Mendelian Genetics Part 1
... are filled in with the gene type from dad’s gametes (B) 4. The 4 boxes in the square are filled in with the gene type from mom’s gametes (b) ...
... are filled in with the gene type from dad’s gametes (B) 4. The 4 boxes in the square are filled in with the gene type from mom’s gametes (b) ...
Genetics and Heredity
... The alleles are either dominant or recessive. To show the recessive trait, two recessive alleles must be inherited. ...
... The alleles are either dominant or recessive. To show the recessive trait, two recessive alleles must be inherited. ...
ppt
... Given the allele frequencies that you calculated earlier for Cooper’s Rock Kalmia latifolia, what is the probability of observing two “white” alleles in a sample of two plants? ...
... Given the allele frequencies that you calculated earlier for Cooper’s Rock Kalmia latifolia, what is the probability of observing two “white” alleles in a sample of two plants? ...
Molecular-3
... Genetic drift can explain a high frequency of a deleterious disease allele in a population. For example, when a new mutation occurs in a small population, its frequency is represented by only one copy among all the copies of that gene in the population. Random effects of environment or other chance ...
... Genetic drift can explain a high frequency of a deleterious disease allele in a population. For example, when a new mutation occurs in a small population, its frequency is represented by only one copy among all the copies of that gene in the population. Random effects of environment or other chance ...
BIO-NMD: Discovery and validation of biomarkers for NMDs * an EU
... genetic heterogeneity, are usually incurable and can be associated with severe complications including sudden death. In the past 25 years the strategies and methods applied have allowed us to identify neuromuscular disease genes mainly in larger families and for more frequently occurring genetic con ...
... genetic heterogeneity, are usually incurable and can be associated with severe complications including sudden death. In the past 25 years the strategies and methods applied have allowed us to identify neuromuscular disease genes mainly in larger families and for more frequently occurring genetic con ...
Mechanisms of Evolution 1. In their first attempts to genetically
... The genetic variation of the new population will be drastically reduced from that of the original population since only the alleles carried by the founding members will be present in the new population. Specific genetic traits from the original population can be lost or over-represented by the new p ...
... The genetic variation of the new population will be drastically reduced from that of the original population since only the alleles carried by the founding members will be present in the new population. Specific genetic traits from the original population can be lost or over-represented by the new p ...
Random Genetic Drift
... 3. GENETIC FIXITY of SPECIES is NOT possible as long as there are a lot of populations, because RGD will do something different in each population. There is continual change of allele frequencies in finite populations by chance, RGD. ...
... 3. GENETIC FIXITY of SPECIES is NOT possible as long as there are a lot of populations, because RGD will do something different in each population. There is continual change of allele frequencies in finite populations by chance, RGD. ...
Every living organism is made up of many different traits or
... Beyond Mendelian Genetics Mendelian Genetics Mendel found that inherited traits were either ________________ or ____________ Dominant allele always being expressed Mendel was lucky Peas are genetically _______________ Most traits are controlled by a _________________ gene Each gene has only ___ alle ...
... Beyond Mendelian Genetics Mendelian Genetics Mendel found that inherited traits were either ________________ or ____________ Dominant allele always being expressed Mendel was lucky Peas are genetically _______________ Most traits are controlled by a _________________ gene Each gene has only ___ alle ...
slides - Dorman external link
... forward in time, it leads to the conclusion that ultimate there will remain only one allele in the population. While at first it is very easy to remove alleles, the numbers of the remaining alleles increase and it is less likely that they will be removed at each generation. However, there is always ...
... forward in time, it leads to the conclusion that ultimate there will remain only one allele in the population. While at first it is very easy to remove alleles, the numbers of the remaining alleles increase and it is less likely that they will be removed at each generation. However, there is always ...
Genetics Notes - Biloxi Public Schools
... passed from one generation to acid) the next—blueprint of an organism Before a cell divides, it makes a copy of its DNA. This ensures that both new cells have all the genetic information they need. A genome is the complete sequence of an organism’s DNA. ...
... passed from one generation to acid) the next—blueprint of an organism Before a cell divides, it makes a copy of its DNA. This ensures that both new cells have all the genetic information they need. A genome is the complete sequence of an organism’s DNA. ...
10 Genetics and evolution
... Meiosis leads to the independent assortment of chromosomes and a unique composition of alleles in the four daughter cells. Crossing over is the exchange of DNA material between non-sister chromosomes of haploid cells. It produces new combinations of alleles on the chromosomes of the haploid cells, s ...
... Meiosis leads to the independent assortment of chromosomes and a unique composition of alleles in the four daughter cells. Crossing over is the exchange of DNA material between non-sister chromosomes of haploid cells. It produces new combinations of alleles on the chromosomes of the haploid cells, s ...
Biology 4E03: Population Genetics Course Outline: Term II, 2010
... derivation of Fst, relation between Fst and gene flow (Nm), relation between Fst, H and Nm, measuring gene flow from Fst, distribution of Fst at loci and role of selection, gene flow between mainland and Island. Reading: Halliburton Chapter 9 Week 11: Molecular Evolution Cost of selection (1-W) and ...
... derivation of Fst, relation between Fst and gene flow (Nm), relation between Fst, H and Nm, measuring gene flow from Fst, distribution of Fst at loci and role of selection, gene flow between mainland and Island. Reading: Halliburton Chapter 9 Week 11: Molecular Evolution Cost of selection (1-W) and ...
genetic study guide/quiz
... 2. He used ______ plants to study heredity. Garden pea plants reproduce sexually, which means they use the process of _________ to produce haploid ____________, also called male and female sex cells. The male gamete in peas forms in the ________ and the female gamete forms in the female reproductive ...
... 2. He used ______ plants to study heredity. Garden pea plants reproduce sexually, which means they use the process of _________ to produce haploid ____________, also called male and female sex cells. The male gamete in peas forms in the ________ and the female gamete forms in the female reproductive ...
Heredity – notes - Effingham County Schools
... On each homolog are sites where specific genes are located ...
... On each homolog are sites where specific genes are located ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... (alleles) are together in an individual, only one of them seems to be expressed at the phenotypic level (i.e. at the level of an observable trait). For example, a human carrying an allele for brown eyes and one for blue eyes will actually have brown eye colour. Thus, of the two alleles at the eye co ...
... (alleles) are together in an individual, only one of them seems to be expressed at the phenotypic level (i.e. at the level of an observable trait). For example, a human carrying an allele for brown eyes and one for blue eyes will actually have brown eye colour. Thus, of the two alleles at the eye co ...
Key Terms Foldable CH. 5 Heredity
... Definitions Go On The Inside A process in cell division during which the number of chromosomes decreases to half the original number by two divisions of the nucleus, which results in the production of sex cells (gametes or spores). One of the pair of chromosomes that determines the sex of an indivi ...
... Definitions Go On The Inside A process in cell division during which the number of chromosomes decreases to half the original number by two divisions of the nucleus, which results in the production of sex cells (gametes or spores). One of the pair of chromosomes that determines the sex of an indivi ...
10. population genetics
... • With p and q frequencies you can calculate • frequencies of three genotypes (p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1) ...
... • With p and q frequencies you can calculate • frequencies of three genotypes (p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1) ...
Exam 3 Practice Exam - Iowa State University
... B) idea that hasn’t been tested yet C) idea that may or may not be true D) a hypothesis that has been tested and is well supported by data 29.) The precise location of a gene on a chromosome is known as its A) loci B) trait C) sequence D) character 30.) The frequency with which crossing over occurs ...
... B) idea that hasn’t been tested yet C) idea that may or may not be true D) a hypothesis that has been tested and is well supported by data 29.) The precise location of a gene on a chromosome is known as its A) loci B) trait C) sequence D) character 30.) The frequency with which crossing over occurs ...
2245_notes_03_17
... •Question 2: What can Ensatina eschscholtzii tell us about the process of speciation? What would have to happen in order for reproductively isolated populations of this species to be considered different species? ...
... •Question 2: What can Ensatina eschscholtzii tell us about the process of speciation? What would have to happen in order for reproductively isolated populations of this species to be considered different species? ...
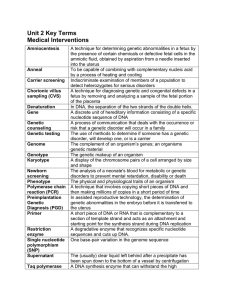
Unit 2 Terms
... make one or more genetically identical individuals The alteration of the genes of a person afflicted with a genetic disease A procedure in which gametes are fertilized in a dish in the laboratory, and the resulting zygote is implanted in the uterus for development In assisted reproductive technology ...
... make one or more genetically identical individuals The alteration of the genes of a person afflicted with a genetic disease A procedure in which gametes are fertilized in a dish in the laboratory, and the resulting zygote is implanted in the uterus for development In assisted reproductive technology ...
Genetic drift

Genetic drift (or allelic drift) is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces. A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation.When there are few copies of an allele, the effect of genetic drift is larger, and when there are many copies the effect is smaller. In the early twentieth century vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at the most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims that most instances where a genetic change spreads across a population (although not necessarily changes in phenotypes) are caused by genetic drift. There is currently a scientific debate about how much of evolution has been caused by natural selection, and how much by genetic drift.