Study Guide - Southington Public Schools
... DNA studies (molecular biology). Summarize the theory of natural selection and give an example of adaptations that living things have that show natural selection—especially peppered moths, pesticide-resistant insect populations and the bacteria/antibiotic battle. Explain what is meant by the phr ...
... DNA studies (molecular biology). Summarize the theory of natural selection and give an example of adaptations that living things have that show natural selection—especially peppered moths, pesticide-resistant insect populations and the bacteria/antibiotic battle. Explain what is meant by the phr ...
BIO101-01 Winter 04 Exam III Study Guide
... population are NOT genetically identical and therefore, will have some phenotypes or traits that vary). These two observations are essential to understanding how natural selection works. A ‘universal feature’ of life is replication/reproduction—all individuals of all species in a community or an eco ...
... population are NOT genetically identical and therefore, will have some phenotypes or traits that vary). These two observations are essential to understanding how natural selection works. A ‘universal feature’ of life is replication/reproduction—all individuals of all species in a community or an eco ...
Unit IIA Practice Exam (KEY) Unit_IIA_Exam_2.0_Key
... 29. Probability that the genotype Aa will be produced by the parents Aa x Aa (2002-66) D 30. Probability that the genotype ccdd will be produced by the parents CcDd x CcDd (2002-67) )B ...
... 29. Probability that the genotype Aa will be produced by the parents Aa x Aa (2002-66) D 30. Probability that the genotype ccdd will be produced by the parents CcDd x CcDd (2002-67) )B ...
Lesson4 sp2012 (online)
... A trait like blindness is an evolutionary detriment to a horse, making them more susceptible to predators and injury. Explain why the blind horses of this herd do not die before reaching reproductive age. (Multiple reasons are given in the article and are acceptable.) Explain why only removing or ge ...
... A trait like blindness is an evolutionary detriment to a horse, making them more susceptible to predators and injury. Explain why the blind horses of this herd do not die before reaching reproductive age. (Multiple reasons are given in the article and are acceptable.) Explain why only removing or ge ...
GENETIC CHARACTERIZATION OF CINTA SENESE PIG BREED: ANALYSIS OF POLYMORPHISMS IN FOUR GENES AFFECTING PERFORMANCE AND PHENOTYPIC TRAITS
... allele. A low level of variability was observed also at the ESR locus. Allele A was the most frequent (~0.93) and only 9 animals were heterozygous for the B allele. This allele, in other breeds [11], has been associated with an increased litter size and it will be interesting to evaluate if the same ...
... allele. A low level of variability was observed also at the ESR locus. Allele A was the most frequent (~0.93) and only 9 animals were heterozygous for the B allele. This allele, in other breeds [11], has been associated with an increased litter size and it will be interesting to evaluate if the same ...
Name: Date - TeacherWeb
... LAW OF SEGREGATION-STATES YOU CAN ONLY GET ONE ALLELE FROM EACH PARENT. 9. What is produced by each parent and shown along the sides of a Punnett square? GAMETES 10. Who carried out the first studies of heredity? GREGOR MENDEL 11. What did he use to carry out these studies? PEA PLANTS 12. Be able to ...
... LAW OF SEGREGATION-STATES YOU CAN ONLY GET ONE ALLELE FROM EACH PARENT. 9. What is produced by each parent and shown along the sides of a Punnett square? GAMETES 10. Who carried out the first studies of heredity? GREGOR MENDEL 11. What did he use to carry out these studies? PEA PLANTS 12. Be able to ...
2017 N3 Week 2
... 3. In some chickens, the gene for feather color is controlled by codominance. The allele for black is B and the allele for white is W. The heterozygous phenotype is known as ...
... 3. In some chickens, the gene for feather color is controlled by codominance. The allele for black is B and the allele for white is W. The heterozygous phenotype is known as ...
CH3L2
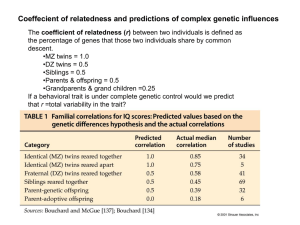
... Coeffecient of relatedness and predictions of complex genetic influences The coefficient of relatedness (r) between two individuals is defined as the percentage of genes that those two individuals share by common descent. •MZ twins = 1.0 •DZ twins = 0.5 •Siblings = 0.5 •Parents & offspring = 0.5 •Gr ...
... Coeffecient of relatedness and predictions of complex genetic influences The coefficient of relatedness (r) between two individuals is defined as the percentage of genes that those two individuals share by common descent. •MZ twins = 1.0 •DZ twins = 0.5 •Siblings = 0.5 •Parents & offspring = 0.5 •Gr ...
Study Questions for Exam 1 Biology 354 Lecture 1: Natural selection
... What is meant by saying that there’s a balance between mutation and selection? What is “balanced”? In the example of water snakes around Lake Erie, most mainland snakes were all banded, except a population on the peninsular mainland. Derive two hypotheses for why those particular snakes have some un ...
... What is meant by saying that there’s a balance between mutation and selection? What is “balanced”? In the example of water snakes around Lake Erie, most mainland snakes were all banded, except a population on the peninsular mainland. Derive two hypotheses for why those particular snakes have some un ...
Since the entire class represents a breeding population, find a large
... CASE IV (Genetic Drive, optional) In Case I, the role of small populations in genetic drift was suggested. It is possible to use our simulation to look at this phenomenon in more detail. Divide the lab into several smaller populations (for example, a class of 30 could be divided into 3 populations o ...
... CASE IV (Genetic Drive, optional) In Case I, the role of small populations in genetic drift was suggested. It is possible to use our simulation to look at this phenomenon in more detail. Divide the lab into several smaller populations (for example, a class of 30 could be divided into 3 populations o ...
Lecture#12 Page 1 BIOLOGY 207 - Dr.McDermid Lecture#12 Alleles
... 1. From the wide variety of mutational possibilities for most genes, we can usually distinguish only functional and non-functional alleles. 2. The functional allele is usually dominant to the non-functional allele in individuals with both alleles (heterozygote). 3. Offspring from heterozygous parent ...
... 1. From the wide variety of mutational possibilities for most genes, we can usually distinguish only functional and non-functional alleles. 2. The functional allele is usually dominant to the non-functional allele in individuals with both alleles (heterozygote). 3. Offspring from heterozygous parent ...
12-3 Probability and Heredity Understanding Main
... In pea plants, the allele for tall stems (T) is dominant over the allele for short stems (t). Suppose two heterozygous parent plants are crossed. List all the possible genotypes for their offspring. For each genotype, calculate its probability as a percent, name the phenotype, and describe the plant ...
... In pea plants, the allele for tall stems (T) is dominant over the allele for short stems (t). Suppose two heterozygous parent plants are crossed. List all the possible genotypes for their offspring. For each genotype, calculate its probability as a percent, name the phenotype, and describe the plant ...
1 - Acpsd.net
... offspring would be Red and white in the same flower. Incomplete dominance- offspring is in-between that of the parents. Ex. Cross between Red and white makes a Pink flower. Complete dominance – One allele will be completely dominant over the recessive. Ex. Red parent crossed with a white parent and ...
... offspring would be Red and white in the same flower. Incomplete dominance- offspring is in-between that of the parents. Ex. Cross between Red and white makes a Pink flower. Complete dominance – One allele will be completely dominant over the recessive. Ex. Red parent crossed with a white parent and ...
6SC06 Tutorial: Genetics – study of heredity
... states that genes are carried via chromosomes from the parents to their offspring. Each sex cell contains exactly half of each parent’s total number of chromosomes through a process known as meiosis. All organisms have a specific number of chromosomes that are different according to their particular ...
... states that genes are carried via chromosomes from the parents to their offspring. Each sex cell contains exactly half of each parent’s total number of chromosomes through a process known as meiosis. All organisms have a specific number of chromosomes that are different according to their particular ...
CHAPTER 22 Population Genetics
... 5. Effects of genetic drift: a. Allelic frequencies will change over time, and may reach values of 0.0 or 1.0. When this occurs, the remaining allele is “fixed” in the population, and only mutation can change its frequency. This reduces the heterozygosity of the population, resulting in reduced gen ...
... 5. Effects of genetic drift: a. Allelic frequencies will change over time, and may reach values of 0.0 or 1.0. When this occurs, the remaining allele is “fixed” in the population, and only mutation can change its frequency. This reduces the heterozygosity of the population, resulting in reduced gen ...
Evolution
... • Stable populations tend to behave according the Hardy-Weinberg principle (see pp. 92-95) – maintain stable allele frequencies. – Large population size – Random mating – No mutations ...
... • Stable populations tend to behave according the Hardy-Weinberg principle (see pp. 92-95) – maintain stable allele frequencies. – Large population size – Random mating – No mutations ...
Lab: Breeding Bunnies
... note that these frequencies have been chosen arbitrarily for this activity.) 6. Without looking at the beads, select two at a time, and record the results on the data form next to "Generation 1." For instance, if you draw one purple and one black bead, place a mark in the chart (see Table 1 at end o ...
... note that these frequencies have been chosen arbitrarily for this activity.) 6. Without looking at the beads, select two at a time, and record the results on the data form next to "Generation 1." For instance, if you draw one purple and one black bead, place a mark in the chart (see Table 1 at end o ...
Mendel’s Laws of Heredity
... genes that make up a gene pair might or might not contain the same information about a trait. If a pair of chromosomes contains different alleles for a trait, that trait is called a hybrid . When a trait has two identical alleles, it’s called pure. ...
... genes that make up a gene pair might or might not contain the same information about a trait. If a pair of chromosomes contains different alleles for a trait, that trait is called a hybrid . When a trait has two identical alleles, it’s called pure. ...
Genetics Constructed Response Answer
... Directions: Please read all parts of the example below and answer all four points for this constructed response completely. Be sure to read carefully, and check your answers once done. There is a genetic disorder that is sex-linked and is caused by a recessive allele (e). The allele for the unaffect ...
... Directions: Please read all parts of the example below and answer all four points for this constructed response completely. Be sure to read carefully, and check your answers once done. There is a genetic disorder that is sex-linked and is caused by a recessive allele (e). The allele for the unaffect ...
Genetic drift

Genetic drift (or allelic drift) is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces. A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation.When there are few copies of an allele, the effect of genetic drift is larger, and when there are many copies the effect is smaller. In the early twentieth century vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at the most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims that most instances where a genetic change spreads across a population (although not necessarily changes in phenotypes) are caused by genetic drift. There is currently a scientific debate about how much of evolution has been caused by natural selection, and how much by genetic drift.