Causes of Evolution
... Types of Natural Selection 1. STABILIZING Selection = favors average individuals in a population • reduces variation in organisms Ex: lizards – large captured easily & small cannot run fast enough 2. DIRECTIONAL Selection = favors one of the extreme variations of a trait • can lead to rapid evolutio ...
... Types of Natural Selection 1. STABILIZING Selection = favors average individuals in a population • reduces variation in organisms Ex: lizards – large captured easily & small cannot run fast enough 2. DIRECTIONAL Selection = favors one of the extreme variations of a trait • can lead to rapid evolutio ...
Evolutionary Mechanisms
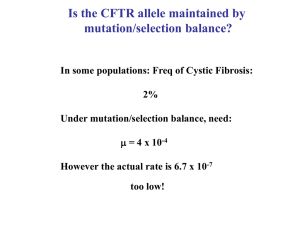
... A population geneticist studies a population of American Robins and finds that the allele for the normal form of alcohol dehydrogenase has a frequency of 0.92 while a recessive allele that produces a defective form of the enzyme has a frequency of 0.08. (Robins often eat fermenting berries, and may ...
... A population geneticist studies a population of American Robins and finds that the allele for the normal form of alcohol dehydrogenase has a frequency of 0.92 while a recessive allele that produces a defective form of the enzyme has a frequency of 0.08. (Robins often eat fermenting berries, and may ...
Evolutionary forces: in small populations
... 1. Mutation: the only source of new genetic information. Mutation: any heritable change in the structure or amount of genetic material. Different levels of mutation DNA: point and frame shift mutations (mistakes made during DNA replication) Arrangements of DNA +/- of single chromosomes + complete se ...
... 1. Mutation: the only source of new genetic information. Mutation: any heritable change in the structure or amount of genetic material. Different levels of mutation DNA: point and frame shift mutations (mistakes made during DNA replication) Arrangements of DNA +/- of single chromosomes + complete se ...
Population Genetics
... • Founder Effect: a few leave the larger population to start a new colony and thereby change the allele frequencies i.e. 1814 British colony founded on an island One individual was a carrier for retinitis pigmentosa which causes blindness Harmful recessive (aa) By the 1960’s 4 people had disease, 9 ...
... • Founder Effect: a few leave the larger population to start a new colony and thereby change the allele frequencies i.e. 1814 British colony founded on an island One individual was a carrier for retinitis pigmentosa which causes blindness Harmful recessive (aa) By the 1960’s 4 people had disease, 9 ...
Mechanism of Evolution
... The South Atlantic island of Tristan da Cunha was colonized by 15 Britons in 1814, one of them carrying an allele for retinitis pigmentosum. Among their 240 descendents living on the island today, 4 are blind by the disease and 9 others are ...
... The South Atlantic island of Tristan da Cunha was colonized by 15 Britons in 1814, one of them carrying an allele for retinitis pigmentosum. Among their 240 descendents living on the island today, 4 are blind by the disease and 9 others are ...
Document
... Depends upon: (2Nu) number of mutations arising at locus per generation, and initial frequency of new allele (1/2N) ...
... Depends upon: (2Nu) number of mutations arising at locus per generation, and initial frequency of new allele (1/2N) ...
Natural selection Differential survival or reproduction of individuals
... a group of orgs. that interbreed under natural conditions to produce fertile offspring “special case” of natural selection; pressures that affect an individual’s success in mating Splitting of one species into two or more different species members of a species are isolated from one another due to a ...
... a group of orgs. that interbreed under natural conditions to produce fertile offspring “special case” of natural selection; pressures that affect an individual’s success in mating Splitting of one species into two or more different species members of a species are isolated from one another due to a ...
Enriched Biology Dremann Metzendorf Bag 3
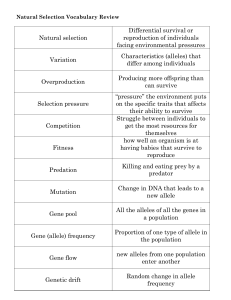
... 5. All the genes of all members of a particular population make up the population’s… 6. In a population, the sum of the relative frequencies of all alleles for a particular trait is… 7. A change in a sequence of DNA is called a… 8. The two main sources of genetic variation are… 9. In genetic drift, ...
... 5. All the genes of all members of a particular population make up the population’s… 6. In a population, the sum of the relative frequencies of all alleles for a particular trait is… 7. A change in a sequence of DNA is called a… 8. The two main sources of genetic variation are… 9. In genetic drift, ...
Quiz 3, February 6, 2003
... a. MUTATION is the original source of genetic variation within populations. b. NATURAL SELECTION is a process by which individuals with particular heritable characters survive and reproduce at a higher rate than other individuals in a population. c. GENETIC DRIFT is a random process that is most inf ...
... a. MUTATION is the original source of genetic variation within populations. b. NATURAL SELECTION is a process by which individuals with particular heritable characters survive and reproduce at a higher rate than other individuals in a population. c. GENETIC DRIFT is a random process that is most inf ...
QS039--Ch21--Mechanisms of Evolution
... b. Bottleneck Effect: _____________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ ...
... b. Bottleneck Effect: _____________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ ...
Genetic Drift
... Selection of new beneficial traits according to selective pressures at the time Natural selection produces adaptation of an organism ...
... Selection of new beneficial traits according to selective pressures at the time Natural selection produces adaptation of an organism ...
Changing Allele Frequencies
... Genetic Drift Chance sampling of alleles from the whole population Due to: ...
... Genetic Drift Chance sampling of alleles from the whole population Due to: ...
Mechanisms of Evolution
... • is the transfer of alleles or genes from one population to another. • This makes separate populations more similar genetically. ...
... • is the transfer of alleles or genes from one population to another. • This makes separate populations more similar genetically. ...
More Evolution and Hardy Weinberg! KEY
... 1. What are the mechanisms for evolution? Give a brief description of each Genetic drift: change in gene pool in a small population (chance) gene flow: immigration or emigration of genes mutation: random change of the genes natural selection: a random act upon population evolve 2. What is the bottl ...
... 1. What are the mechanisms for evolution? Give a brief description of each Genetic drift: change in gene pool in a small population (chance) gene flow: immigration or emigration of genes mutation: random change of the genes natural selection: a random act upon population evolve 2. What is the bottl ...
Factors Causing Evolution
... Prairie dogs live in dense colonies consisting of a few dozen members. For much of the year they prevent other prairie dogs from joining their colony. In late summer, however, mature male pups are permitted to enter new colonies, thereby affecting both gene pools. ...
... Prairie dogs live in dense colonies consisting of a few dozen members. For much of the year they prevent other prairie dogs from joining their colony. In late summer, however, mature male pups are permitted to enter new colonies, thereby affecting both gene pools. ...
Genetic drift

Genetic drift (or allelic drift) is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces. A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation.When there are few copies of an allele, the effect of genetic drift is larger, and when there are many copies the effect is smaller. In the early twentieth century vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at the most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims that most instances where a genetic change spreads across a population (although not necessarily changes in phenotypes) are caused by genetic drift. There is currently a scientific debate about how much of evolution has been caused by natural selection, and how much by genetic drift.