DISRUPTING GENETIC EQUILIBRIUM
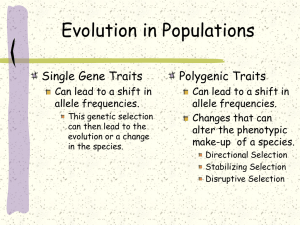
... A population is the smallest level evolution can work on, changing the genetic composition of the population over time. Gene Pool = the total genetic material available in a population Adapting to new selection factors can only use existing genes found in the population Allele Frequency = the number ...
... A population is the smallest level evolution can work on, changing the genetic composition of the population over time. Gene Pool = the total genetic material available in a population Adapting to new selection factors can only use existing genes found in the population Allele Frequency = the number ...
Population Genetics, Speciation, and Classification
... alleles that are present, then you could predict expected genotypes and frequencies of alleles. ...
... alleles that are present, then you could predict expected genotypes and frequencies of alleles. ...
Evolution Review
... Name Date Period Evolution Review: Answer the following questions and make a flash card for each question. 1. In natural selection, those with _________ traits for the environment ___________ and get to ____________. 2. How keeps lethal recessive alleles in a population? __________________ 3. What i ...
... Name Date Period Evolution Review: Answer the following questions and make a flash card for each question. 1. In natural selection, those with _________ traits for the environment ___________ and get to ____________. 2. How keeps lethal recessive alleles in a population? __________________ 3. What i ...
A1992HJ46800001
... that the beach populations were relatively small and periodically bottlenecked, we also attributed the interpopulation variation to genetic drift rather than to natural selection. This interpretation undoubtedly raised the eyebrows of many mammalogistsand evolutionists, because, in the dogma of the ...
... that the beach populations were relatively small and periodically bottlenecked, we also attributed the interpopulation variation to genetic drift rather than to natural selection. This interpretation undoubtedly raised the eyebrows of many mammalogistsand evolutionists, because, in the dogma of the ...
Mechanisms of Evolution
... What drives this ‘speciation’? ISOLATING MECHANISMS • Behavioral• Geographical• Temporal- ...
... What drives this ‘speciation’? ISOLATING MECHANISMS • Behavioral• Geographical• Temporal- ...
populations
... Genes that contains the sequence TATA in its promoter are more likely to have evolved than that of a genes that do not have TATA in its promoter. ...
... Genes that contains the sequence TATA in its promoter are more likely to have evolved than that of a genes that do not have TATA in its promoter. ...
Name: Block: ______ Lab Biology Chapter 16 The Evolution of
... Fifty percent of an experimental population of four o’clock flowers are red flowered plants, and 50 percent are white flowered plants. What is the frequency of the r ...
... Fifty percent of an experimental population of four o’clock flowers are red flowered plants, and 50 percent are white flowered plants. What is the frequency of the r ...
Evolution WKS - Sardis Secondary
... ___ 3. different versions of genes ___ 4. idea stating that under certain conditions, allele frequencies in the population remain stable from generation to generation ___ 5. constant state of allele frequency ___ 6. accidental change in gene frequency ___ 7. a change in allele frequencies within a p ...
... ___ 3. different versions of genes ___ 4. idea stating that under certain conditions, allele frequencies in the population remain stable from generation to generation ___ 5. constant state of allele frequency ___ 6. accidental change in gene frequency ___ 7. a change in allele frequencies within a p ...
that evolution would not occur
... following are key for evolution to occur: I. When a population is small, chance fluctuations can cause changes in allele frequencies II. When mating is nonrandom, individuals preferred as mates will pass on their alleles in greater numbers then those who are not preferred III. When genetic mutations ...
... following are key for evolution to occur: I. When a population is small, chance fluctuations can cause changes in allele frequencies II. When mating is nonrandom, individuals preferred as mates will pass on their alleles in greater numbers then those who are not preferred III. When genetic mutations ...
Slide 1
... following are key for evolution to occur: I. When a population is small, chance fluctuations can cause changes in allele frequencies II. When mating is nonrandom, individuals preferred as mates will pass on their alleles in greater numbers then those who are not preferred III. When genetic mutations ...
... following are key for evolution to occur: I. When a population is small, chance fluctuations can cause changes in allele frequencies II. When mating is nonrandom, individuals preferred as mates will pass on their alleles in greater numbers then those who are not preferred III. When genetic mutations ...
The Evolution of Populations
... G. Hardy and W. Weinberg 1908 showed that genotype frequencies in a population stay the same over time as log as certain conditions are met. These frequencies can be predicted. ...
... G. Hardy and W. Weinberg 1908 showed that genotype frequencies in a population stay the same over time as log as certain conditions are met. These frequencies can be predicted. ...
File
... Population has experienced a “bottleneck” and certain alleles may be over-represented ...
... Population has experienced a “bottleneck” and certain alleles may be over-represented ...
013368718X_CH17_267
... 10. Reproductive isolation occurs when members of two populations do not interbreed and produce fertile offspring. 11. The separation of two populations by barriers such as rivers or mountains results in temporal isolation. 12. The Hardy-Weinberg principle states that allele frequencies in a populat ...
... 10. Reproductive isolation occurs when members of two populations do not interbreed and produce fertile offspring. 11. The separation of two populations by barriers such as rivers or mountains results in temporal isolation. 12. The Hardy-Weinberg principle states that allele frequencies in a populat ...
Genetic drift

Genetic drift (or allelic drift) is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces. A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation.When there are few copies of an allele, the effect of genetic drift is larger, and when there are many copies the effect is smaller. In the early twentieth century vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at the most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims that most instances where a genetic change spreads across a population (although not necessarily changes in phenotypes) are caused by genetic drift. There is currently a scientific debate about how much of evolution has been caused by natural selection, and how much by genetic drift.