Random Genetic Drift
... POPULATION All populations started out with identical gene pools, but with time, the gene frequencies will change. The populations will become different from each other over time. DRIFT CAUSES AN INCREASE OF GENETIC VARIABILITY BETWEEN POPULATIONS ...
... POPULATION All populations started out with identical gene pools, but with time, the gene frequencies will change. The populations will become different from each other over time. DRIFT CAUSES AN INCREASE OF GENETIC VARIABILITY BETWEEN POPULATIONS ...
Microevolution is a change in a population*s gene pool
... generation change in the frequencies of alleles within a population ...
... generation change in the frequencies of alleles within a population ...
Enriched Biology DeCamp BB3
... and______________________. 5. All the genes of all members of a particular population make up the population’s… 6. In a population, the sum of the relative frequencies of all alleles for a particular trait is… 7. A change in a sequence of DNA is called a… 8. The two main sources of genetic variation ...
... and______________________. 5. All the genes of all members of a particular population make up the population’s… 6. In a population, the sum of the relative frequencies of all alleles for a particular trait is… 7. A change in a sequence of DNA is called a… 8. The two main sources of genetic variation ...
Natural Selection Depends on Genetic Variation
... Genetic variation that is favored by selection & is manifested as a trait that provides an advantage to an organism in a particular environment ...
... Genetic variation that is favored by selection & is manifested as a trait that provides an advantage to an organism in a particular environment ...
Old Final Exam WITH ANSWERS!!
... (NOT APPLICABLE FOR 2005 EXAM) 3. Tell me an example of a qualitative trait and a quantitative trait. Use whatever organism you would like. (8 points) qualitative (Mendelian) trait: plant height in peas (tall v. dwarf) quantitative (polygenic) trait: seed yield in pea 4. Tell me what the Hardy-Weinb ...
... (NOT APPLICABLE FOR 2005 EXAM) 3. Tell me an example of a qualitative trait and a quantitative trait. Use whatever organism you would like. (8 points) qualitative (Mendelian) trait: plant height in peas (tall v. dwarf) quantitative (polygenic) trait: seed yield in pea 4. Tell me what the Hardy-Weinb ...
Genetic drift is random
... Allele frequencies fluctuate at random within a population, until eventually one or another allele becomes fixed Frequency of heterozygotes H = 2p(1-p) declines Rate of decline in heterozygosity is used as a measure of rate of genetic drift Genetic drift The probability that a given allele w ...
... Allele frequencies fluctuate at random within a population, until eventually one or another allele becomes fixed Frequency of heterozygotes H = 2p(1-p) declines Rate of decline in heterozygosity is used as a measure of rate of genetic drift Genetic drift The probability that a given allele w ...
READING GUIDE: 17.1 – Genes and Variation (p. 482
... 9) ANALYZING DATA: (see p. 491) Imagine that you know of a genetic condition controlled by 2 alleles: R and r, which follow the rule of simple dominance at a single locus. The condition affects only homozygous recessive individuals. (the heterozygous phenotype shows no symptoms). The population you ...
... 9) ANALYZING DATA: (see p. 491) Imagine that you know of a genetic condition controlled by 2 alleles: R and r, which follow the rule of simple dominance at a single locus. The condition affects only homozygous recessive individuals. (the heterozygous phenotype shows no symptoms). The population you ...
Ways Genetic Eqilibrium can Change
... • Selection of mates other than by chance. Selective breeding by populations (most do this). • Ex. Herd of elk, elephant seals, peafowl, red cross-bills. ...
... • Selection of mates other than by chance. Selective breeding by populations (most do this). • Ex. Herd of elk, elephant seals, peafowl, red cross-bills. ...
Genetic Drift
... Genetic Drift is the change in a gene pool due to chance. There are 2 examples: Bottleneck effect Founder effect ...
... Genetic Drift is the change in a gene pool due to chance. There are 2 examples: Bottleneck effect Founder effect ...
Mechanisms of Evolution
... • Selection of mates other than by chance. Selective breeding by populations (most do this). • Ex. Herd of elk, elephant seals, peafowl, red cross-bills. ...
... • Selection of mates other than by chance. Selective breeding by populations (most do this). • Ex. Herd of elk, elephant seals, peafowl, red cross-bills. ...
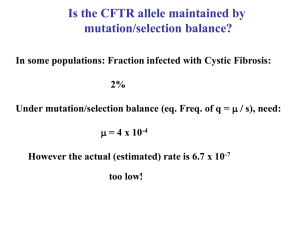
Is the CFTR allele maintained by mutation/selection balance?
... Neutralist view: allele substitution and polymorphism are determined by the same evolutionary process. ...
... Neutralist view: allele substitution and polymorphism are determined by the same evolutionary process. ...
13 Evolution 2015
... Adaptation- inherited characteristic that increases an organism’s chance of survival Descent with Modification- each living species has descended, with changes, from other species over time Fitness- ability of an organism to survive and reproduce in its environment ...
... Adaptation- inherited characteristic that increases an organism’s chance of survival Descent with Modification- each living species has descended, with changes, from other species over time Fitness- ability of an organism to survive and reproduce in its environment ...
05 Evolutionary Mechanisms
... genome (bacteria) to about 1 or more per gamete in larger genome. ...
... genome (bacteria) to about 1 or more per gamete in larger genome. ...
Genetic drift

Genetic drift (or allelic drift) is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces. A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation.When there are few copies of an allele, the effect of genetic drift is larger, and when there are many copies the effect is smaller. In the early twentieth century vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at the most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims that most instances where a genetic change spreads across a population (although not necessarily changes in phenotypes) are caused by genetic drift. There is currently a scientific debate about how much of evolution has been caused by natural selection, and how much by genetic drift.