRCA1/2 gene mutation carrier and there is a strong possibility that this gene mutation will have been passed on to me. According to NHS England policy E01/P/b, Clinical Commissioning Policy: Genetic ...
... My maternal/paternal (select one) mother/father/grandmother/grandfather/uncle/aunt (select one) is a BRCA1/2 gene mutation carrier and there is a strong possibility that this gene mutation will have been passed on to me. According to NHS England policy E01/P/b, Clinical Commissioning Policy: Genetic ...
Evolutionary Computation
... • Each individual is represented by a genetic code (chromosome) , which corresponds to one solution of the problem • Initial population is usually randomly generated ...
... • Each individual is represented by a genetic code (chromosome) , which corresponds to one solution of the problem • Initial population is usually randomly generated ...
Machine Evolution
... • A crossover point is selected at random and parts of the two parent chromosomes are swapped to create two offspring with a probability which is called crossover rate. ...
... • A crossover point is selected at random and parts of the two parent chromosomes are swapped to create two offspring with a probability which is called crossover rate. ...
Name Date Class
... 1. Is the long-haired cat in the P generation a hybrid or a purebred? Explain your answer. 2. Is the short-haired cat in the P generation a hybrid or a purebred? Explain your answer. 3. If the short-haired cat in the P generation were purebred, what would you expect the offspring to look like? 4. In ...
... 1. Is the long-haired cat in the P generation a hybrid or a purebred? Explain your answer. 2. Is the short-haired cat in the P generation a hybrid or a purebred? Explain your answer. 3. If the short-haired cat in the P generation were purebred, what would you expect the offspring to look like? 4. In ...
Lecture 25 Population Genetics Until now, we have been carrying
... To see how this would happen, consider a gene in a very large population with a single major dominant allele A and 10 minor recessive alleles a1, a2, a3 ...a10 with allele frequencies ƒ(a1) = ƒ(a2) = ƒ(a3) ... = 10-4 and (ƒ(A) ≈ 1) Now imagine that a group of 500 individuals from this population mo ...
... To see how this would happen, consider a gene in a very large population with a single major dominant allele A and 10 minor recessive alleles a1, a2, a3 ...a10 with allele frequencies ƒ(a1) = ƒ(a2) = ƒ(a3) ... = 10-4 and (ƒ(A) ≈ 1) Now imagine that a group of 500 individuals from this population mo ...
Genit 2
... chromosomes, but they may have abnormal structures. For example, translocation of segments of one chromosome to another is considered a mutation. The frequency of this type is 6*10-4. This might also result in abortion but the parents of the fetus might be completely normal. - Gene mutations: in thi ...
... chromosomes, but they may have abnormal structures. For example, translocation of segments of one chromosome to another is considered a mutation. The frequency of this type is 6*10-4. This might also result in abortion but the parents of the fetus might be completely normal. - Gene mutations: in thi ...
population subdivision: gene flow
... strength of selection against random change in allele frequencies (drift) and in the homogenizing effects of migration. In the case of heterozygote advantage or overdominance in which both homozygous genotypes have a similar selection coefficient (1-s), we would expect an equilibrium p* = 0.5. Even ...
... strength of selection against random change in allele frequencies (drift) and in the homogenizing effects of migration. In the case of heterozygote advantage or overdominance in which both homozygous genotypes have a similar selection coefficient (1-s), we would expect an equilibrium p* = 0.5. Even ...
Quiz 6
... In 1990, the Asian shore crab was introduced to the southern coast of Maine. As of today, Asian shore crabs have not migrated to the waters off northern Maine. Asian shore crabs are more aggressive than green crabs, and were able to break the thicker shells the mussels developed in response to the g ...
... In 1990, the Asian shore crab was introduced to the southern coast of Maine. As of today, Asian shore crabs have not migrated to the waters off northern Maine. Asian shore crabs are more aggressive than green crabs, and were able to break the thicker shells the mussels developed in response to the g ...
Genetic drift

Genetic drift (or allelic drift) is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces. A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation.When there are few copies of an allele, the effect of genetic drift is larger, and when there are many copies the effect is smaller. In the early twentieth century vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at the most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims that most instances where a genetic change spreads across a population (although not necessarily changes in phenotypes) are caused by genetic drift. There is currently a scientific debate about how much of evolution has been caused by natural selection, and how much by genetic drift.